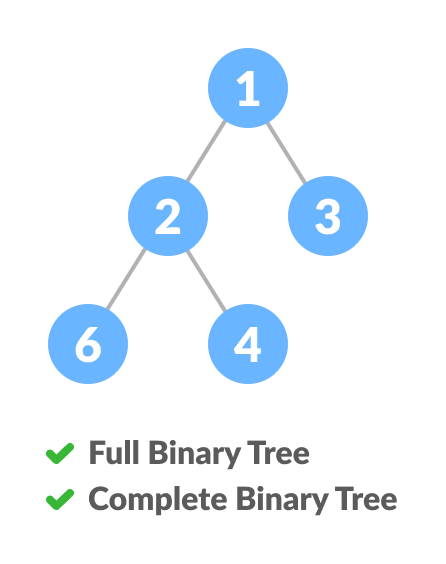
完全二叉树是一种二叉树,其中除了最低层外,所有层都已完全填充,最低层可能只从左边开始填充。
完全二叉树与满二叉树非常相似,但有两个主要区别
- 所有叶节点必须靠左对齐。
- 最后一个叶节点可能没有右兄弟,即完全二叉树不一定是满二叉树。
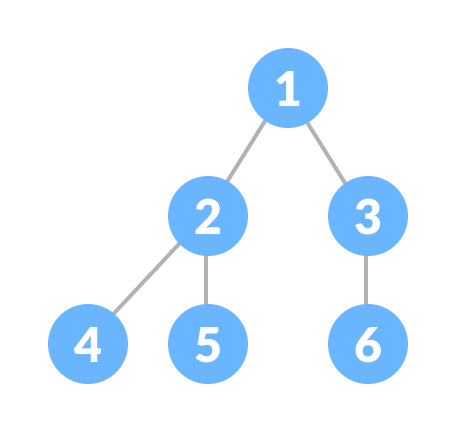
满二叉树与完全二叉树
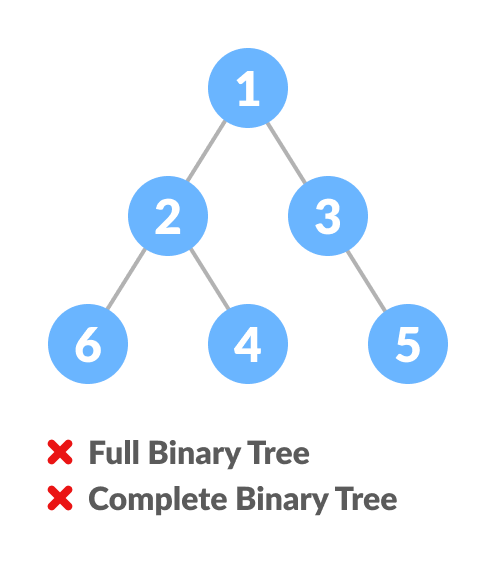
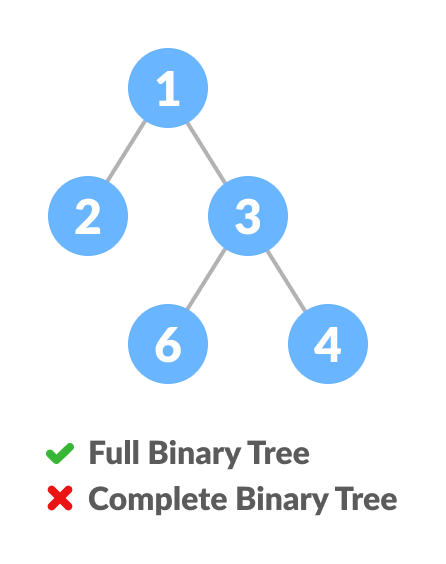
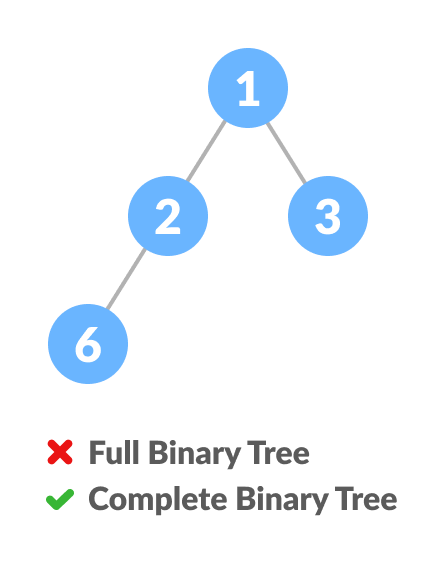
如何创建完全二叉树?
- 选择列表的第一个元素作为根节点。(第一层元素数量:1)

选择第一个元素作为根 - 将第二个元素作为根节点的左子节点,第三个元素作为右子节点。(第二层元素数量:2)

12 作为左子节点,9 作为右子节点 - 将接下来的两个元素作为第二层左节点的子节点。同样,将接下来的两个元素作为第二层右节点的子节点(第三层元素数量:4)。
- 一直重复这个过程,直到处理完最后一个元素。

5 作为左子节点,6 作为右子节点
Python、Java 和 C/C++ 示例
# Checking if a binary tree is a complete binary tree in Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, item):
self.item = item
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Count the number of nodes
def count_nodes(root):
if root is None:
return 0
return (1 + count_nodes(root.left) + count_nodes(root.right))
# Check if the tree is complete binary tree
def is_complete(root, index, numberNodes):
# Check if the tree is empty
if root is None:
return True
if index >= numberNodes:
return False
return (is_complete(root.left, 2 * index + 1, numberNodes)
and is_complete(root.right, 2 * index + 2, numberNodes))
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
node_count = count_nodes(root)
index = 0
if is_complete(root, index, node_count):
print("The tree is a complete binary tree")
else:
print("The tree is not a complete binary tree")
// Checking if a binary tree is a complete binary tree in Java
// Node creation
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item) {
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
// Count the number of nodes
int countNumNodes(Node root) {
if (root == null)
return (0);
return (1 + countNumNodes(root.left) + countNumNodes(root.right));
}
// Check for complete binary tree
boolean checkComplete(Node root, int index, int numberNodes) {
// Check if the tree is empty
if (root == null)
return true;
if (index >= numberNodes)
return false;
return (checkComplete(root.left, 2 * index + 1, numberNodes)
&& checkComplete(root.right, 2 * index + 2, numberNodes));
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
int node_count = tree.countNumNodes(tree.root);
int index = 0;
if (tree.checkComplete(tree.root, index, node_count))
System.out.println("The tree is a complete binary tree");
else
System.out.println("The tree is not a complete binary tree");
}
}// Checking if a binary tree is a complete binary tree in C
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Node creation
struct Node *newNode(char k) {
struct Node *node = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->key = k;
node->right = node->left = NULL;
return node;
}
// Count the number of nodes
int countNumNodes(struct Node *root) {
if (root == NULL)
return (0);
return (1 + countNumNodes(root->left) + countNumNodes(root->right));
}
// Check if the tree is a complete binary tree
bool checkComplete(struct Node *root, int index, int numberNodes) {
// Check if the tree is complete
if (root == NULL)
return true;
if (index >= numberNodes)
return false;
return (checkComplete(root->left, 2 * index + 1, numberNodes) && checkComplete(root->right, 2 * index + 2, numberNodes));
}
int main() {
struct Node *root = NULL;
root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
int node_count = countNumNodes(root);
int index = 0;
if (checkComplete(root, index, node_count))
printf("The tree is a complete binary tree\n");
else
printf("The tree is not a complete binary tree\n");
}// Checking if a binary tree is a complete binary tree in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Create node
struct Node *newNode(char k) {
struct Node *node = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->key = k;
node->right = node->left = NULL;
return node;
}
// Count the number of nodes
int countNumNodes(struct Node *root) {
if (root == NULL)
return (0);
return (1 + countNumNodes(root->left) + countNumNodes(root->right));
}
// Check if the tree is a complete binary tree
bool checkComplete(struct Node *root, int index, int numberNodes) {
// Check if the tree is empty
if (root == NULL)
return true;
if (index >= numberNodes)
return false;
return (checkComplete(root->left, 2 * index + 1, numberNodes) && checkComplete(root->right, 2 * index + 2, numberNodes));
}
int main() {
struct Node *root = NULL;
root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
int node_count = countNumNodes(root);
int index = 0;
if (checkComplete(root, index, node_count))
cout << "The tree is a complete binary tree\n";
else
cout << "The tree is not a complete binary tree\n";
}
数组索引与树元素的对应关系
完全二叉树有一个有趣的特性,我们可以用它来查找任何节点的子节点和父节点。
如果在数组中某个元素的索引是 i,则索引为 2i+1 的元素将成为左子节点,索引为 2i+2 的元素将成为右子节点。同样,索引为 i 的任何元素的父节点由 (i-1)/2 的下取整给出。
让我们来测试一下,
Left child of 1 (index 0) = element in (2*0+1) index = element in 1 index = 12 Right child of 1 = element in (2*0+2) index = element in 2 index = 9 Similarly, Left child of 12 (index 1) = element in (2*1+1) index = element in 3 index = 5 Right child of 12 = element in (2*1+2) index = element in 4 index = 6
我们还应该确认这些规则在查找任何节点的父节点时是否成立
Parent of 9 (position 2) = (2-1)/2 = ½ = 0.5 ~ 0 index = 1 Parent of 12 (position 1) = (1-1)/2 = 0 index = 1
理解数组索引到树位置的这种映射对于理解 堆数据结构 的工作原理以及如何使用它来实现 堆排序 至关重要。
完全二叉树的应用
- 基于堆的数据结构
- 堆排序



