STL 中的 stack 在 C++ 中提供了堆栈数据结构的功能。
stack 数据结构遵循 **LIFO (后进先出)** 原则。也就是说,最后添加的元素会最先被移除。
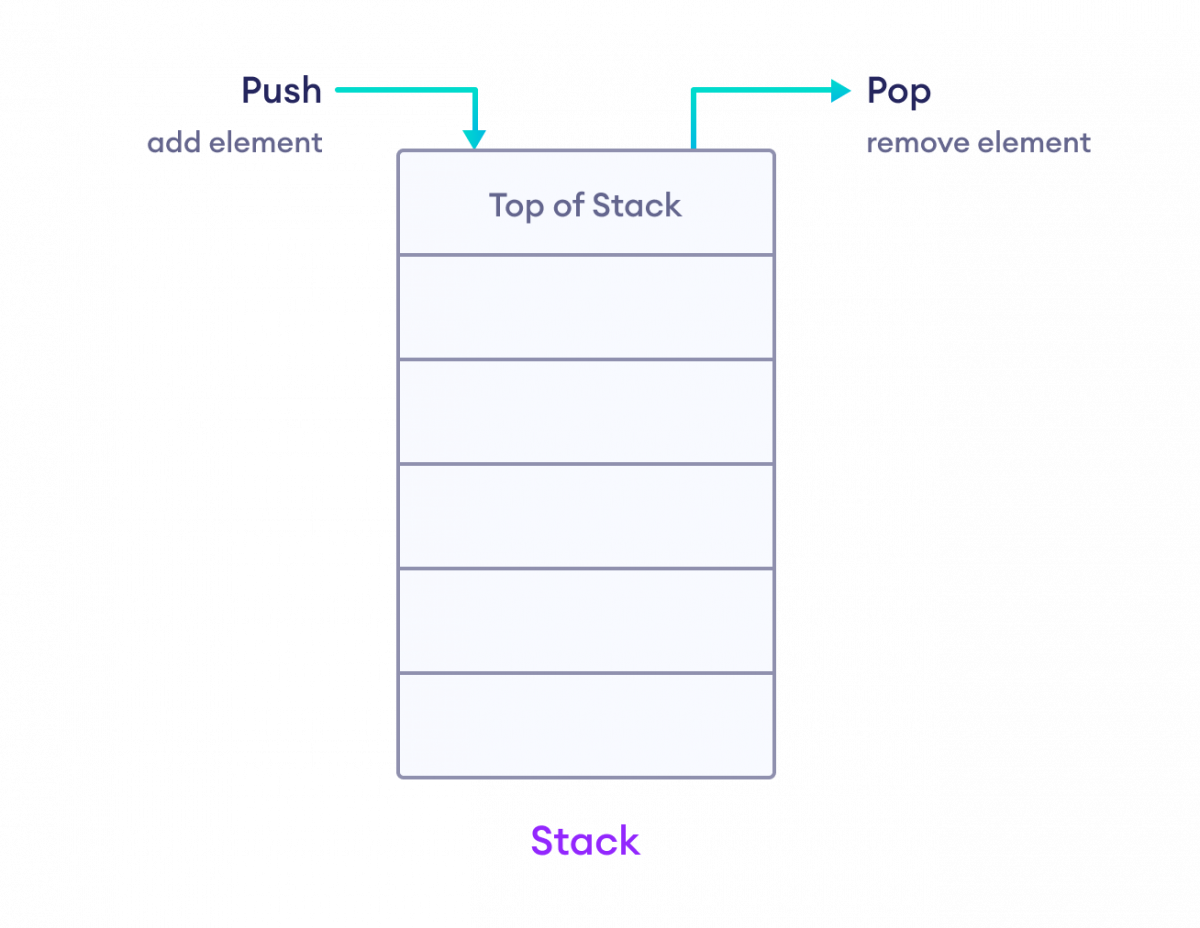
要了解更多关于堆栈的信息,请访问我们关于栈数据结构的教程。
创建堆栈
为了在 C++ 中创建堆栈,我们首先需要包含 stack 头文件。
#include <stack>导入此文件后,我们可以使用以下语法创建 stack
stack<type> st;这里,type 表示我们要存储在堆栈中的数据类型。例如,
// create a stack of integers
stack<int> integer_stack;
// create a stack of strings
stack<string> string_stack;示例:C++ STL 堆栈
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a stack of strings
stack<string> languages;
// add element to the Stack
languages.push("C++");
languages.push("Java");
languages.push("Python");
// print top element
cout << languages.top();
return 0;
}输出
Python
在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个名为 languages 的字符串堆栈。
在这里,我们使用了 push() 方法向堆栈添加元素。然后我们使用 top() 方法显示顶部元素。
我们将在本教程的后续部分了解更多关于 push() 和 top() 方法的信息。
堆栈方法
在 C++ 中,stack 类提供了多种方法来对堆栈执行不同的操作。
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
push() |
将元素添加到堆栈中 |
pop() |
从堆栈中移除元素 |
top() |
返回堆栈顶部的元素 |
size() |
返回堆栈中的元素数量 |
empty() |
如果堆栈为空,则返回 true |
将元素添加到堆栈中
我们使用 push() 方法将元素添加到堆栈中。例如,
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a stack of strings
stack<string> colors;
// push elements into the stack
colors.push("Red");
colors.push("Orange");
cout << "Stack: ";
// print elements of stack
while(!colors.empty()) {
cout << colors.top() << ", ";
colors.pop();
}
return 0;
}输出
Stack: Orange, Red,
在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个名为 colors 的字符串堆栈。然后,我们使用 push() 方法将元素添加到堆栈中。
colors.push("Red");
colors.push("Orange");我们使用了 while 循环和各种堆栈方法来打印堆栈的内容,而不是直接打印。
while(!colors.empty()) {
cout << colors.top() << ", ";
colors.pop();
}要打印堆栈中的所有元素,我们在循环中打印其顶部元素,然后弹出 (移除) 它。此过程会重复进行,直到堆栈为空。
我们将在接下来的部分中学习 pop()、top() 和 empty() 方法。
另外请注意,我们以 {"Red", "Orange"} 的顺序插入了元素。
但是打印元素时,我们得到的是 {"Orange", "Red"}。
这是因为堆栈是 LIFO 数据结构,这意味着最后插入的元素最先被检索。
注意:与 vectors 或其他容器不同,我们不能使用范围 for 循环来迭代堆栈。这是因为 STL 堆栈是STL 容器适配器,它提供了限制性访问,使其能够像标准堆栈数据结构一样运行。
从堆栈中移除元素
我们可以使用 pop() 方法从堆栈中移除元素。例如,
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// function prototype for display_stack utility
void display_stack(stack<string> st);
int main() {
// create a stack of strings
stack<string> colors;
// push elements into the stack
colors.push("Red");
colors.push("Orange");
colors.push("Blue");
cout << "Initial Stack: ";
// print elements of stack
display_stack(colors);
// removes "Blue" as it was inserted last
colors.pop();
cout << "Final Stack: ";
// print elements of stack
display_stack(colors);
return 0;
}
// utility function to display stack elements
void display_stack(stack<string> st) {
while(!st.empty()) {
cout << st.top() << ", ";
st.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}输出
Initial Stack: Blue, Orange, Red, Final Stack: Orange, Red,
在上面的示例中,我们使用 pop() 方法从堆栈中移除了一个元素。
最初,堆栈的内容是 {"Blue", "Orange", "Red"}。
然后我们使用 pop() 方法移除了该元素。
// removes top element
colors.pop() 这会移除 stack 顶部的元素,即最后插入的元素,即 "Blue"。
因此,最终的堆栈变为 {"Orange", "Red"}。
访问堆栈中的元素
我们使用 top() 方法访问堆栈顶部的元素。例如,
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a stack of strings
stack<string> colors;
// push element into the stack
colors.push("Red");
colors.push("Orange");
colors.push("Blue");
// get top element
string top = colors.top();
cout << "Top Element: " << top;
return 0;
}输出
Top Element: Blue
在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个名为 colors 的字符串堆栈,并添加了以下元素:"Red"、"Orange" 和 "Blue"。
然后我们使用 top() 方法访问顶部元素。
string top = colors.top(); 在这里,"Blue" 是最后插入的,所以它是顶部元素。
获取堆栈的大小
我们使用 size() 方法获取 stack 中元素的数量。例如,
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a stack of int
stack<int> prime_nums;
// push elements into the stack
prime_nums.push(2);
prime_nums.push(3);
prime_nums.push(5);
// get the size of the stack
int size = prime_nums.size();
cout << "Size of the stack: " << size;
return 0;
}输出
Size of the stack: 3
在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个名为 prime_nums 的整数堆栈,并向其中添加了三个元素。
然后我们使用 size() 方法查找堆栈中的元素数量。
prime_nums.size();由于我们向堆栈添加了 3 个元素,因此 prime_nums.size() 返回 3。
检查堆栈是否为空
我们使用 empty() 方法检查堆栈是否为空。此方法返回
- 1 (true) - 如果堆栈为空
- 0 (false) - 如果堆栈不为空
例如,
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a stack of double
stack<double> nums;
cout << "Is the stack empty? ";
// check if the stack is empty
if (nums.empty()) {
cout << "Yes" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "No" << endl;
}
cout << "Pushing elements..." << endl;
// push element into the stack
nums.push(2.3);
nums.push(9.7);
cout << "Is the stack empty? ";
// check if the stack is empty
if (nums.empty()) {
cout << "Yes";
}
else {
cout << "No";
}
return 0;
}输出
Is the stack empty? Yes Pushing elements... Is the stack empty? No
在上面的示例中,我们使用 empty() 方法来确定 stack 是否为空,
if(nums.empty()) { // returns false
cout << "Yes" << end;;
}
else {
cout << "No" << endl;
}最初,堆栈中没有元素。因此 nums.empty() 返回 true。
然后我们向堆栈添加了元素。
再次,我们使用 nums.empty() 来确定堆栈是否为空。这次,它返回 false。