优先队列是一种特殊的队列,其中每个元素都与一个优先级值相关联。并且,元素是根据它们的优先级来服务的。也就是说,优先级高的元素先被服务。
但是,如果出现相同优先级的元素,它们将根据它们在队列中的顺序被服务。
分配优先级值
通常,元素本身的值被用于分配优先级。例如,
值最大的元素被视为最高优先级的元素。然而,在其他情况下,我们可以假设值最小的元素是最高优先级的元素。
我们也可以根据我们的需求设置优先级。

优先队列与普通队列的区别
队列实现的是先进先出规则,而优先队列是根据优先级移除值。优先级最高的元素首先被移除。
优先队列的实现
优先队列可以使用数组、链表、堆数据结构或二叉搜索树来实现。在这些数据结构中,堆数据结构提供了高效的优先队列实现。
因此,在本教程中,我们将使用堆数据结构来实现优先队列。以下操作实现了最大堆。如果您想了解更多关于它的信息,请访问最大堆和最小堆。
下面给出了对不同优先队列实现方案的比较分析。
| 操作 | 查看 | 插入 | 删除 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 链表 | O(1) |
O(n) |
O(1) |
| 二叉堆 | O(1) |
O(log n) |
O(log n) |
| 二叉搜索树 | O(1) |
O(log n) |
O(log n) |
优先队列操作
优先队列的基本操作是插入、移除和查看元素。
在学习优先队列之前,请参考堆数据结构以更好地理解二叉堆,因为它在本文中用于实现优先队列。
1. 将元素插入优先队列
将元素插入优先队列(最大堆)通过以下步骤完成。
- 将新元素插入树的末尾。

将元素插入队列末尾 - 堆化树。

插入后的堆化
向优先队列(最大堆)插入元素的算法
If there is no node, create a newNode. else (a node is already present) insert the newNode at the end (last node from left to right.) heapify the array
对于最小堆,上述算法进行了修改,使得parentNode始终小于newNode。
2. 从优先队列中删除元素
从优先队列(最大堆)中删除元素如下操作:
- 选择要删除的元素。

选择要删除的元素 - 将其与最后一个元素交换。
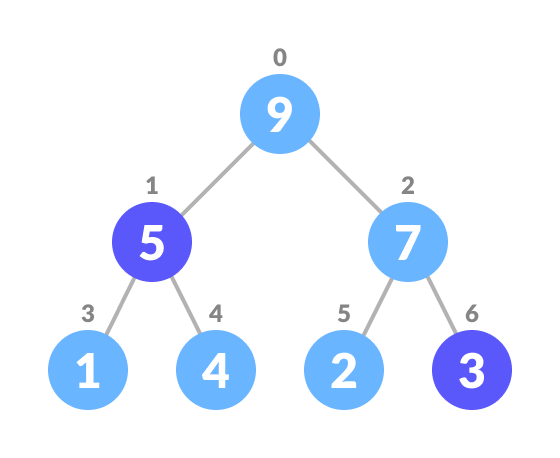
与最后一个叶子节点元素交换 - 移除最后一个元素。

移除最后一个叶子节点元素 - 堆化树。

堆化优先队列
从优先队列(最大堆)中删除元素的算法
If nodeToBeDeleted is the leafNode remove the node Else swap nodeToBeDeleted with the lastLeafNode remove noteToBeDeleted heapify the array
对于最小堆,上述算法进行了修改,使得childNodes都小于currentNode。
3. 从优先队列中查看(查找最大/最小值)
查看操作会在不删除节点的情况下返回最大堆中的最大元素或最小堆中的最小元素。
对于最大堆和最小堆
return rootNode
4. 从优先队列中提取最大/最小值
Extract-Max 返回从最大堆中移除后的最大值节点,而 Extract-Min 返回从最小堆中移除后的最小值节点。
Python、Java、C 和 C++ 中的优先队列实现
# Priority Queue implementation in Python
# Function to heapify the tree
def heapify(arr, n, i):
# Find the largest among root, left child, and right child
largest = i
l = 2 * i + 1
r = 2 * i + 2
if l < n and arr[i] < arr[l]:
largest = l
if r < n and arr[largest] < arr[r]:
largest = r
# Swap and continue heapifying if root is not the largest
if largest != i:
arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i]
heapify(arr, n, largest)
# Function to insert an element into the tree
def insert(array, newNum):
size = len(array)
if size == 0:
array.append(newNum)
else:
array.append(newNum)
for i in range((size // 2) - 1, -1, -1):
heapify(array, size, i)
# Function to delete an element from the tree
def deleteNode(array, num):
size = len(array)
i = 0
for i in range(0, size):
if num == array[i]:
break
# Swap the element to delete with the last element
array[i], array[size - 1] = array[size - 1], array[i]
# Remove the last element (the one we want to delete)
array.pop()
# Rebuild the heap
for i in range((len(array) // 2) - 1, -1, -1):
heapify(array, len(array), i)
arr = []
insert(arr, 3)
insert(arr, 4)
insert(arr, 9)
insert(arr, 5)
insert(arr, 2)
print("Max-Heap array: " + str(arr))
deleteNode(arr, 4)
print("After deleting an element: " + str(arr))// Priority Queue implementation in Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Heap {
// Function to heapify the tree
void heapify(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int i) {
int size = hT.size();
// Find the largest among root, left child and right child
int largest = i;
int l = 2 * i + 1;
int r = 2 * i + 2;
if (l < size && hT.get(l) > hT.get(largest))
largest = l;
if (r < size && hT.get(r) > hT.get(largest))
largest = r;
// Swap and continue heapifying if root is not largest
if (largest != i) {
int temp = hT.get(largest);
hT.set(largest, hT.get(i));
hT.set(i, temp);
heapify(hT, largest);
}
}
// Function to insert an element into the tree
void insert(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int newNum) {
int size = hT.size();
if (size == 0) {
hT.add(newNum);
} else {
hT.add(newNum);
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(hT, i);
}
}
}
// Function to delete an element from the tree
void deleteNode(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int num) {
int size = hT.size();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (num == hT.get(i))
break;
}
int temp = hT.get(i);
hT.set(i, hT.get(size - 1));
hT.set(size - 1, temp);
hT.remove(size - 1);
for (int j = size / 2 - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
heapify(hT, j);
}
}
// Print the tree
void printArray(ArrayList<Integer> array, int size) {
for (Integer i : array) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int size = array.size();
Heap h = new Heap();
h.insert(array, 3);
h.insert(array, 4);
h.insert(array, 9);
h.insert(array, 5);
h.insert(array, 2);
System.out.println("Max-Heap array: ");
h.printArray(array, size);
h.deleteNode(array, 4);
System.out.println("After deleting an element: ");
h.printArray(array, size);
}
}// Priority Queue implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
int size = 0;
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *b;
*b = *a;
*a = temp;
}
// Function to heapify the tree
void heapify(int array[], int size, int i) {
if (size == 1) {
printf("Single element in the heap");
} else {
// Find the largest among root, left child and right child
int largest = i;
int l = 2 * i + 1;
int r = 2 * i + 2;
if (l < size && array[l] > array[largest])
largest = l;
if (r < size && array[r] > array[largest])
largest = r;
// Swap and continue heapifying if root is not largest
if (largest != i) {
swap(&array[i], &array[largest]);
heapify(array, size, largest);
}
}
}
// Function to insert an element into the tree
void insert(int array[], int newNum) {
if (size == 0) {
array[0] = newNum;
size += 1;
} else {
array[size] = newNum;
size += 1;
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(array, size, i);
}
}
}
// Function to delete an element from the tree
void deleteRoot(int array[], int num) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (num == array[i])
break;
}
swap(&array[i], &array[size - 1]);
size -= 1;
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(array, size, i);
}
}
// Print the array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
printf("%d ", array[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int array[10];
insert(array, 3);
insert(array, 4);
insert(array, 9);
insert(array, 5);
insert(array, 2);
printf("Max-Heap array: ");
printArray(array, size);
deleteRoot(array, 4);
printf("After deleting an element: ");
printArray(array, size);
}// Priority Queue implementation in C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Function to swap position of two elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *b;
*b = *a;
*a = temp;
}
// Function to heapify the tree
void heapify(vector<int> &hT, int i) {
int size = hT.size();
// Find the largest among root, left child and right child
int largest = i;
int l = 2 * i + 1;
int r = 2 * i + 2;
if (l < size && hT[l] > hT[largest])
largest = l;
if (r < size && hT[r] > hT[largest])
largest = r;
// Swap and continue heapifying if root is not largest
if (largest != i) {
swap(&hT[i], &hT[largest]);
heapify(hT, largest);
}
}
// Function to insert an element into the tree
void insert(vector<int> &hT, int newNum) {
int size = hT.size();
if (size == 0) {
hT.push_back(newNum);
} else {
hT.push_back(newNum);
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(hT, i);
}
}
}
// Function to delete an element from the tree
void deleteNode(vector<int> &hT, int num) {
int size = hT.size();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (num == hT[i])
break;
}
swap(&hT[i], &hT[size - 1]);
hT.pop_back();
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(hT, i);
}
}
// Print the tree
void printArray(vector<int> &hT) {
for (int i = 0; i < hT.size(); ++i)
cout << hT[i] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
// Driver code
int main() {
vector<int> heapTree;
insert(heapTree, 3);
insert(heapTree, 4);
insert(heapTree, 9);
insert(heapTree, 5);
insert(heapTree, 2);
cout << "Max-Heap array: ";
printArray(heapTree);
deleteNode(heapTree, 4);
cout << "After deleting an element: ";
printArray(heapTree);
}优先队列的应用
优先队列的一些应用包括:
- Dijkstra 算法
- 用于实现栈
- 用于操作系统中的负载均衡和中断处理
- 用于 Huffman 编码中的数据压缩






