Python 字典是一种项目集合,类似于列表和元组。但是,与列表和元组不同,字典中的每个项目都是一个**键值**对(由一个键和一个值组成)。
创建字典
我们通过将 `key: value` 对放在花括号 `{}` 内并用逗号分隔来创建字典。例如:
# creating a dictionary
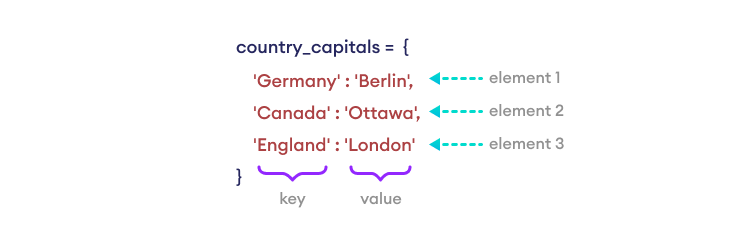
country_capitals = {
"Germany": "Berlin",
"Canada": "Ottawa",
"England": "London"
}
# printing the dictionary
print(country_capitals)输出
{'Germany': 'Berlin', 'Canada': 'Ottawa', 'England': 'London'}
`country_capitals` 字典有三个元素(键值对),其中 `'Germany'` 是键,`'Berlin'` 是分配给它的值,以此类推。
注意事项:
- 字典键必须是不可变的,例如元组、字符串、整数等。我们不能使用可变(可更改)对象(如列表)作为键。
- 我们还可以使用 Python 内置函数 `dict()` 创建字典。要了解更多信息,请访问 Python dict()。
有效和无效的字典
不可变对象一旦创建就不能更改。Python 中的一些不可变对象是整数、元组和字符串。
# valid dictionary
# integer as a key
my_dict = {1: "one", 2: "two", 3: "three"}
# valid dictionary
# tuple as a key
my_dict = {(1, 2): "one two", 3: "three"}
# invalid dictionary
# Error: using a list as a key is not allowed
my_dict = {1: "Hello", [1, 2]: "Hello Hi"}
# valid dictionary
# string as a key, list as a value
my_dict = {"USA": ["Chicago", "California", "New York"]}在此示例中,我们使用整数、元组和字符串作为字典的键。当我们使用列表作为键时,由于列表的可变性而出现错误消息。
**注意:** 字典的值可以是任何数据类型,包括列表等可变类型。
字典的键必须是唯一的。如果存在重复的键,则键的后一个值会覆盖前一个值。
hogwarts_houses = {
"Harry Potter": "Gryffindor",
"Hermione Granger": "Gryffindor",
"Ron Weasley": "Gryffindor",
# duplicate key with a different house
"Harry Potter": "Slytherin"
}
print(hogwarts_houses)输出
{'Harry Potter': 'Slytherin', 'Hermione Granger': 'Gryffindor', 'Ron Weasley': 'Gryffindor'}
在这里,键 `Harry Potter` 最初被分配给 `Gryffindor`。但是,第二个条目将 `Harry Potter` 分配给 `Slytherin`。
由于字典中不允许重复的键,因此最后一个条目 `Slytherin` 会覆盖前一个值 `Gryffindor`。
访问字典项目
我们可以通过将键放在方括号内来访问字典项目的值。
country_capitals = {
"Germany": "Berlin",
"Canada": "Ottawa",
"England": "London"
}
# access the value of keys
print(country_capitals["Germany"]) # Output: Berlin
print(country_capitals["England"]) # Output: London**注意:** 我们也可以使用 get() 方法来访问字典项目。
向字典添加项目
我们可以通过为新键分配值来向字典添加项目。例如:
country_capitals = {
"Germany": "Berlin",
"Canada": "Ottawa",
}
# add an item with "Italy" as key and "Rome" as its value
country_capitals["Italy"] = "Rome"
print(country_capitals)输出
{'Germany': 'Berlin', 'Canada': 'Ottawa', 'Italy': 'Rome'}
删除字典项目
我们可以使用 del 语句从字典中删除元素。例如:
country_capitals = {
"Germany": "Berlin",
"Canada": "Ottawa",
}
# delete item having "Germany" key
del country_capitals["Germany"]
print(country_capitals)输出
{'Canada': 'Ottawa'}
**注意**:我们也可以使用 pop() 方法从字典中删除项目。
如果我们需要一次性删除字典中的所有项目,我们可以使用 clear() 方法。
country_capitals = {
"Germany": "Berlin",
"Canada": "Ottawa",
}
# clear the dictionary
country_capitals.clear()
print(country_capitals) 输出
{}
更改字典项目
Python 字典是可变的(可更改的)。我们可以通过引用其键来更改字典元素的值。例如:
country_capitals = {
"Germany": "Berlin",
"Italy": "Naples",
"England": "London"
}
# change the value of "Italy" key to "Rome"
country_capitals["Italy"] = "Rome"
print(country_capitals)输出
{'Germany': 'Berlin', 'Italy': 'Rome', 'England': 'London'}
**注意**:我们也可以使用 update() 方法添加或更改字典项目。
遍历字典
字典是项目的有序集合(从 Python 3.7 开始),因此它保持其项目的顺序。
我们可以使用 for 循环 逐一遍历字典键。
country_capitals = {
"United States": "Washington D.C.",
"Italy": "Rome"
}
# print dictionary keys one by one
for country in country_capitals:
print(country)
print()
# print dictionary values one by one
for country in country_capitals:
capital = country_capitals[country]
print(capital)输出
United States Italy Washington D.C. Rome
查找字典长度
我们可以使用 len() 函数查找字典的长度。
country_capitals = {"England": "London", "Italy": "Rome"}
# get dictionary's length
print(len(country_capitals)) # Output: 2
numbers = {10: "ten", 20: "twenty", 30: "thirty"}
# get dictionary's length
print(len(numbers)) # Output: 3
countries = {}
# get dictionary's length
print(len(countries)) # Output: 0Python 字典方法
以下是一些常用的 字典方法。
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| pop() | 删除具有指定键的项目。 |
| update() | 添加或更改字典项目。 |
| clear() | 从字典中删除所有项目。 |
| keys() | 返回字典的所有键。 |
| values() | 返回字典的所有值。 |
| get() | 返回指定键的值。 |
| popitem() | 将最后插入的键和值作为元组返回。 |
| copy() | 返回字典的副本。 |
字典成员测试
我们可以使用 `in` 和 `not in` 运算符检查字典中是否存在键。
file_types = {
".txt": "Text File",
".pdf": "PDF Document",
".jpg": "JPEG Image",
}
# use of in and not in operators
print(".pdf" in file_types) # Output: True
print(".mp3" in file_types) # Output: False
print(".mp3" not in file_types) # Output: True**注意:** `in` 运算符检查是否存在键;它不检查是否存在值。
