计数排序是一种排序算法,它通过计算数组中每个唯一元素的出现次数来对数组元素进行排序。计数存储在一个辅助数组中,排序通过将计数映射到辅助数组的索引来完成。
计数排序的工作原理
- 找出给定数组中的最大元素(设为
max)。
给定数组 - 初始化一个长度为
max+1的数组,所有元素都为 0。该数组用于存储数组中元素的计数。
计数数组 - 将每个元素的计数存储在其在
count数组中的相应索引处。
例如:如果元素 3 的计数为 2,则 2 存储在 count 数组的第 3 个位置。如果数组中不存在元素 "5",则第 5 个位置存储 0。
每个元素的计数已存储 - 存储计数数组元素的累加和。这有助于将元素放置到已排序数组的正确索引中。

累加计数 - 找出原始数组中每个元素在计数数组中的索引。这会给出累加计数。将元素放置在通过下面图示计算出的索引处。
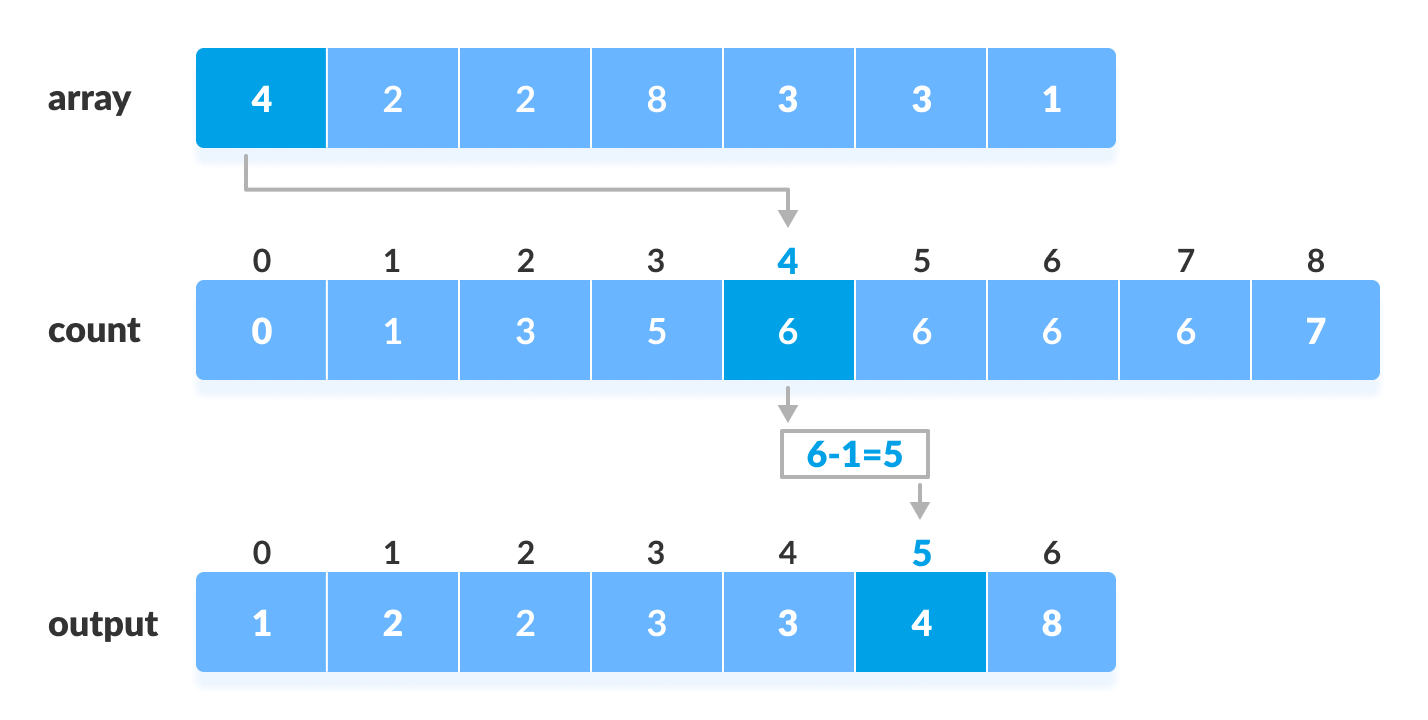
计数排序 - 在将每个元素放置到其正确位置后,将其计数减一。
计数排序算法
countingSort(array, size)
max <- find largest element in array
initialize count array with all zeros
for j <- 0 to size
find the total count of each unique element and
store the count at jth index in count array
for i <- 1 to max
find the cumulative sum and store it in count array itself
for j <- size down to 1
restore the elements to array
decrease count of each element restored by 1Python、Java 和 C/C++ 中的计数排序代码
# Counting sort in Python programming
def countingSort(array):
size = len(array)
output = [0] * size
# Initialize count array
count = [0] * (max(array) + 1)
# Store the count of each elements in count array
for i in range(0, size):
count[array[i]] += 1
# Store the cummulative count
for i in range(1, (max(array) + 1)):
count[i] += count[i - 1]
# Find the index of each element of the original array in count array
# place the elements in output array
i = size - 1
while i >= 0:
output[count[array[i]] - 1] = array[i]
count[array[i]] -= 1
i -= 1
# Copy the sorted elements into original array
for i in range(0, size):
array[i] = output[i]
data = [4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1]
countingSort(data)
print("Sorted Array in Ascending Order: ")
print(data)// Counting sort in Java programming
import java.util.Arrays;
class CountingSort {
void countSort(int array[], int size) {
int[] output = new int[size + 1];
// Find the largest element of the array
int max = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if (array[i] > max)
max = array[i];
}
int[] count = new int[max + 1];
// Initialize count array with all zeros.
for (int i = 0; i < max; ++i) {
count[i] = 0;
}
// Store the count of each element
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
count[array[i]]++;
}
// Store the cummulative count of each array
for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) {
count[i] += count[i - 1];
}
// Find the index of each element of the original array in count array, and
// place the elements in output array
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[array[i]] - 1] = array[i];
count[array[i]]--;
}
// Copy the sorted elements into original array
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = output[i];
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { 4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1 };
int size = data.length;
CountingSort cs = new CountingSort();
cs.countSort(data, size);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}// Counting sort in C programming
#include <stdio.h>
void countingSort(int array[], int size) {
int output[10];
// Find the largest element of the array
int max = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if (array[i] > max)
max = array[i];
}
// The size of count must be at least (max+1) but
// we cannot declare it as int count(max+1) in C as
// it does not support dynamic memory allocation.
// So, its size is provided statically.
int count[10];
// Initialize count array with all zeros.
for (int i = 0; i <= max; ++i) {
count[i] = 0;
}
// Store the count of each element
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
count[array[i]]++;
}
// Store the cummulative count of each array
for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) {
count[i] += count[i - 1];
}
// Find the index of each element of the original array in count array, and
// place the elements in output array
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[array[i]] - 1] = array[i];
count[array[i]]--;
}
// Copy the sorted elements into original array
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = output[i];
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int array[] = {4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1};
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
countingSort(array, n);
printArray(array, n);
}// Counting sort in C++ programming
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void countSort(int array[], int size) {
// The size of count must be at least the (max+1) but
// we cannot assign declare it as int count(max+1) in C++ as
// it does not support dynamic memory allocation.
// So, its size is provided statically.
int output[10];
int count[10];
int max = array[0];
// Find the largest element of the array
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if (array[i] > max)
max = array[i];
}
// Initialize count array with all zeros.
for (int i = 0; i <= max; ++i) {
count[i] = 0;
}
// Store the count of each element
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
count[array[i]]++;
}
// Store the cummulative count of each array
for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) {
count[i] += count[i - 1];
}
// Find the index of each element of the original array in count array, and
// place the elements in output array
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[array[i]] - 1] = array[i];
count[array[i]]--;
}
// Copy the sorted elements into original array
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
array[i] = output[i];
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << array[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int array[] = {4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1};
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
countSort(array, n);
printArray(array, n);
}复杂度
| 时间复杂度 | |
|---|---|
| 最佳 | O(n+max) |
| 最坏 | O(n+max) |
| 平均 | O(n+max) |
| 空间复杂度 | O(max) |
| 稳定性 | 是 |
时间复杂度
主要有四个循环。(找到最大值可以在函数外部完成。)
| for 循环 | 计数时间 |
|---|---|
| 第 1 次 | O(max) |
| 第 2 次 | O(size) |
| 第 3 次 | O(max) |
| 第 4 次 | O(size) |
总体复杂度 = O(max)+O(size)+O(max)+O(size) = O(max+size)
- 最坏情况复杂度:
O(n+max) - 最好情况复杂度:
O(n+max) - 平均情况复杂度:
O(n+max)
在以上所有情况中,复杂度都相同,因为无论元素如何放置在数组中,算法都会执行 n+max 次。
它没有元素之间的比较,因此比基于比较的排序技术要好。但是,如果整数非常大,它就不好,因为需要创建那么大的数组。
空间复杂度
计数排序的空间复杂度为 O(max)。元素的范围越大,空间复杂度就越大。
计数排序的应用
当满足以下条件时,使用计数排序:
- 存在具有多个计数的较小整数。
- 需要线性复杂度。
