深度优先搜索或深度优先遍历是一种递归算法,用于搜索图或树数据结构的所有顶点。遍历是指访问图的所有节点。
深度优先搜索算法
标准的DFS实现将图的每个顶点分为两类:
- 已访问
- 未访问
该算法的目的是标记每个顶点为已访问,同时避免循环。
DFS算法工作流程如下:
- 首先将图的任意一个顶点放入堆栈顶部。
- 取出堆栈的顶部元素并将其添加到已访问列表中。
- 创建该顶点邻接节点的列表。将不在已访问列表中的节点添加到堆栈顶部。
- 持续重复步骤2和3,直到堆栈为空。
深度优先搜索示例
让我们通过一个例子来看看深度优先搜索算法是如何工作的。我们使用一个具有5个顶点的无向图。
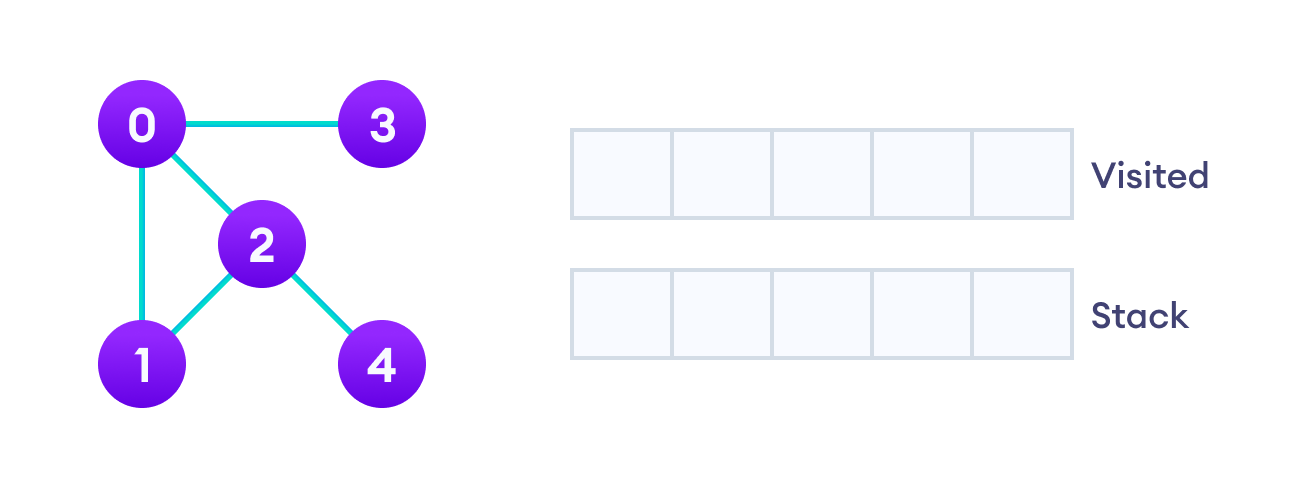

我们从顶点0开始,DFS算法首先将其放入已访问列表,并将所有其邻接顶点放入堆栈。
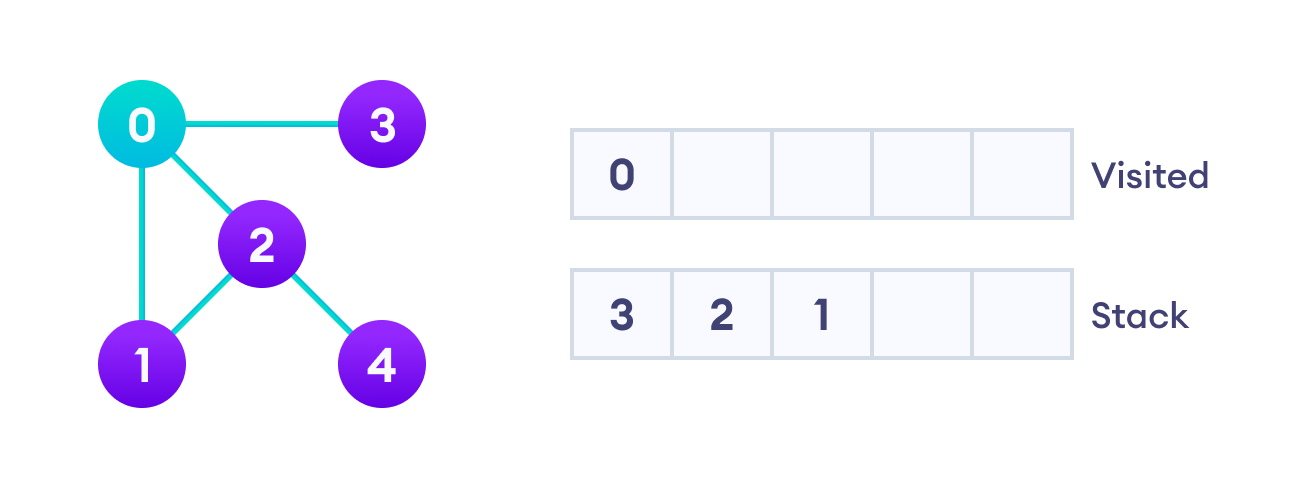
接下来,我们访问堆栈顶部的元素,即1,并转到其邻接节点。由于0已被访问,我们改访问2。
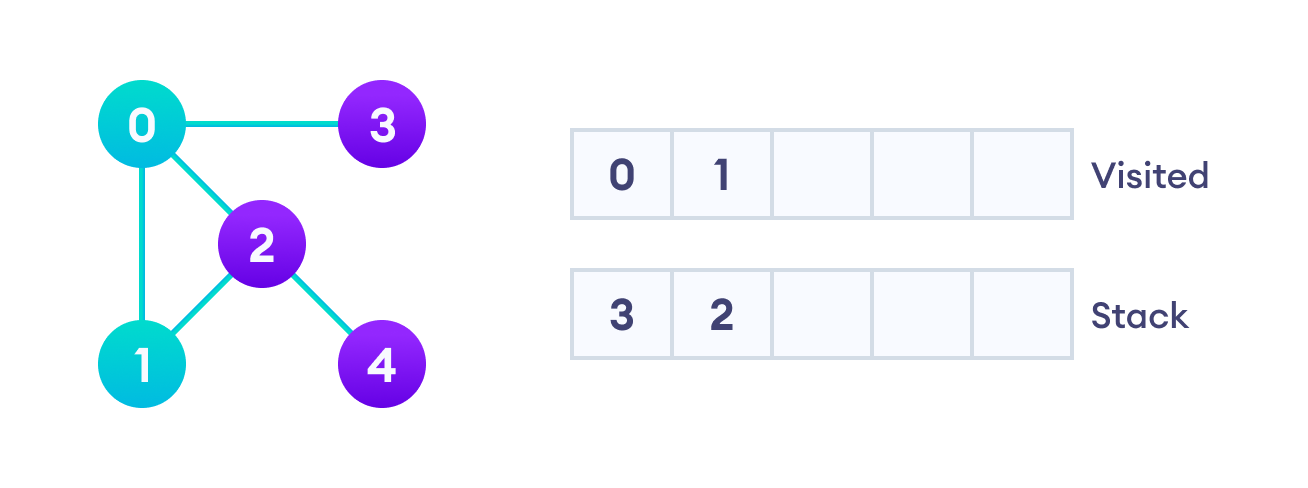
顶点2有一个未访问的邻接顶点4,因此我们将其添加到堆栈顶部并访问它。
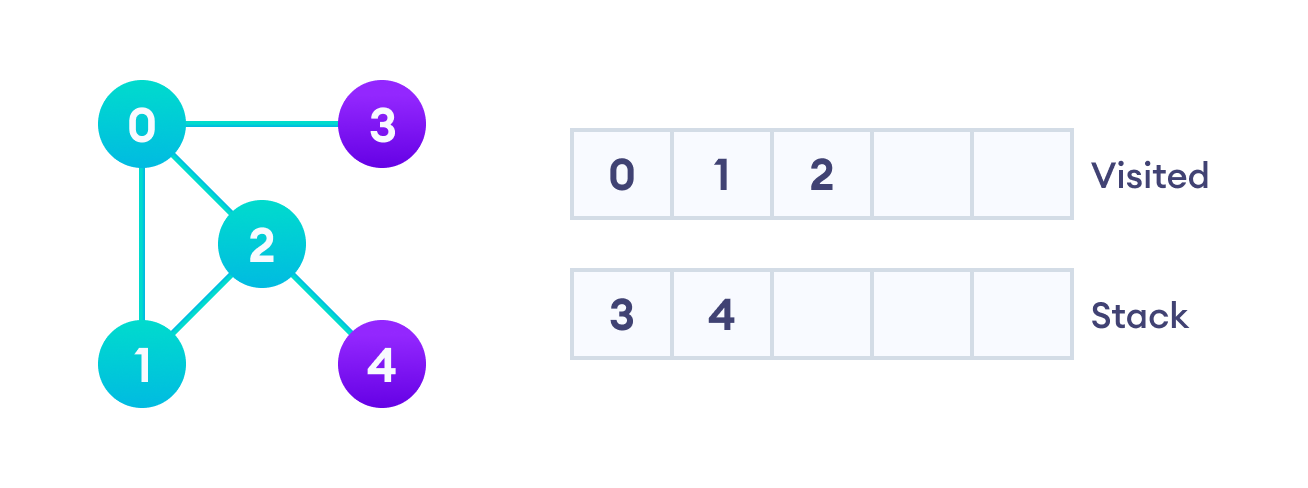
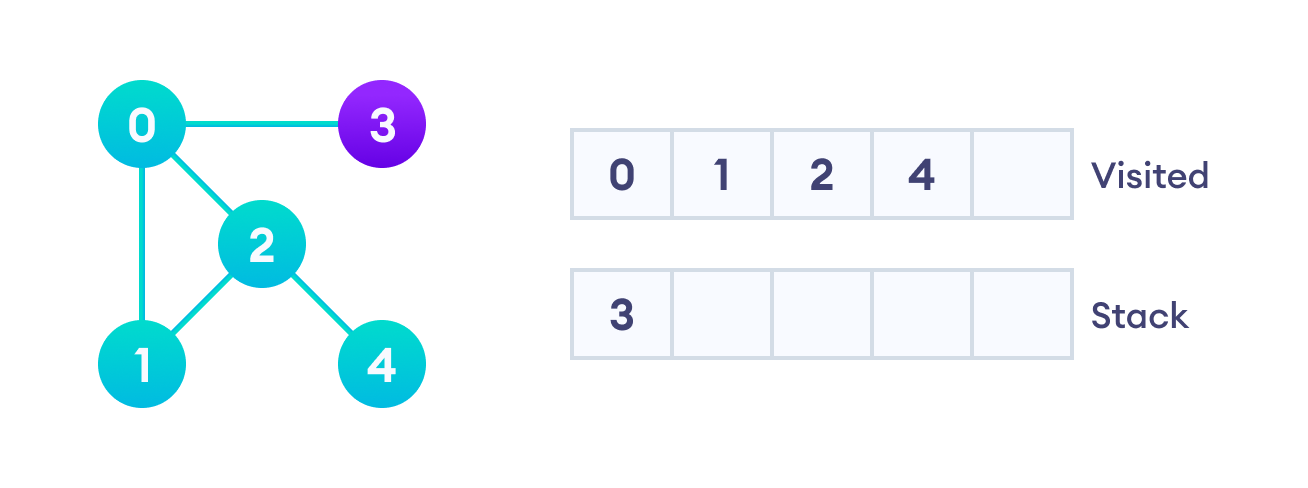
在我们访问最后一个元素3后,它没有任何未访问的邻接节点,因此我们完成了图的深度优先遍历。

DFS伪代码(递归实现)
DFS的伪代码如下所示。在init()函数中,请注意我们对每个节点都运行DFS函数。这是因为图可能存在两个不同的不连通部分,为了确保我们覆盖每个顶点,我们也可以对每个节点运行DFS算法。
DFS(G, u)
u.visited = true
for each v ∈ G.Adj[u]
if v.visited == false
DFS(G,v)
init() {
For each u ∈ G
u.visited = false
For each u ∈ G
DFS(G, u)
}
Python、Java和C/C++中的DFS实现
下面给出了带有示例的深度优先搜索算法的代码。代码已被简化,以便我们可以专注于算法本身,而不是其他细节。
DFS可视化:不要只阅读DFS,亲眼看看它的实际运行过程。通过我们新的DSA可视化工具,逐步了解算法的每一行是如何工作的。 亲自尝试!
# DFS algorithm in Python
# DFS algorithm
def dfs(graph, start, visited=None):
if visited is None:
visited = set()
visited.add(start)
print(start)
for next in graph[start] - visited:
dfs(graph, next, visited)
return visited
graph = {'0': set(['1', '2']),
'1': set(['0', '3', '4']),
'2': set(['0']),
'3': set(['1']),
'4': set(['2', '3'])}
dfs(graph, '0')// DFS algorithm in Java
import java.util.*;
class Graph {
private LinkedList<Integer> adjLists[];
private boolean visited[];
// Graph creation
Graph(int vertices) {
adjLists = new LinkedList[vertices];
visited = new boolean[vertices];
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
adjLists[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
// Add edges
void addEdge(int src, int dest) {
adjLists[src].add(dest);
}
// DFS algorithm
void DFS(int vertex) {
visited[vertex] = true;
System.out.print(vertex + " ");
Iterator<Integer> ite = adjLists[vertex].listIterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
int adj = ite.next();
if (!visited[adj])
DFS(adj);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
System.out.println("Following is Depth First Traversal");
g.DFS(2);
}
}// DFS algorithm in C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int vertex;
struct node* next;
};
struct node* createNode(int v);
struct Graph {
int numVertices;
int* visited;
// We need int** to store a two dimensional array.
// Similary, we need struct node** to store an array of Linked lists
struct node** adjLists;
};
// DFS algo
void DFS(struct Graph* graph, int vertex) {
struct node* adjList = graph->adjLists[vertex];
struct node* temp = adjList;
graph->visited[vertex] = 1;
printf("Visited %d \n", vertex);
while (temp != NULL) {
int connectedVertex = temp->vertex;
if (graph->visited[connectedVertex] == 0) {
DFS(graph, connectedVertex);
}
temp = temp->next;
}
}
// Create a node
struct node* createNode(int v) {
struct node* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->vertex = v;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Create graph
struct Graph* createGraph(int vertices) {
struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph));
graph->numVertices = vertices;
graph->adjLists = malloc(vertices * sizeof(struct node*));
graph->visited = malloc(vertices * sizeof(int));
int i;
for (i = 0; i < vertices; i++) {
graph->adjLists[i] = NULL;
graph->visited[i] = 0;
}
return graph;
}
// Add edge
void addEdge(struct Graph* graph, int src, int dest) {
// Add edge from src to dest
struct node* newNode = createNode(dest);
newNode->next = graph->adjLists[src];
graph->adjLists[src] = newNode;
// Add edge from dest to src
newNode = createNode(src);
newNode->next = graph->adjLists[dest];
graph->adjLists[dest] = newNode;
}
// Print the graph
void printGraph(struct Graph* graph) {
int v;
for (v = 0; v < graph->numVertices; v++) {
struct node* temp = graph->adjLists[v];
printf("\n Adjacency list of vertex %d\n ", v);
while (temp) {
printf("%d -> ", temp->vertex);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main() {
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(4);
addEdge(graph, 0, 1);
addEdge(graph, 0, 2);
addEdge(graph, 1, 2);
addEdge(graph, 2, 3);
printGraph(graph);
DFS(graph, 2);
return 0;
}// DFS algorithm in C++
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
int numVertices;
list<int> *adjLists;
bool *visited;
public:
Graph(int V);
void addEdge(int src, int dest);
void DFS(int vertex);
};
// Initialize graph
Graph::Graph(int vertices) {
numVertices = vertices;
adjLists = new list<int>[vertices];
visited = new bool[vertices];
}
// Add edges
void Graph::addEdge(int src, int dest) {
adjLists[src].push_front(dest);
}
// DFS algorithm
void Graph::DFS(int vertex) {
visited[vertex] = true;
list<int> adjList = adjLists[vertex];
cout << vertex << " ";
list<int>::iterator i;
for (i = adjList.begin(); i != adjList.end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFS(*i);
}
int main() {
Graph g(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.DFS(2);
return 0;
}深度优先搜索的复杂度
DFS算法的时间复杂度表示为O(V + E),其中V是节点的数量,E是边的数量。
该算法的空间复杂度为O(V)。
DFS算法的应用
- 用于查找路径
- 用于测试图是否是二分图
- 用于查找图的强连通分量
- 用于检测图中的循环
