作为一门面向对象的语言,Python 支持类的继承。它允许我们从一个已有的类创建一个新的类。
- 新创建的类被称为**子类**(child or derived class)。
- 子类继承的那个已有的类被称为超类(parent or base class)。
Python 继承语法
# define a superclass
class super_class:
# attributes and method definition
# inheritance
class sub_class(super_class):
# attributes and method of super_class
# attributes and method of sub_class这里,我们让 `sub_class` 从 `super_class` 继承。
**注意**:在继续学习继承之前,请确保你了解 Python 类和对象 的工作原理。
示例:Python 继承
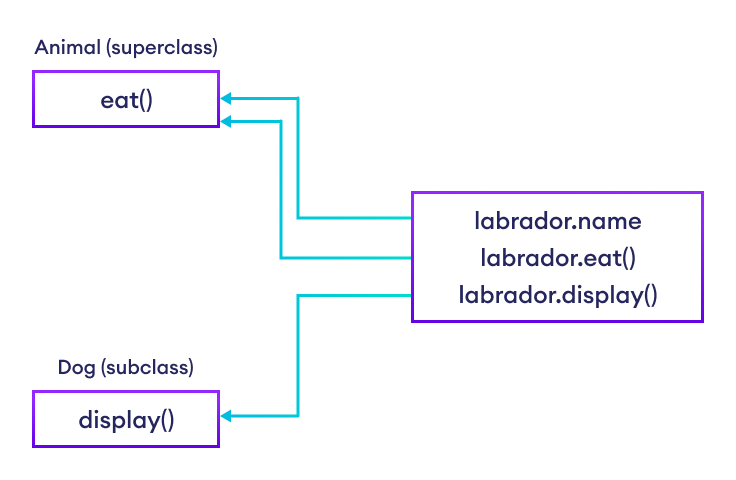
class Animal:
# attribute and method of the parent class
name = ""
def eat(self):
print("I can eat")
# inherit from Animal
class Dog(Animal):
# new method in subclass
def display(self):
# access name attribute of superclass using self
print("My name is ", self.name)
# create an object of the subclass
labrador = Dog()
# access superclass attribute and method
labrador.name = "Rohu"
labrador.eat()
# call subclass method
labrador.display()输出
I can eat My name is Rohu
在上面的示例中,我们从超类 Animal 派生出了一个子类 Dog。注意这些语句:
labrador.name = "Rohu"
labrador.eat()这里,我们使用 labrador(Dog 的对象)来访问 Animal 类的 name 和 `eat()` 方法。
这是可行的,因为子类继承了超类的所有属性和方法。
此外,我们还在 Dog 类的方法内部使用 `self` 访问了 name 属性。
is-a 关系
继承是一种 **is-a** 关系。也就是说,我们仅在两个类之间存在 **is-a** 关系时才使用继承。例如:
- **汽车**是**交通工具**
- **苹果**是**水果**
- **猫**是**动物**
这里,**汽车**可以从**交通工具**继承,**苹果**可以从**水果**继承,以此类推。
Python 继承中的方法重写
在前面的示例中,我们看到子类的对象可以访问超类的方法。
但是,如果同一个方法同时存在于超类和子类中,会发生什么呢?
在这种情况下,子类中的方法会覆盖超类中的方法。这个概念在 Python 中被称为方法重写。
示例:方法重写
class Animal:
# attributes and method of the parent class
name = ""
def eat(self):
print("I can eat")
# inherit from Animal
class Dog(Animal):
# override eat() method
def eat(self):
print("I like to eat bones")
# create an object of the subclass
labrador = Dog()
# call the eat() method on the labrador object
labrador.eat()输出
I like to eat bones
在上面的示例中,Dog 类和 Animal 类中都存在相同的方法 `eat()`。
现在,当我们使用 Dog 子类的对象调用 `eat()` 方法时,调用的是 Dog 类的方法。
这是因为 Dog 子类的 `eat()` 方法重写了 Animal 超类中的同名方法。
继承中的 super() 函数
之前我们看到,子类中相同的方法(函数)会覆盖超类中的方法。
然而,如果我们需要从子类中访问超类的方法,我们使用 `super()` 函数。例如:
class Animal:
name = ""
def eat(self):
print("I can eat")
# inherit from Animal
class Dog(Animal):
# override eat() method
def eat(self):
# call the eat() method of the superclass using super()
super().eat()
print("I like to eat bones")
# create an object of the subclass
labrador = Dog()
labrador.eat()输出
I can eat I like to eat bones
在上面的示例中,Dog 子类的 `eat()` 方法重写了 Animal 超类中的同名方法。
在 Dog 类内部,我们使用了
# call method of superclass
super().eat()来从 Dog 子类中调用 Animal 超类的 `eat()` 方法。
所以,当我们使用 labrador 对象调用 `eat()` 方法时
# call the eat() method
labrador.eat()被重写的方法和超类版本的 `eat()` 方法都会被执行。
要了解更多信息,请访问 Python super()。
更多关于 Python 继承
Python 中有 5 种不同类型的继承。它们是:
- **单一继承**:一个子类只从一个父类继承。
- **多重继承**:一个子类从多个父类继承。
- **多级继承**:一个子类从它的父类继承,而这个父类又从它的父类继承。
- **层次继承**:从一个父类创建出多个子类。
- **混合继承**:结合了多种形式的继承。
- **代码可重用性**:由于子类可以继承父类的所有功能,这实现了代码的可重用性。
- **高效开发**:一旦一个功能被开发出来,我们可以简单地继承它,这使得代码更清晰,易于维护。
- **定制化**:由于我们也可以在子类中添加自己的功能,我们可以只继承有用的功能,并定义其他所需的功能。
另请阅读
