栈是一种遵循后进先出 (LIFO) 原则的线性数据结构。这意味着最后压入栈中的元素会最先被移除。
你可以将栈数据结构想象成一摞摞叠起来的盘子。

在这里,你可以
- 将一个新盘子放在顶部
- 移除顶部的盘子
如果你想要底部的盘子,你必须先移除顶部所有的盘子。栈数据结构的工作原理正是如此。
栈的 LIFO 原则
在编程术语中,将一个元素放入栈顶称为压栈 (push),移除一个元素称为弹栈 (pop)。
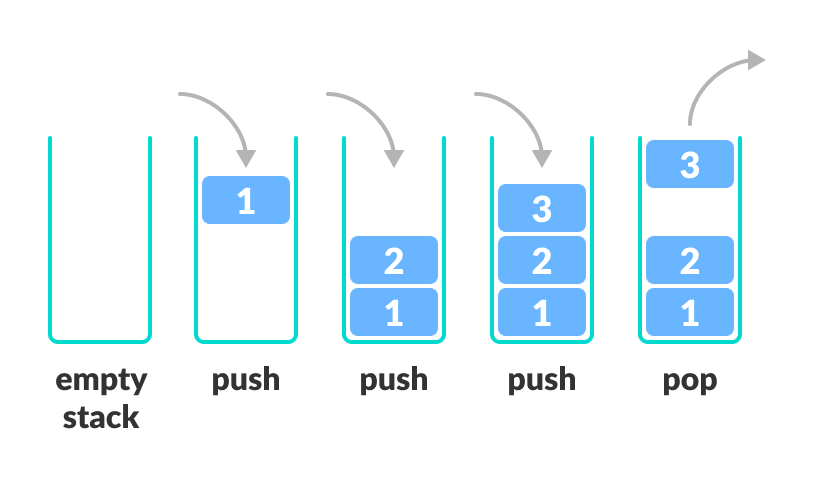
在上图中,虽然元素3是最后压入的,但却是最先被移除的。这正是LIFO (后进先出) 原则的工作方式。
我们可以在任何编程语言中实现栈,例如 C、C++、Java、Python 或 C#,但其规范基本相同。
栈的基本操作
有一些基本操作允许我们对栈执行不同的操作。
- 压栈 (Push):将一个元素添加到栈顶
- 弹栈 (Pop):从栈顶移除一个元素
- IsEmpty:检查栈是否为空
- IsFull:检查栈是否已满
- Peek:获取栈顶元素的值而不移除它
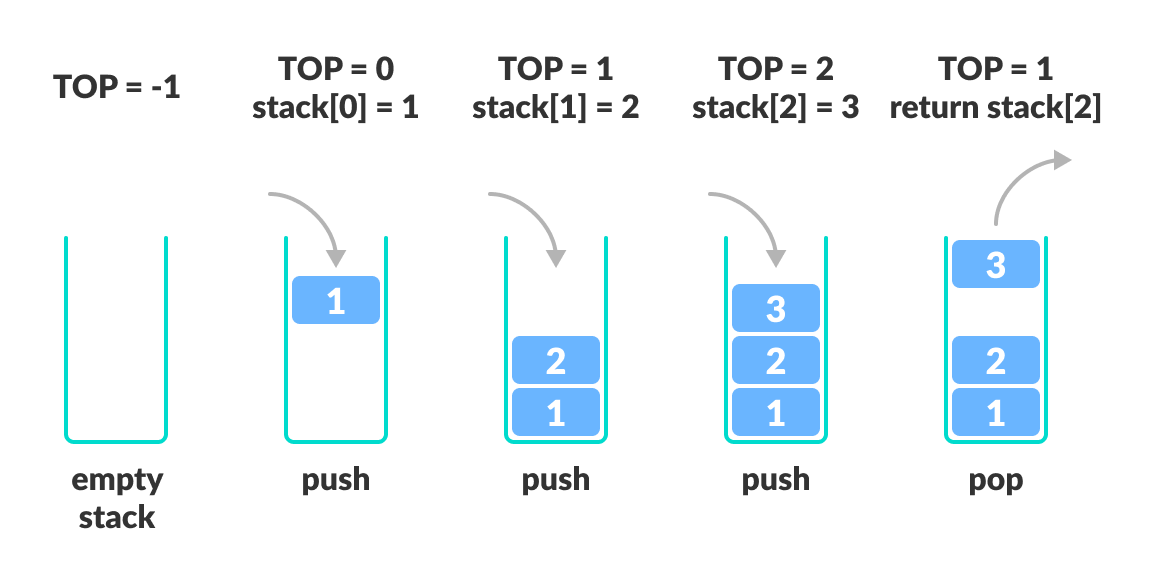
栈数据结构的工作原理
操作的工作方式如下:
- 使用一个名为 TOP 的指针来跟踪栈中的顶部元素。
- 在初始化栈时,我们将 TOP 的值设置为 -1,这样我们就可以通过比较
TOP == -1来检查栈是否为空。 - 在压栈一个元素时,我们增加 TOP 的值,并将新元素放在 TOP 指向的位置。
- 在弹栈一个元素时,我们返回 TOP 指向的元素,并减小 TOP 的值。
- 在压栈之前,我们检查栈是否已满。
- 在弹栈之前,我们检查栈是否已空。
Python、Java、C 和 C++ 中的栈实现
栈可视化:不要只阅读关于栈的内容,实时观看它的运作。通过我们新的 DSA 可视化工具,一步一步地了解数据结构的每一行代码如何工作。 亲自尝试!
最常见的栈实现是使用数组,但也可以使用列表来实现。
# Stack implementation in python
# Creating a stack
def create_stack():
stack = []
return stack
# Creating an empty stack
def check_empty(stack):
return len(stack) == 0
# Adding items into the stack
def push(stack, item):
stack.append(item)
print("pushed item: " + item)
# Removing an element from the stack
def pop(stack):
if (check_empty(stack)):
return "stack is empty"
return stack.pop()
stack = create_stack()
push(stack, str(1))
push(stack, str(2))
push(stack, str(3))
push(stack, str(4))
print("popped item: " + pop(stack))
print("stack after popping an element: " + str(stack))
// Stack implementation in Java
class Stack {
private int arr[];
private int top;
private int capacity;
// Creating a stack
Stack(int size) {
arr = new int[size];
capacity = size;
top = -1;
}
// Add elements into stack
public void push(int x) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("OverFlow\nProgram Terminated\n");
System.exit(1);
}
System.out.println("Inserting " + x);
arr[++top] = x;
}
// Remove element from stack
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("STACK EMPTY");
System.exit(1);
}
return arr[top--];
}
// Utility function to return the size of the stack
public int size() {
return top + 1;
}
// Check if the stack is empty
public Boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
// Check if the stack is full
public Boolean isFull() {
return top == capacity - 1;
}
public void printStack() {
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack = new Stack(5);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.pop();
System.out.println("\nAfter popping out");
stack.printStack();
}
}// Stack implementation in C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX 10
int count = 0;
// Creating a stack
struct stack {
int items[MAX];
int top;
};
typedef struct stack st;
void createEmptyStack(st *s) {
s->top = -1;
}
// Check if the stack is full
int isfull(st *s) {
if (s->top == MAX - 1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Check if the stack is empty
int isempty(st *s) {
if (s->top == -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Add elements into stack
void push(st *s, int newitem) {
if (isfull(s)) {
printf("STACK FULL");
} else {
s->top++;
s->items[s->top] = newitem;
}
count++;
}
// Remove element from stack
void pop(st *s) {
if (isempty(s)) {
printf("\n STACK EMPTY \n");
} else {
printf("Item popped= %d", s->items[s->top]);
s->top--;
}
count--;
printf("\n");
}
// Print elements of stack
void printStack(st *s) {
printf("Stack: ");
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
printf("%d ", s->items[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int ch;
st *s = (st *)malloc(sizeof(st));
createEmptyStack(s);
push(s, 1);
push(s, 2);
push(s, 3);
push(s, 4);
printStack(s);
pop(s);
printf("\nAfter popping out\n");
printStack(s);
}// Stack implementation in C++
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 10
int size = 0;
// Creating a stack
struct stack {
int items[MAX];
int top;
};
typedef struct stack st;
void createEmptyStack(st *s) {
s->top = -1;
}
// Check if the stack is full
int isfull(st *s) {
if (s->top == MAX - 1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Check if the stack is empty
int isempty(st *s) {
if (s->top == -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Add elements into stack
void push(st *s, int newitem) {
if (isfull(s)) {
cout << "STACK FULL";
} else {
s->top++;
s->items[s->top] = newitem;
}
size++;
}
// Remove element from stack
void pop(st *s) {
if (isempty(s)) {
cout << "\n STACK EMPTY \n";
} else {
cout << "Item popped= " << s->items[s->top];
s->top--;
}
size--;
cout << endl;
}
// Print elements of stack
void printStack(st *s) {
printf("Stack: ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << s->items[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int ch;
st *s = (st *)malloc(sizeof(st));
createEmptyStack(s);
push(s, 1);
push(s, 2);
push(s, 3);
push(s, 4);
printStack(s);
pop(s);
cout << "\nAfter popping out\n";
printStack(s);
}栈的时间复杂度
对于基于数组的栈实现,压栈和弹栈操作需要常数时间,即 O(1)。
栈数据结构的应用
尽管栈是一种易于实现的简单数据结构,但它非常强大。栈最常见的用途包括:
- 反转单词 - 将单词中的所有字母压入栈中,然后弹出它们。由于栈的 LIFO 顺序,你将按相反的顺序得到字母。
- 在编译器中 - 编译器使用栈通过将表达式转换为前缀或后缀形式来计算表达式如
2 + 4 / 5 * (7 - 9)的值。 - 在浏览器中 - 浏览器的后退按钮会将你之前访问的所有 URL 保存在栈中。每次访问新页面时,都会将其添加到栈的顶部。当你按下后退按钮时,当前 URL 会从栈中移除,然后访问前一个 URL。
