快速排序是一种基于分治法的排序算法,其中
- 通过选择一个枢轴元素(从数组中选取的元素)将数组划分为子数组。
在划分数组时,枢轴元素应放置在使得小于枢轴的元素位于枢轴的左侧,大于枢轴的元素位于枢轴的右侧的位置。 - 左右子数组也使用相同的方法进行划分。此过程一直持续到每个子数组只包含一个元素。
- 此时,元素已排序。最后,将元素组合起来形成一个已排序的数组。
快速排序算法的工作原理
1. 选择枢轴元素
快速排序有不同的变体,其中枢轴元素从不同的位置选择。在这里,我们将选择数组的最后一个元素作为枢轴元素。

2. 重排数组
现在,数组的元素被重新排列,以便小于枢轴的元素放在左边,大于枢轴的元素放在右边。

我们这样重排数组
- 将一个指针固定在枢轴元素上。将枢轴元素与从第一个索引开始的元素进行比较。
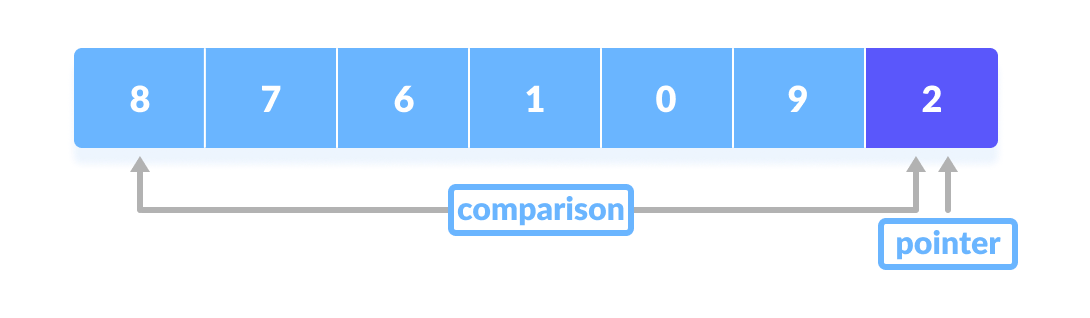
将枢轴元素与从第一个索引开始的元素进行比较 - 如果元素大于枢轴元素,则为该元素设置第二个指针。

如果元素大于枢轴元素,则为该元素设置第二个指针。 - 现在,将枢轴与其他元素进行比较。如果遇到小于枢轴元素的元素,则将较小的元素与之前找到的较大元素进行交换。
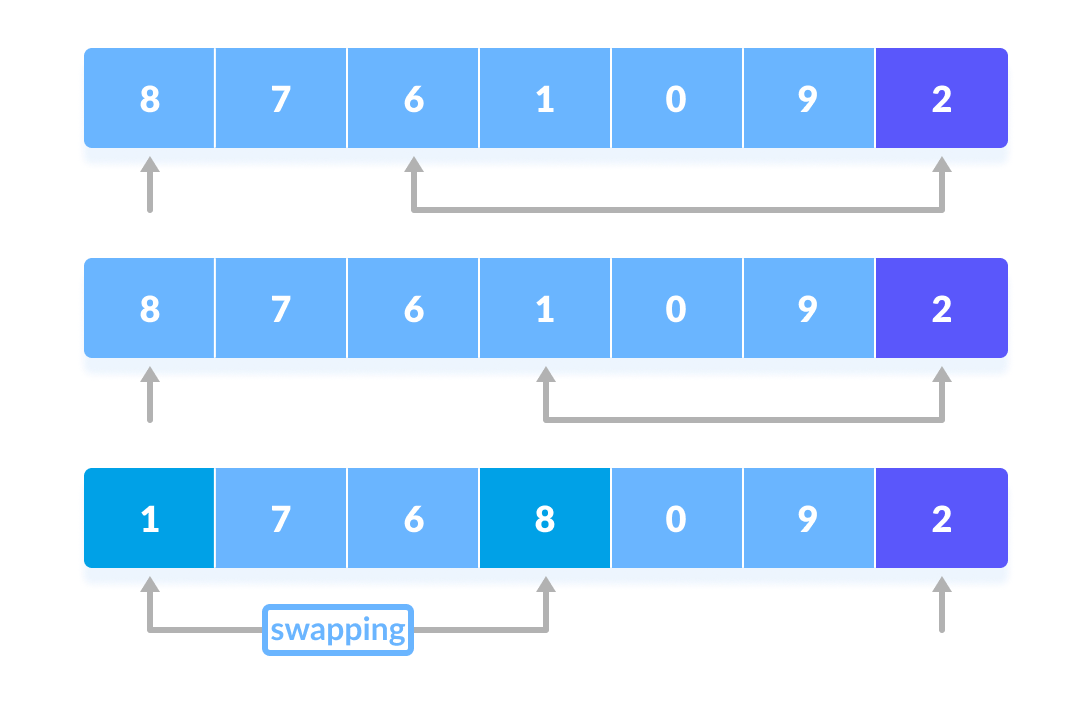
枢轴与其他元素进行比较。 - 再次,重复此过程,将下一个较大的元素设置为第二个指针。然后,将其与另一个较小的元素交换。
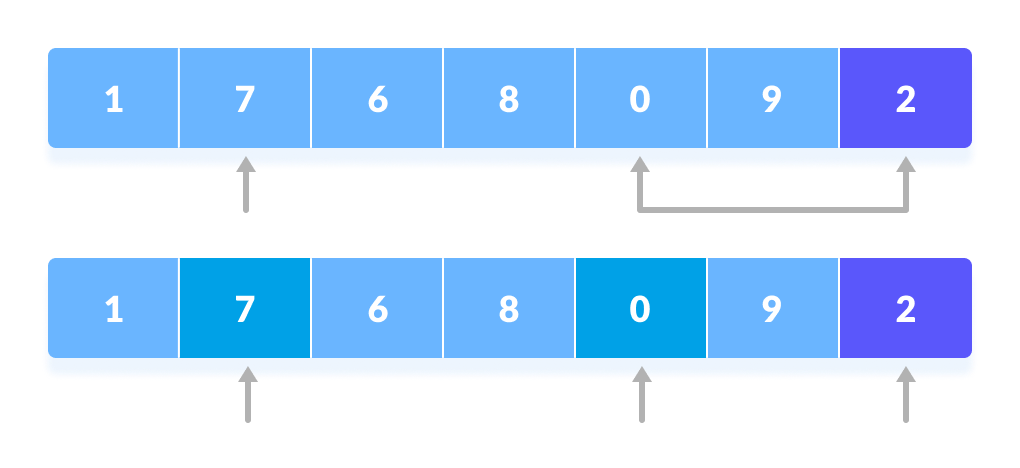
重复此过程,将下一个较大的元素设置为第二个指针。 - 过程一直持续到到达倒数第二个元素。
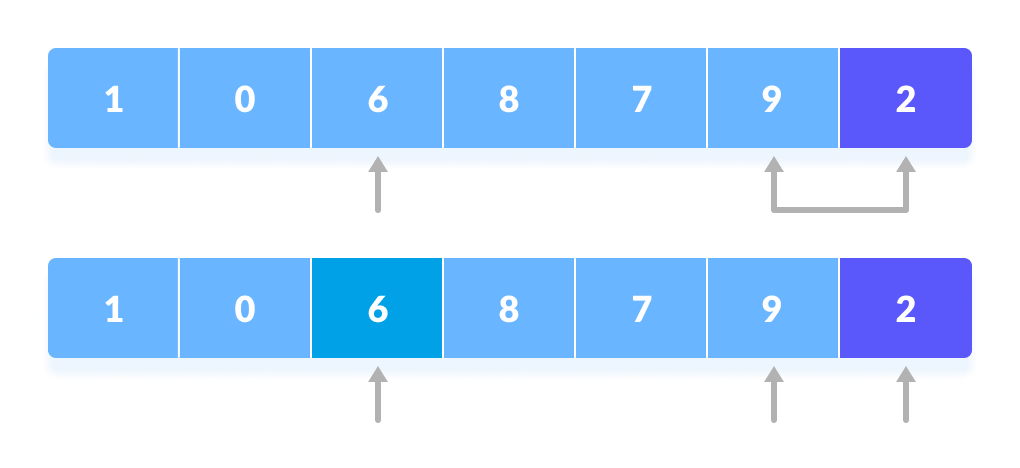
过程一直持续到到达倒数第二个元素。 - 最后,将枢轴元素与第二个指针交换。
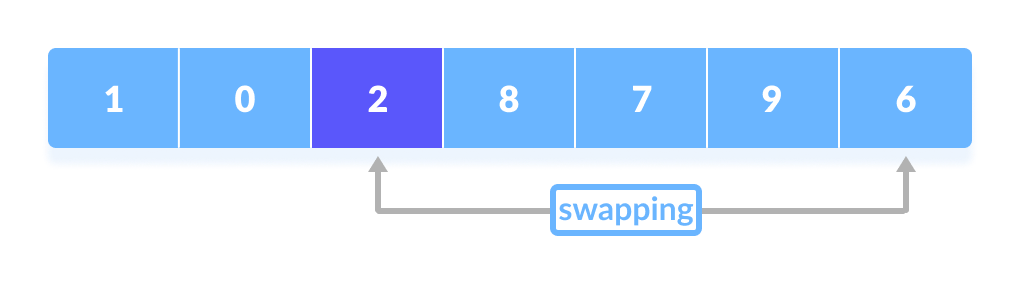
最后,将枢轴元素与第二个指针交换。
3. 划分子数组
再次分别选择左右子部分的枢轴元素。然后,重复步骤 2。
子数组被划分,直到每个子数组由单个元素组成。此时,数组已排序。
快速排序算法
quickSort(array, leftmostIndex, rightmostIndex)
if (leftmostIndex < rightmostIndex)
pivotIndex <- partition(array,leftmostIndex, rightmostIndex)
quickSort(array, leftmostIndex, pivotIndex - 1)
quickSort(array, pivotIndex, rightmostIndex)
partition(array, leftmostIndex, rightmostIndex)
set rightmostIndex as pivotIndex
storeIndex <- leftmostIndex - 1
for i <- leftmostIndex + 1 to rightmostIndex
if element[i] < pivotElement
swap element[i] and element[storeIndex]
storeIndex++
swap pivotElement and element[storeIndex+1]
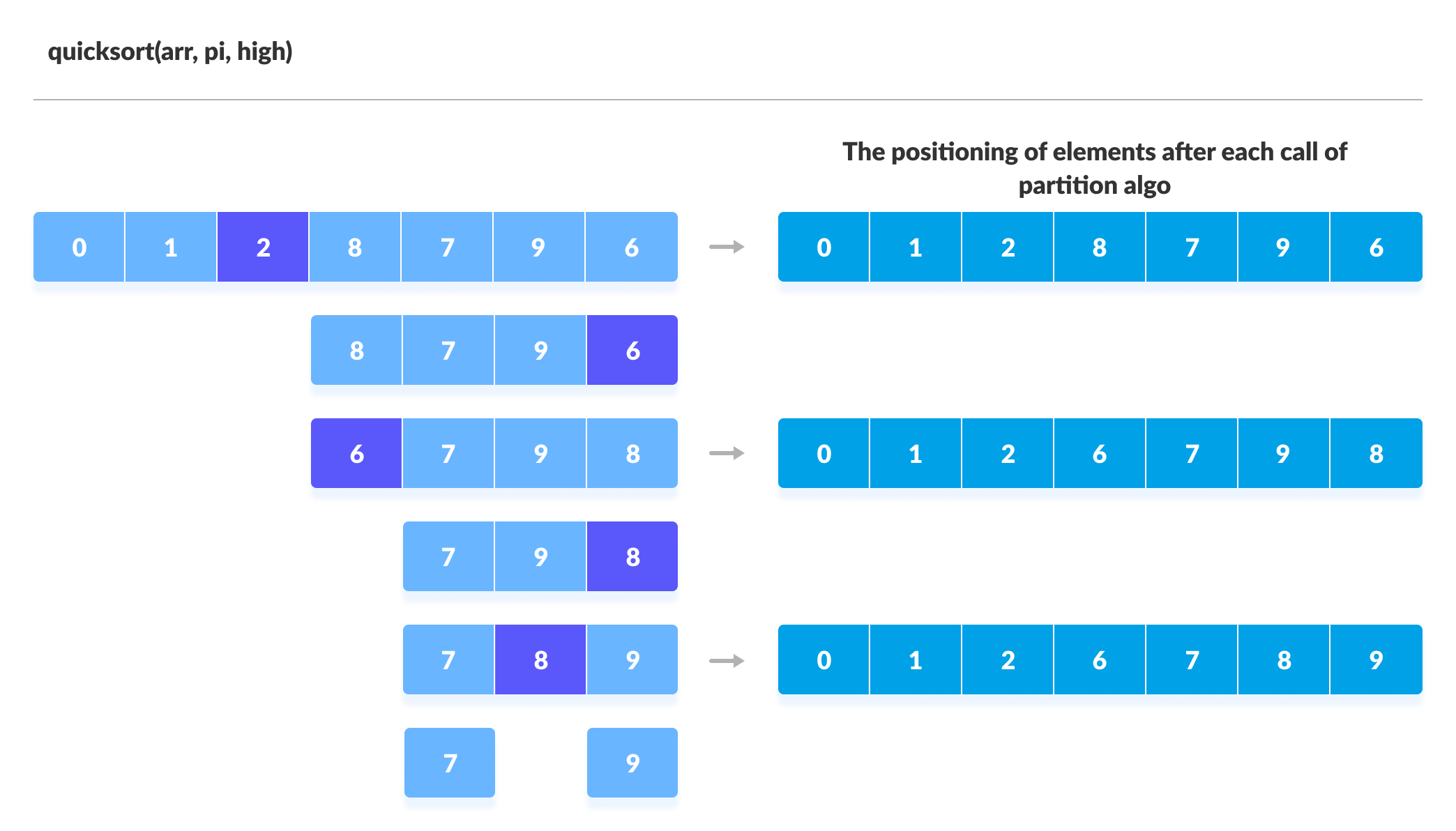
return storeIndex + 1快速排序算法的直观图
您可以通过下面的图示来理解快速排序算法的工作原理。
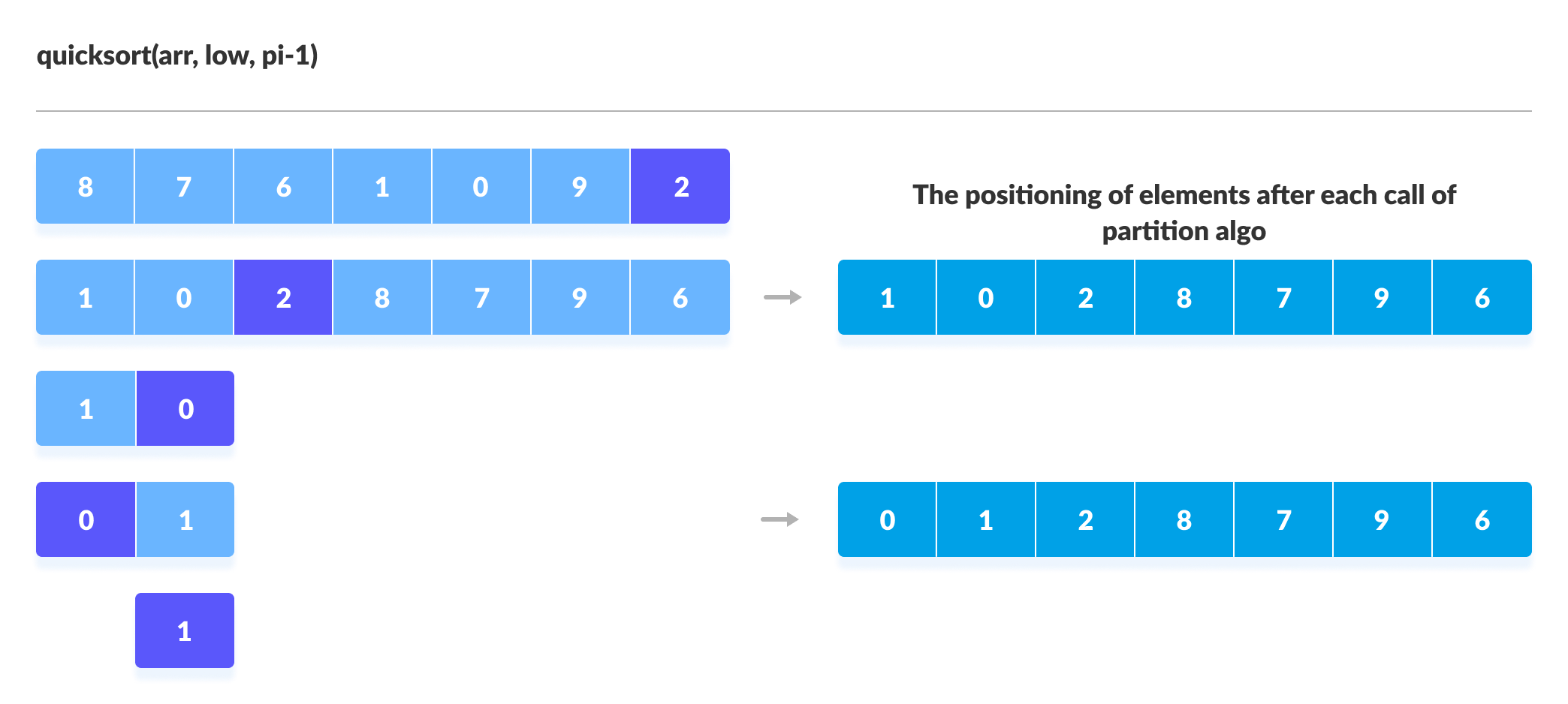
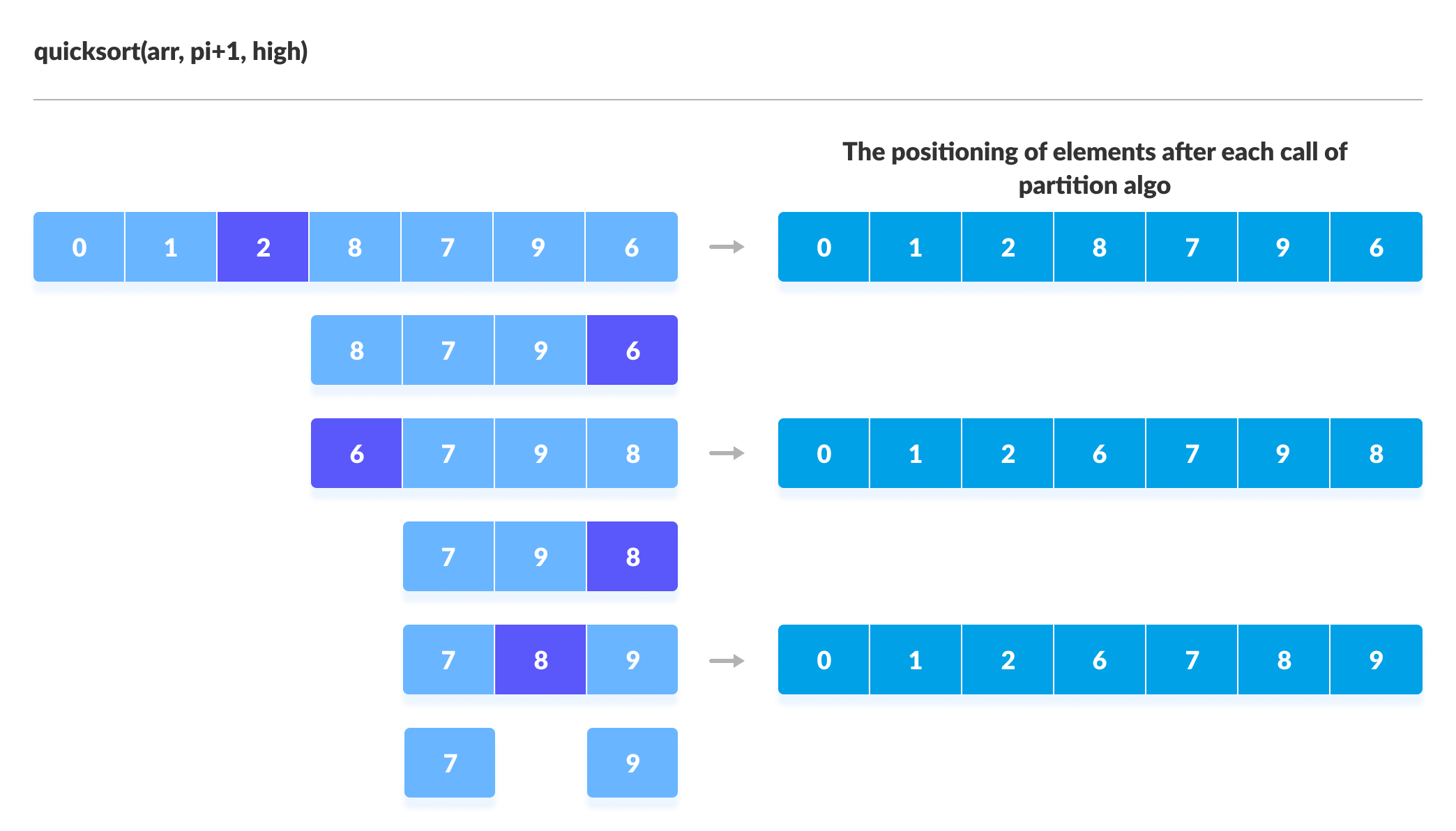
Python、Java 和 C/C++ 中的快速排序代码
# Quick sort in Python
# function to find the partition position
def partition(array, low, high):
# choose the rightmost element as pivot
pivot = array[high]
# pointer for greater element
i = low - 1
# traverse through all elements
# compare each element with pivot
for j in range(low, high):
if array[j] <= pivot:
# if element smaller than pivot is found
# swap it with the greater element pointed by i
i = i + 1
# swapping element at i with element at j
(array[i], array[j]) = (array[j], array[i])
# swap the pivot element with the greater element specified by i
(array[i + 1], array[high]) = (array[high], array[i + 1])
# return the position from where partition is done
return i + 1
# function to perform quicksort
def quickSort(array, low, high):
if low < high:
# find pivot element such that
# element smaller than pivot are on the left
# element greater than pivot are on the right
pi = partition(array, low, high)
# recursive call on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1)
# recursive call on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high)
data = [8, 7, 2, 1, 0, 9, 6]
print("Unsorted Array")
print(data)
size = len(data)
quickSort(data, 0, size - 1)
print('Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')
print(data)// Quick sort in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class Quicksort {
// method to find the partition position
static int partition(int array[], int low, int high) {
// choose the rightmost element as pivot
int pivot = array[high];
// pointer for greater element
int i = (low - 1);
// traverse through all elements
// compare each element with pivot
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
// if element smaller than pivot is found
// swap it with the greatr element pointed by i
i++;
// swapping element at i with element at j
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
// swapt the pivot element with the greater element specified by i
int temp = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = array[high];
array[high] = temp;
// return the position from where partition is done
return (i + 1);
}
static void quickSort(int array[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// find pivot element such that
// elements smaller than pivot are on the left
// elements greater than pivot are on the right
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
// recursive call on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
// recursive call on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
}
// Main class
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { 8, 7, 2, 1, 0, 9, 6 };
System.out.println("Unsorted Array");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
int size = data.length;
// call quicksort() on array data
Quicksort.quickSort(data, 0, size - 1);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}// Quick sort in C
#include <stdio.h>
// function to swap elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
// function to find the partition position
int partition(int array[], int low, int high) {
// select the rightmost element as pivot
int pivot = array[high];
// pointer for greater element
int i = (low - 1);
// traverse each element of the array
// compare them with the pivot
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
// if element smaller than pivot is found
// swap it with the greater element pointed by i
i++;
// swap element at i with element at j
swap(&array[i], &array[j]);
}
}
// swap the pivot element with the greater element at i
swap(&array[i + 1], &array[high]);
// return the partition point
return (i + 1);
}
void quickSort(int array[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// find the pivot element such that
// elements smaller than pivot are on left of pivot
// elements greater than pivot are on right of pivot
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
// recursive call on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
// recursive call on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// function to print array elements
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// main function
int main() {
int data[] = {8, 7, 2, 1, 0, 9, 6};
int n = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
printf("Unsorted Array\n");
printArray(data, n);
// perform quicksort on data
quickSort(data, 0, n - 1);
printf("Sorted array in ascending order: \n");
printArray(data, n);
}// Quick sort in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// function to swap elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
// function to print the array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << array[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// function to rearrange array (find the partition point)
int partition(int array[], int low, int high) {
// select the rightmost element as pivot
int pivot = array[high];
// pointer for greater element
int i = (low - 1);
// traverse each element of the array
// compare them with the pivot
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
// if element smaller than pivot is found
// swap it with the greater element pointed by i
i++;
// swap element at i with element at j
swap(&array[i], &array[j]);
}
}
// swap pivot with the greater element at i
swap(&array[i + 1], &array[high]);
// return the partition point
return (i + 1);
}
void quickSort(int array[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// find the pivot element such that
// elements smaller than pivot are on left of pivot
// elements greater than pivot are on righ of pivot
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
// recursive call on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
// recursive call on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {8, 7, 6, 1, 0, 9, 2};
int n = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
cout << "Unsorted Array: \n";
printArray(data, n);
// perform quicksort on data
quickSort(data, 0, n - 1);
cout << "Sorted array in ascending order: \n";
printArray(data, n);
}快速排序复杂度
| 时间复杂度 | |
|---|---|
| 最佳 | O(n*log n) |
| 最坏 | O(n2) |
| 平均 | O(n*log n) |
| 空间复杂度 | O(log n) |
| 稳定性 | 否 |
1. 时间复杂度
- 最坏情况复杂度 [Big-O]:
O(n2)
当选择的枢轴元素是最大或最小元素时,就会发生这种情况。
这种情况导致枢轴元素位于已排序数组的极端末端。一个子数组始终为空,另一个子数组包含n - 1个元素。因此,快速排序仅在此子数组上调用。
然而,对于分散的枢轴,快速排序算法的性能更好。
- 最佳情况复杂度 [Big-omega]:
O(n*log n)
当枢轴元素始终是中间元素或接近中间元素时,就会发生这种情况。 - 平均情况复杂度 [Big-theta]:
O(n*log n)
当上述情况不发生时,就会发生这种情况。
2. 空间复杂度
快速排序的空间复杂度为 O(log n)。
快速排序的应用
当以下情况时,使用快速排序算法
- 编程语言适合递归
- 时间复杂度很重要
- 空间复杂度很重要
