集合是唯一数据的集合,这意味着集合中的元素不能重复。
例如,如果我们需要存储学生 ID 信息,集合是合适的,因为学生 ID 不能有重复。

在 Python 中创建集合
在 Python 中,我们通过将所有元素放在花括号 {} 中并用逗号分隔来创建集合。
集合可以包含任意数量的项,并且它们可以是不同类型(整数、浮点数、元组、字符串等)。但是集合不能包含可变元素,例如列表、集合或字典作为其元素。
让我们看一个例子,
# create a set of integer type
student_id = {112, 114, 116, 118, 115}
print('Student ID:', student_id)
# create a set of string type
vowel_letters = {'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'}
print('Vowel Letters:', vowel_letters)
# create a set of mixed data types
mixed_set = {'Hello', 101, -2, 'Bye'}
print('Set of mixed data types:', mixed_set)输出
Student ID: {112, 114, 115, 116, 118}
Vowel Letters: {'u', 'a', 'e', 'i', 'o'}
Set of mixed data types: {'Hello', 'Bye', 101, -2}
在上面的示例中,我们通过将所有元素放在花括号 {} 中创建了不同类型的集合。
注意:当你运行此代码时,你可能会得到不同顺序的输出。这是因为集合没有特定的顺序。
在 Python 中创建空集合
创建空集合有点棘手。空花括号 {} 将在 Python 中创建一个空字典。
要创建一个不带任何元素的集合,我们使用不带任何参数的 set() 函数。例如:
# create an empty set
empty_set = set()
# create an empty dictionary
empty_dictionary = { }
# check data type of empty_set
print('Data type of empty_set:', type(empty_set))
# check data type of dictionary_set
print('Data type of empty_dictionary:', type(empty_dictionary))输出
Data type of empty_set: <class 'set'> Data type of empty_dictionary: <class 'dict'>
这里,
- empty_set - 使用
set()创建的空集合 - empty_dictionary - 使用
{}创建的空字典
最后,我们使用 type() 函数来了解 empty_set 和 empty_dictionary 属于哪个类。
集合中的重复项
让我们看看如果我们尝试在集合中包含重复项会发生什么。
numbers = {2, 4, 6, 6, 2, 8}
print(numbers) # {8, 2, 4, 6}这里,我们可以看到集合中没有重复项,因为集合不能包含重复项。
在 Python 中添加和更新集合项
集合是可变的。然而,由于它们是无序的,索引没有意义。
我们不能使用索引或切片访问或更改集合的元素。集合数据类型不支持它。
在 Python 中向集合添加项
在 Python 中,我们使用 add() 方法向集合添加项。例如:
numbers = {21, 34, 54, 12}
print('Initial Set:',numbers)
# using add() method
numbers.add(32)
print('Updated Set:', numbers) 输出
Initial Set: {34, 12, 21, 54}
Updated Set: {32, 34, 12, 21, 54}
在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个名为 numbers 的集合。注意这行:
numbers.add(32)这里,add() 将 32 添加到我们的集合中。
更新 Python 集合
update() 方法用于使用其他集合类型(列表、元组、集合等)的项更新集合。例如:
companies = {'Lacoste', 'Ralph Lauren'}
tech_companies = ['apple', 'google', 'apple']
# using update() method
companies.update(tech_companies)
print(companies)
# Output: {'google', 'apple', 'Lacoste', 'Ralph Lauren'}这里,tech_companies 的所有唯一元素都添加到了 companies 集合中。
从集合中删除元素
我们使用 discard() 方法从集合中删除指定的元素。例如:
languages = {'Swift', 'Java', 'Python'}
print('Initial Set:',languages)
# remove 'Java' from a set
removedValue = languages.discard('Java')
print('Set after remove():', languages)输出
Initial Set: {'Python', 'Swift', 'Java'}
Set after remove(): {'Python', 'Swift'}
这里,我们使用了 discard() 方法从 languages 集合中删除 'Java'。
集合的内置函数
以下是一些常用的内置函数,它们允许我们对集合执行不同的操作。
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| all() | 如果集合的所有元素都为 true(或集合为空),则返回 True。 |
| any() | 如果集合的任何元素为 true,则返回 True。如果集合为空,则返回 False。 |
| enumerate() | 返回一个枚举对象。它包含集合所有项的索引和值对。 |
| len() | 返回集合的长度(项数)。 |
| max() | 返回集合中最大的项。 |
| min() | 返回集合中最小的项。 |
| sorted() | 返回一个包含集合中元素的新排序列表(不排序集合本身)。 |
| sum() | 返回集合中所有元素的总和。 |
在 Python 中迭代集合
fruits = {"Apple", "Peach", "Mango"}
# for loop to access each fruits
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)输出
Mango Peach Apple
这里,我们使用了 for 循环 在 Python 中迭代集合。
查找集合元素的数量
我们可以使用 len() 方法来查找集合中存在的元素数量。例如:
even_numbers = {2,4,6,8}
print('Set:',even_numbers)
# find number of elements
print('Total Elements:', len(even_numbers))输出
Set: {8, 2, 4, 6}
Total Elements: 4
这里,我们使用了 len() 方法来查找集合中存在的元素数量。
Python 集合操作
Python 集合提供了不同的内置方法来执行数学集合操作,如并集、交集、差集和对称差集。
两个集合的并集
两个集合 A 和 B 的并集包括集合 A 和 B 的所有元素。
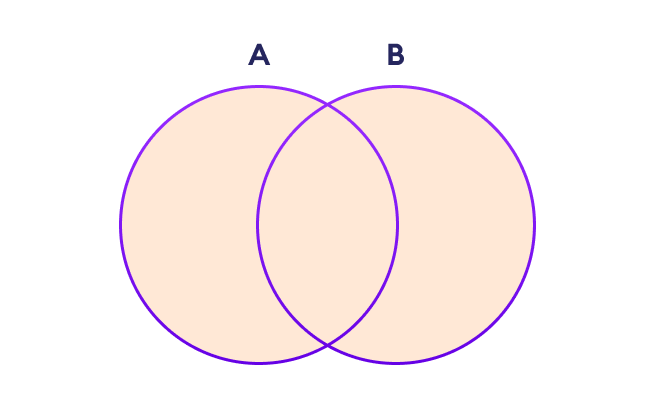
我们使用 | 运算符或 union() 方法来执行集合并集操作。例如:
# first set
A = {1, 3, 5}
# second set
B = {0, 2, 4}
# perform union operation using |
print('Union using |:', A | B)
# perform union operation using union()
print('Union using union():', A.union(B)) 输出
Union using |: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Union using union(): {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
注意:A|B 和 union() 等同于 A ⋃ B 集合操作。
集合交集
两个集合 A 和 B 的交集包括集合 A 和 B 之间的共同元素。
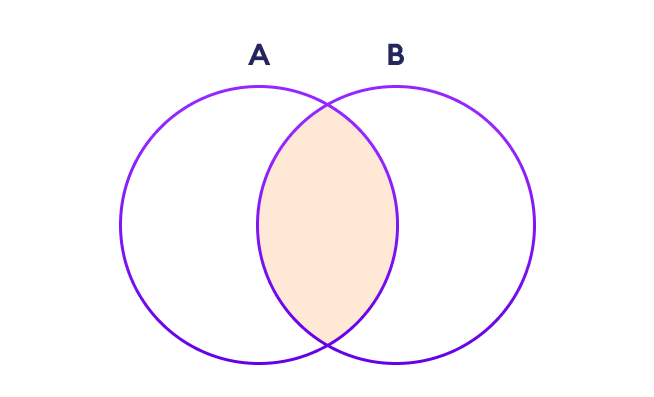
在 Python 中,我们使用 & 运算符或 intersection() 方法来执行集合交集操作。例如:
# first set
A = {1, 3, 5}
# second set
B = {1, 2, 3}
# perform intersection operation using &
print('Intersection using &:', A & B)
# perform intersection operation using intersection()
print('Intersection using intersection():', A.intersection(B)) 输出
Intersection using &: {1, 3}
Intersection using intersection(): {1, 3}
注意: A&B 和 intersection() 等同于 A ⋂ B 集合操作。
两个集合之间的差集
两个集合 A 和 B 的差集包括集合 A 中不存在于集合 B 中的元素。
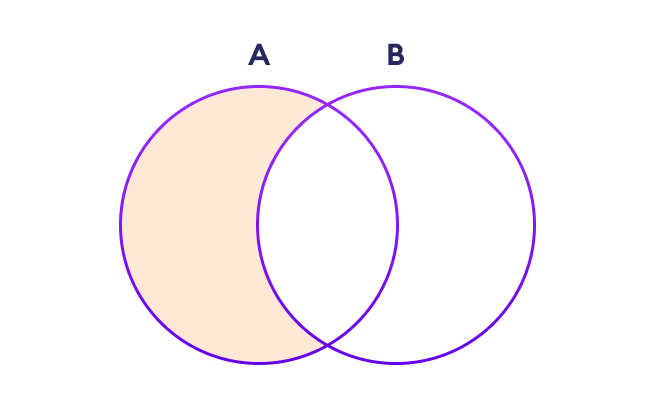
我们使用 - 运算符或 difference() 方法来执行两个集合之间的差集操作。例如:
# first set
A = {2, 3, 5}
# second set
B = {1, 2, 6}
# perform difference operation using &
print('Difference using &:', A - B)
# perform difference operation using difference()
print('Difference using difference():', A.difference(B)) 输出
Difference using &: {3, 5}
Difference using difference(): {3, 5}
注意:A - B 和 A.difference(B) 等同于 A - B 集合操作。
集合对称差集
两个集合 A 和 B 的对称差集包括 A 和 B 的所有元素,但不包括共同元素。
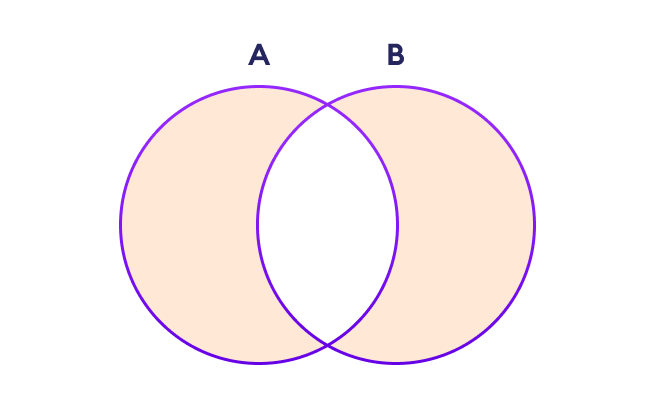
在 Python 中,我们使用 ^ 运算符或 symmetric_difference() 方法来执行两个集合之间的对称差集。例如:
# first set
A = {2, 3, 5}
# second set
B = {1, 2, 6}
# perform difference operation using &
print('using ^:', A ^ B)
# using symmetric_difference()
print('using symmetric_difference():', A.symmetric_difference(B)) 输出
using ^: {1, 3, 5, 6}
using symmetric_difference(): {1, 3, 5, 6}
检查两个集合是否相等
我们可以使用 == 运算符来检查两个集合是否相等。例如:
# first set
A = {1, 3, 5}
# second set
B = {3, 5, 1}
# perform difference operation using &
if A == B:
print('Set A and Set B are equal')
else:
print('Set A and Set B are not equal')输出
Set A and Set B are equal
在上面的示例中,A 和 B 具有相同的元素,所以条件
if A == B计算结果为 True。因此,if 中的语句 print('Set A and Set B are equal') 被执行。
其他 Python 集合方法
有许多集合方法,其中一些我们已经在上面使用过。以下是集合对象可用的所有方法的列表:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| add() | 向集合添加元素 |
| clear() | 从集合中删除所有元素 |
| copy() | 返回集合的副本 |
| difference() | 返回两个或多个集合的差集作为新集合 |
| difference_update() | 从该集合中删除另一个集合的所有元素 |
| discard() | 如果元素是成员,则从集合中删除该元素。(如果元素不在集合中,则不执行任何操作) |
| intersection() | 返回两个集合的交集作为新集合 |
| intersection_update() | 用集合本身与另一个集合的交集更新集合 |
| isdisjoint() | 如果两个集合的交集为空,则返回 True |
| issubset() | 如果另一个集合包含此集合,则返回 True |
| issuperset() | 如果此集合包含另一个集合,则返回 True |
| pop() | 删除并返回一个任意集合元素。如果集合为空,则引发 KeyError |
| remove() | 从集合中删除元素。如果元素不是成员,则引发 KeyError |
| symmetric_difference() | 返回两个集合的对称差集作为新集合 |
| symmetric_difference_update() | 用集合本身与另一个集合的对称差集更新集合 |
| union() | 在新集合中返回集合的并集 |
| update() | 用集合本身与其他集合的并集更新集合 |
另请阅读
