Ford-Fulkerson 算法是一种贪心方法,用于计算网络或图中的最大可能流量。
术语流网络用于描述具有源(S)和汇(T)的顶点和边组成的网络。除S和T外,每个顶点都可以通过它发送和接收等量的物质。S只能发送,T只能接收物质。
我们可以通过不同容量管道网络中的液体流动来可视化对该算法的理解。每根管道在某个时刻都有一定的液体传输能力。对于此算法,我们将找出从源到汇在某个时刻通过网络可以流动的液体量。
使用的术语
增广路径
这是流网络中存在的路径。
残余图
它表示具有附加可能流量的流网络。
残余容量
它是边在从最大容量减去流量后的容量。
Ford-Fulkerson 算法如何工作?
算法遵循
- 将所有边的流量初始化为 0。
- 只要源和汇之间存在增广路径,就将此路径添加到流量中。
- 更新残余图。
如果需要,我们还可以考虑反向路径,因为如果我们不考虑它们,我们可能永远找不到最大流量。
上述概念可以通过下面的示例来理解。
Ford-Fulkerson 示例
开始时所有边的流量均为 0。
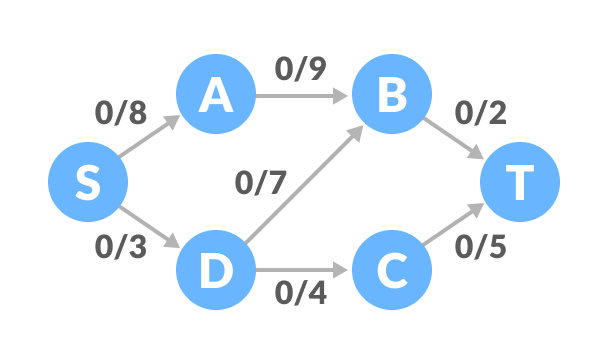
- 从 S 到 T 选择任意路径。在此步骤中,我们选择了路径 S-A-B-T。

查找路径
这三条边中的最小容量为 2(B-T)。基于此,更新每条路径的流量/容量。
更新容量 - 选择另一条路径 S-D-C-T。这些边中的最小容量为 3(S-D)。

查找下一条路径
根据此更新容量。
更新容量 - 现在,我们也要考虑反向路径 B-D。选择路径 S-A-B-D-C-T。边中的最小残余容量为 1(D-C)。

查找下一条路径
更新容量。
更新容量
前向和反向路径的容量是分开考虑的。 - 将所有流量相加 = 2 + 3 + 1 = 6,这是流网络上的最大可能流量。
请注意,如果任何边的容量已满,则该路径无法使用。
Python、Java 和 C/C++ 示例
# Ford-Fulkerson algorith in Python
from collections import defaultdict
class Graph:
def __init__(self, graph):
self.graph = graph
self. ROW = len(graph)
# Using BFS as a searching algorithm
def searching_algo_BFS(self, s, t, parent):
visited = [False] * (self.ROW)
queue = []
queue.append(s)
visited[s] = True
while queue:
u = queue.pop(0)
for ind, val in enumerate(self.graph[u]):
if visited[ind] == False and val > 0:
queue.append(ind)
visited[ind] = True
parent[ind] = u
return True if visited[t] else False
# Applying fordfulkerson algorithm
def ford_fulkerson(self, source, sink):
parent = [-1] * (self.ROW)
max_flow = 0
while self.searching_algo_BFS(source, sink, parent):
path_flow = float("Inf")
s = sink
while(s != source):
path_flow = min(path_flow, self.graph[parent[s]][s])
s = parent[s]
# Adding the path flows
max_flow += path_flow
# Updating the residual values of edges
v = sink
while(v != source):
u = parent[v]
self.graph[u][v] -= path_flow
self.graph[v][u] += path_flow
v = parent[v]
return max_flow
graph = [[0, 8, 0, 0, 3, 0],
[0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 2],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5],
[0, 0, 7, 4, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
g = Graph(graph)
source = 0
sink = 5
print("Max Flow: %d " % g.ford_fulkerson(source, sink))// Ford-Fulkerson algorith in Java
import java.util.LinkedList;
class FordFulkerson {
static final int V = 6;
// Using BFS as a searching algorithm
boolean bfs(int Graph[][], int s, int t, int p[]) {
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
visited[i] = false;
LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
p[s] = -1;
while (queue.size() != 0) {
int u = queue.poll();
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
if (visited[v] == false && Graph[u][v] > 0) {
queue.add(v);
p[v] = u;
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
return (visited[t] == true);
}
// Applying fordfulkerson algorithm
int fordFulkerson(int graph[][], int s, int t) {
int u, v;
int Graph[][] = new int[V][V];
for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
Graph[u][v] = graph[u][v];
int p[] = new int[V];
int max_flow = 0;
# Updating the residual calues of edges
while (bfs(Graph, s, t, p)) {
int path_flow = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (v = t; v != s; v = p[v]) {
u = p[v];
path_flow = Math.min(path_flow, Graph[u][v]);
}
for (v = t; v != s; v = p[v]) {
u = p[v];
Graph[u][v] -= path_flow;
Graph[v][u] += path_flow;
}
// Adding the path flows
max_flow += path_flow;
}
return max_flow;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws java.lang.Exception {
int graph[][] = new int[][] { { 0, 8, 0, 0, 3, 0 }, { 0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 2 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5 }, { 0, 0, 7, 4, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
FordFulkerson m = new FordFulkerson();
System.out.println("Max Flow: " + m.fordFulkerson(graph, 0, 5));
}
}/ Ford - Fulkerson algorith in C
#include <stdio.h>
#define A 0
#define B 1
#define C 2
#define MAX_NODES 1000
#define O 1000000000
int n;
int e;
int capacity[MAX_NODES][MAX_NODES];
int flow[MAX_NODES][MAX_NODES];
int color[MAX_NODES];
int pred[MAX_NODES];
int min(int x, int y) {
return x < y ? x : y;
}
int head, tail;
int q[MAX_NODES + 2];
void enqueue(int x) {
q[tail] = x;
tail++;
color[x] = B;
}
int dequeue() {
int x = q[head];
head++;
color[x] = C;
return x;
}
// Using BFS as a searching algorithm
int bfs(int start, int target) {
int u, v;
for (u = 0; u < n; u++) {
color[u] = A;
}
head = tail = 0;
enqueue(start);
pred[start] = -1;
while (head != tail) {
u = dequeue();
for (v = 0; v < n; v++) {
if (color[v] == A && capacity[u][v] - flow[u][v] > 0) {
enqueue(v);
pred[v] = u;
}
}
}
return color[target] == C;
}
// Applying fordfulkerson algorithm
int fordFulkerson(int source, int sink) {
int i, j, u;
int max_flow = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
flow[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// Updating the residual values of edges
while (bfs(source, sink)) {
int increment = O;
for (u = n - 1; pred[u] >= 0; u = pred[u]) {
increment = min(increment, capacity[pred[u]][u] - flow[pred[u]][u]);
}
for (u = n - 1; pred[u] >= 0; u = pred[u]) {
flow[pred[u]][u] += increment;
flow[u][pred[u]] -= increment;
}
// Adding the path flows
max_flow += increment;
}
return max_flow;
}
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
capacity[i][j] = 0;
}
}
n = 6;
e = 7;
capacity[0][1] = 8;
capacity[0][4] = 3;
capacity[1][2] = 9;
capacity[2][4] = 7;
capacity[2][5] = 2;
capacity[3][5] = 5;
capacity[4][2] = 7;
capacity[4][3] = 4;
int s = 0, t = 5;
printf("Max Flow: %d\n", fordFulkerson(s, t));
}// Ford-Fulkerson algorith in C++
#include <limits.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define V 6
// Using BFS as a searching algorithm
bool bfs(int rGraph[V][V], int s, int t, int parent[]) {
bool visited[V];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
if (visited[v] == false && rGraph[u][v] > 0) {
q.push(v);
parent[v] = u;
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
return (visited[t] == true);
}
// Applying fordfulkerson algorithm
int fordFulkerson(int graph[V][V], int s, int t) {
int u, v;
int rGraph[V][V];
for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
rGraph[u][v] = graph[u][v];
int parent[V];
int max_flow = 0;
// Updating the residual values of edges
while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent)) {
int path_flow = INT_MAX;
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
path_flow = min(path_flow, rGraph[u][v]);
}
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u][v] -= path_flow;
rGraph[v][u] += path_flow;
}
// Adding the path flows
max_flow += path_flow;
}
return max_flow;
}
int main() {
int graph[V][V] = {{0, 8, 0, 0, 3, 0},
{0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 2},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5},
{0, 0, 7, 4, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}};
cout << "Max Flow: " << fordFulkerson(graph, 0, 5) << endl;
}Ford-Fulkerson 的应用
- 供水管道
- 二分匹配问题
- 带需求的循环






