桶排序是一种排序算法,它将待排序数组的元素分成若干个组,称为桶。然后,使用任何合适的 排序算法 或递归地应用相同的桶算法对每个桶进行排序。
最后,将排序后的桶合并,形成一个最终的排序数组。
散布-收集方法
桶排序的过程可以理解为一种散布-收集方法。在这里,元素首先被散布到桶中,然后对每个桶中的元素进行排序。最后,按顺序收集元素。
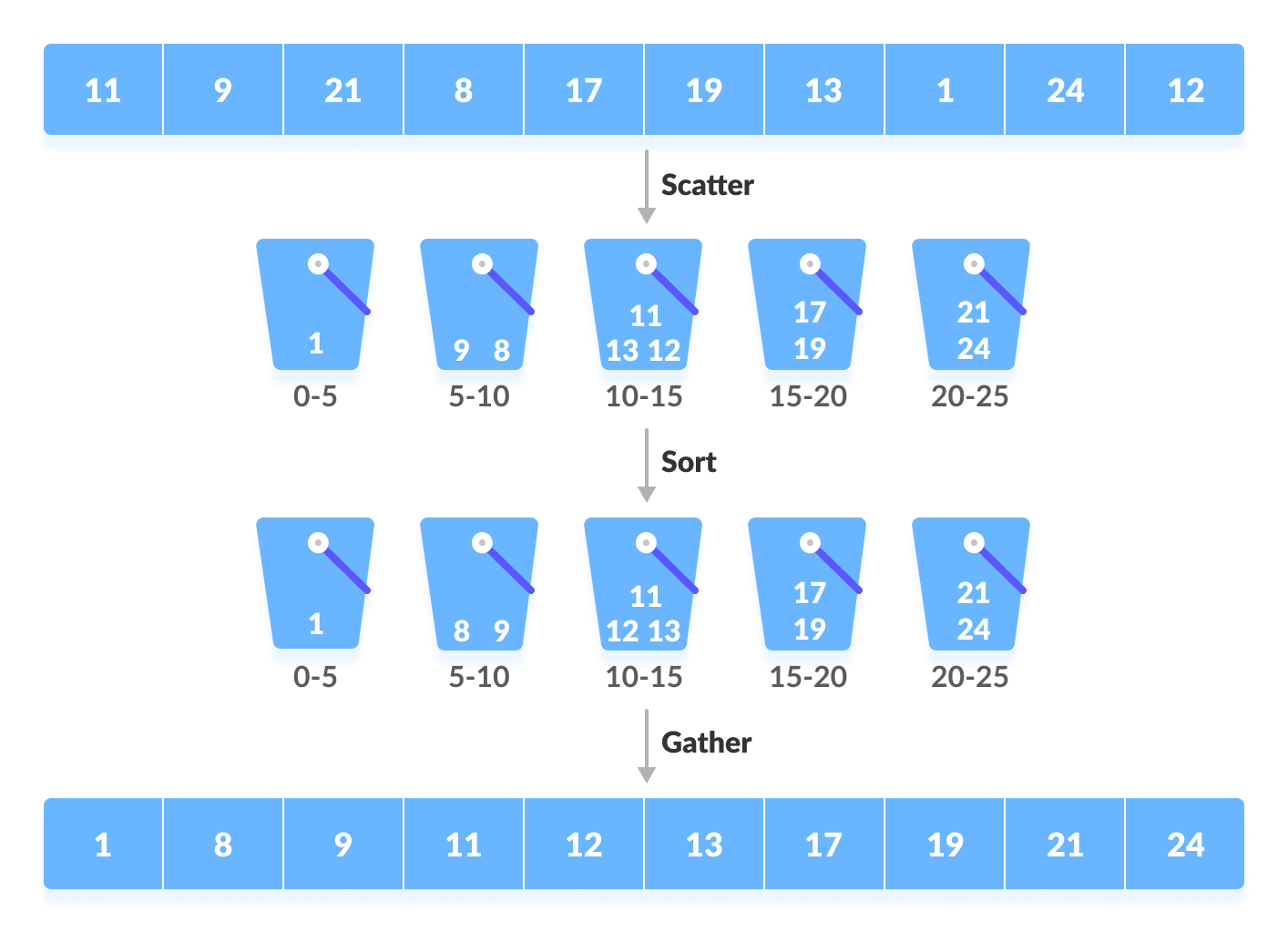
桶排序的工作原理
- 假设输入数组是
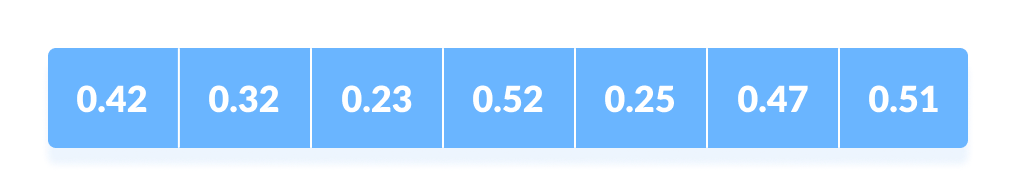
输入数组
创建一个大小为 10 的数组。该数组的每个槽都用作存储元素的桶。
数组中的每个位置都是一个桶 - 根据桶的范围将元素从数组插入桶中。
在我们示例代码中,我们有范围从 0 到 1、1 到 2、2 到 3、...... (n-1) 到 n 的桶。
假设,取输入元素.23。将其乘以size = 10(即.23*10=2.3)。然后,将其转换为整数(即2.3≈2)。最后,将 .23 插入桶 2。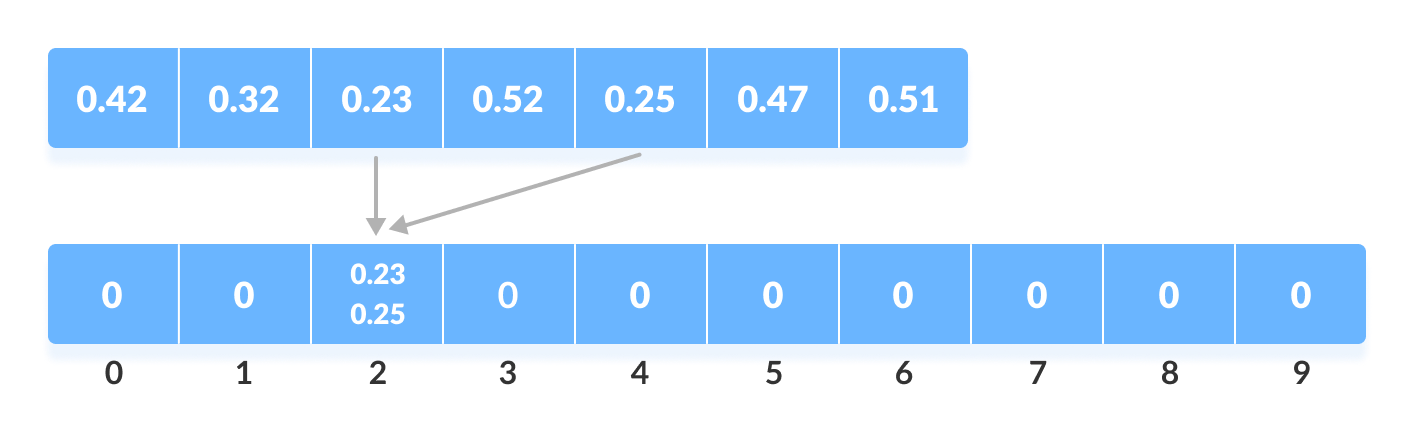
将元素从数组插入桶中
类似地,.25 也插入到同一个桶中。每次都取浮点数的向下取整值。
如果我们以整数作为输入,我们需要将其除以区间(此处为 10)来获取向下取整的值。
同样,其他元素也插入到它们各自的桶中。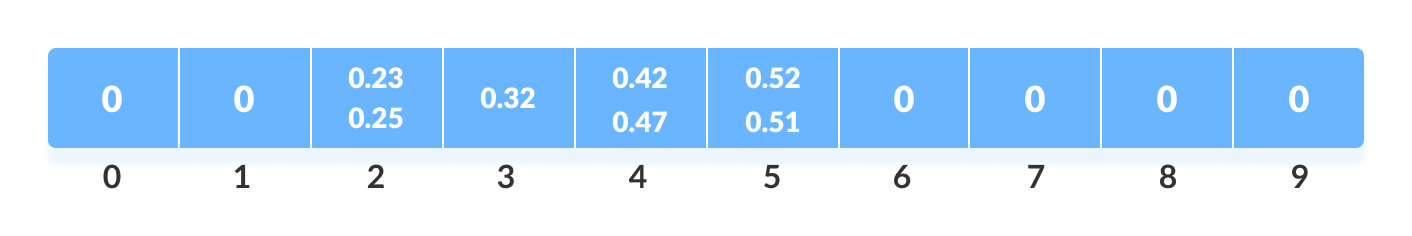
将数组中的所有元素插入到桶中 - 使用任何稳定的排序算法对每个桶中的元素进行排序。这里我们使用了快速排序(内置函数)。
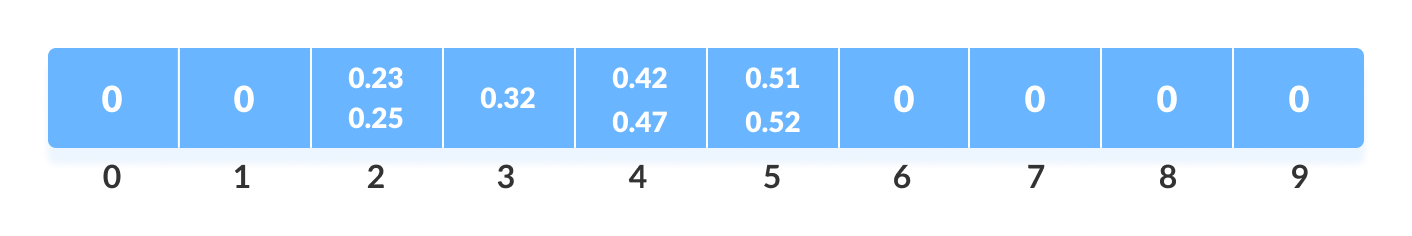
对每个桶中的元素进行排序 - 从每个桶中收集元素。
这是通过迭代桶并在每个周期中将单个元素插入原始数组来完成的。一旦元素从桶中复制到原始数组,就会将其从桶中删除。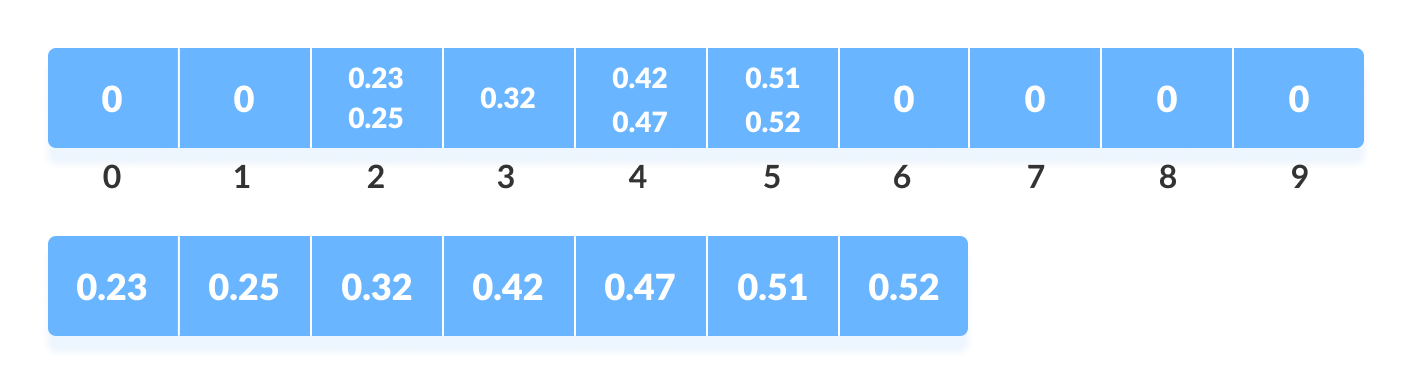
从每个桶收集元素
桶排序算法
bucketSort()
create N buckets each of which can hold a range of values
for all the buckets
initialize each bucket with 0 values
for all the buckets
put elements into buckets matching the range
for all the buckets
sort elements in each bucket
gather elements from each bucket
end bucketSortPython、Java 和 C/C++ 中的桶排序代码
# Bucket Sort in Python
def bucketSort(array):
bucket = []
# Create empty buckets
for i in range(len(array)):
bucket.append([])
# Insert elements into their respective buckets
for j in array:
index_b = int(10 * j)
bucket[index_b].append(j)
# Sort the elements of each bucket
for i in range(len(array)):
bucket[i] = sorted(bucket[i])
# Get the sorted elements
k = 0
for i in range(len(array)):
for j in range(len(bucket[i])):
array[k] = bucket[i][j]
k += 1
return array
array = [.42, .32, .33, .52, .37, .47, .51]
print("Sorted Array in descending order is")
print(bucketSort(array))// Bucket sort in Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class BucketSort {
public void bucketSort(float[] arr, int n) {
if (n <= 0)
return;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ArrayList<Float>[] bucket = new ArrayList[n];
// Create empty buckets
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
bucket[i] = new ArrayList<Float>();
// Add elements into the buckets
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int bucketIndex = (int) arr[i] * n;
bucket[bucketIndex].add(arr[i]);
}
// Sort the elements of each bucket
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Collections.sort((bucket[i]));
}
// Get the sorted array
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0, size = bucket[i].size(); j < size; j++) {
arr[index++] = bucket[i].get(j);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
BucketSort b = new BucketSort();
float[] arr = { (float) 0.42, (float) 0.32, (float) 0.33, (float) 0.52, (float) 0.37, (float) 0.47,
(float) 0.51 };
b.bucketSort(arr, 7);
for (float i : arr)
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}// Bucket sort in C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define NARRAY 7 // Array size
#define NBUCKET 6 // Number of buckets
#define INTERVAL 10 // Each bucket capacity
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void BucketSort(int arr[]);
struct Node *InsertionSort(struct Node *list);
void print(int arr[]);
void printBuckets(struct Node *list);
int getBucketIndex(int value);
// Sorting function
void BucketSort(int arr[]) {
int i, j;
struct Node **buckets;
// Create buckets and allocate memory size
buckets = (struct Node **)malloc(sizeof(struct Node *) * NBUCKET);
// Initialize empty buckets
for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; ++i) {
buckets[i] = NULL;
}
// Fill the buckets with respective elements
for (i = 0; i < NARRAY; ++i) {
struct Node *current;
int pos = getBucketIndex(arr[i]);
current = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
current->data = arr[i];
current->next = buckets[pos];
buckets[pos] = current;
}
// Print the buckets along with their elements
for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; i++) {
printf("Bucket[%d]: ", i);
printBuckets(buckets[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Sort the elements of each bucket
for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; ++i) {
buckets[i] = InsertionSort(buckets[i]);
}
printf("-------------\n");
printf("Bucktets after sorting\n");
for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; i++) {
printf("Bucket[%d]: ", i);
printBuckets(buckets[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Put sorted elements on arr
for (j = 0, i = 0; i < NBUCKET; ++i) {
struct Node *node;
node = buckets[i];
while (node) {
arr[j++] = node->data;
node = node->next;
}
}
return;
}
// Function to sort the elements of each bucket
struct Node *InsertionSort(struct Node *list) {
struct Node *k, *nodeList;
if (list == 0 || list->next == 0) {
return list;
}
nodeList = list;
k = list->next;
nodeList->next = 0;
while (k != 0) {
struct Node *ptr;
if (nodeList->data > k->data) {
struct Node *tmp;
tmp = k;
k = k->next;
tmp->next = nodeList;
nodeList = tmp;
continue;
}
for (ptr = nodeList; ptr->next != 0; ptr = ptr->next) {
if (ptr->next->data > k->data)
break;
}
if (ptr->next != 0) {
struct Node *tmp;
tmp = k;
k = k->next;
tmp->next = ptr->next;
ptr->next = tmp;
continue;
} else {
ptr->next = k;
k = k->next;
ptr->next->next = 0;
continue;
}
}
return nodeList;
}
int getBucketIndex(int value) {
return value / INTERVAL;
}
void print(int ar[]) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < NARRAY; ++i) {
printf("%d ", ar[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Print buckets
void printBuckets(struct Node *list) {
struct Node *cur = list;
while (cur) {
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
}
// Driver code
int main(void) {
int array[NARRAY] = {42, 32, 33, 52, 37, 47, 51};
printf("Initial array: ");
print(array);
printf("-------------\n");
BucketSort(array);
printf("-------------\n");
printf("Sorted array: ");
print(array);
return 0;
}// Bucket sort in C++
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define NARRAY 7 // Array size
#define NBUCKET 6 // Number of buckets
#define INTERVAL 10 // Each bucket capacity
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void BucketSort(int arr[]);
struct Node *InsertionSort(struct Node *list);
void print(int arr[]);
void printBuckets(struct Node *list);
int getBucketIndex(int value);
// Sorting function
void BucketSort(int arr[]) {
int i, j;
struct Node **buckets;
// Create buckets and allocate memory size
buckets = (struct Node **)malloc(sizeof(struct Node *) * NBUCKET);
// Initialize empty buckets
for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; ++i) {
buckets[i] = NULL;
}
// Fill the buckets with respective elements
for (i = 0; i < NARRAY; ++i) {
struct Node *current;
int pos = getBucketIndex(arr[i]);
current = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
current->data = arr[i];
current->next = buckets[pos];
buckets[pos] = current;
}
// Print the buckets along with their elements
for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; i++) {
cout << "Bucket[" << i << "] : ";
printBuckets(buckets[i]);
cout << endl;
}
// Sort the elements of each bucket
for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; ++i) {
buckets[i] = InsertionSort(buckets[i]);
}
cout << "-------------" << endl;
cout << "Bucktets after sorted" << endl;
for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; i++) {
cout << "Bucket[" << i << "] : ";
printBuckets(buckets[i]);
cout << endl;
}
// Put sorted elements on arr
for (j = 0, i = 0; i < NBUCKET; ++i) {
struct Node *node;
node = buckets[i];
while (node) {
arr[j++] = node->data;
node = node->next;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < NBUCKET; ++i) {
struct Node *node;
node = buckets[i];
while (node) {
struct Node *tmp;
tmp = node;
node = node->next;
free(tmp);
}
}
free(buckets);
return;
}
// Function to sort the elements of each bucket
struct Node *InsertionSort(struct Node *list) {
struct Node *k, *nodeList;
if (list == 0 || list->next == 0) {
return list;
}
nodeList = list;
k = list->next;
nodeList->next = 0;
while (k != 0) {
struct Node *ptr;
if (nodeList->data > k->data) {
struct Node *tmp;
tmp = k;
k = k->next;
tmp->next = nodeList;
nodeList = tmp;
continue;
}
for (ptr = nodeList; ptr->next != 0; ptr = ptr->next) {
if (ptr->next->data > k->data)
break;
}
if (ptr->next != 0) {
struct Node *tmp;
tmp = k;
k = k->next;
tmp->next = ptr->next;
ptr->next = tmp;
continue;
} else {
ptr->next = k;
k = k->next;
ptr->next->next = 0;
continue;
}
}
return nodeList;
}
int getBucketIndex(int value) {
return value / INTERVAL;
}
// Print buckets
void print(int ar[]) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < NARRAY; ++i) {
cout << setw(3) << ar[i];
}
cout << endl;
}
void printBuckets(struct Node *list) {
struct Node *cur = list;
while (cur) {
cout << setw(3) << cur->data;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
// Driver code
int main(void) {
int array[NARRAY] = {42, 32, 33, 52, 37, 47, 51};
cout << "Initial array: " << endl;
print(array);
cout << "-------------" << endl;
BucketSort(array);
cout << "-------------" << endl;
cout << "Sorted array: " << endl;
print(array);
}桶排序复杂度
| 时间复杂度 | |
|---|---|
| 最佳 | O(n+k) |
| 最坏 | O(n2) |
| 平均 | O(n) |
| 空间复杂度 | O(n+k) |
| 稳定性 | 是 |
- 最坏情况复杂度:
O(n2)
当数组中的元素范围接近时,它们很可能被放入同一个桶中。这可能导致某些桶中的元素比其他桶多。
这使得复杂度取决于用于对桶中的元素进行排序的算法。
当元素按相反的顺序排列时,复杂度会变得更糟。如果使用插入排序对桶中的元素进行排序,则时间复杂度将为O(n^2)。 - 最佳情况复杂度:
O(n+k)
当元素在桶中均匀分布,并且每个桶中的元素数量大致相等时,就会发生这种情况。
如果桶内的元素已经排序,复杂度会更好。
如果使用插入排序对桶中的元素进行排序,那么最佳情况下的整体复杂度将是线性的,即O(n+k)。O(n)是创建桶的复杂度,而O(k)是使用在最佳情况下具有线性时间复杂度的算法对桶中的元素进行排序的复杂度。 - 平均情况复杂度:
O(n)
当元素在数组中随机分布时,就会发生这种情况。即使元素没有均匀分布,桶排序也能以线性时间运行。只要桶大小的平方和是总元素数量的线性函数,它就成立。
桶排序的应用
当以下情况时使用桶排序
- 输入在给定范围内均匀分布。
- 存在浮点数值
