在 C++ 编程中,我们可以为 函数 参数提供默认值。
如果一个带有默认参数的函数在调用时没有传递参数,那么就会使用默认参数。
但是,如果在调用函数时传递了参数,则会忽略默认参数。
默认参数的工作原理
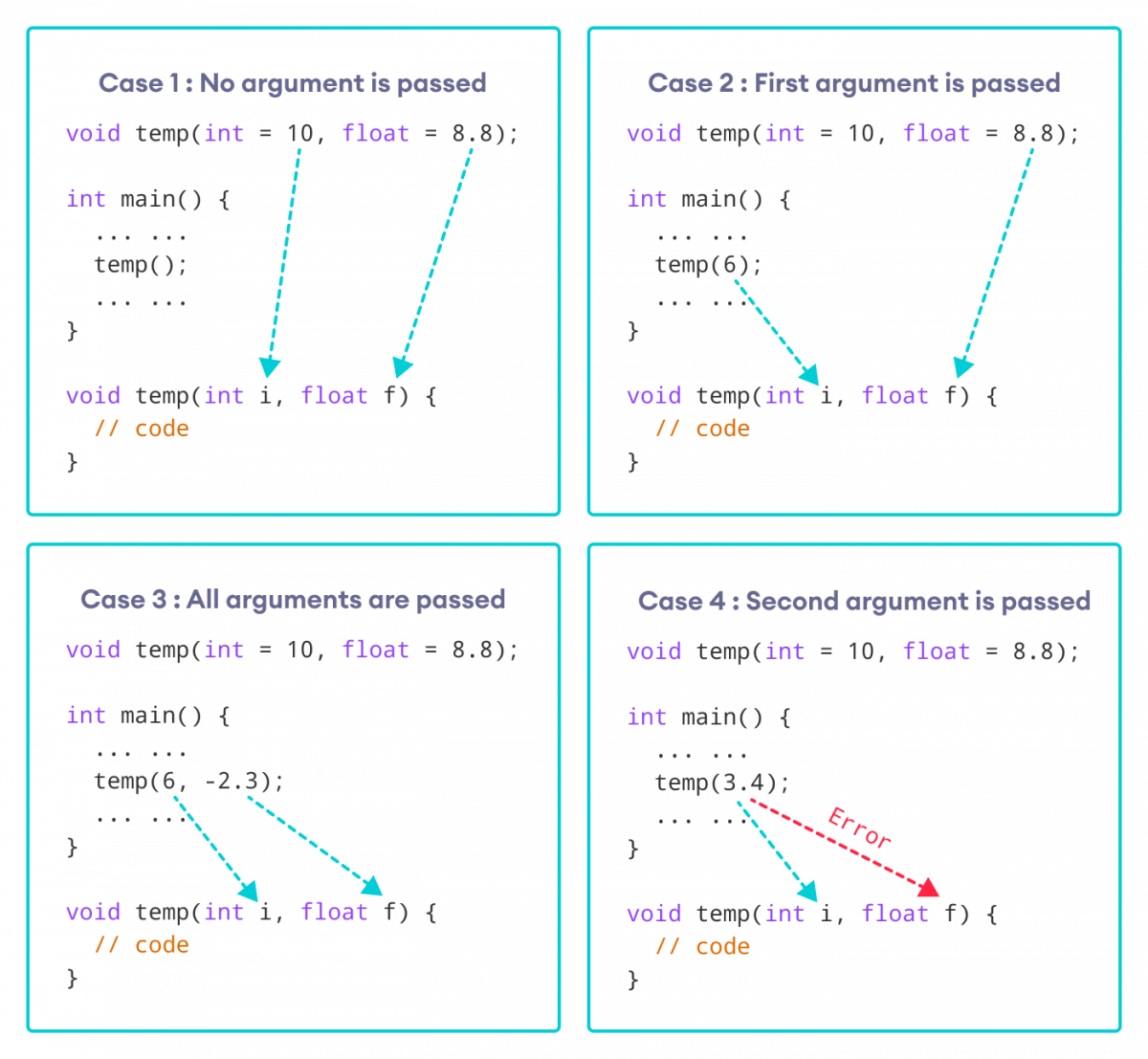
我们可以从上面的图片理解默认参数的工作原理。
- 当调用 `temp()` 时,函数将使用两个默认参数。
- 当调用 `temp(6)` 时,第一个参数变为 `6`,而第二个参数使用默认值。
- 当调用 `temp(6, -2.3)` 时,两个默认参数都被覆盖,结果是 `i = 6` 和 `f = -2.3`。
- 当传递 `temp(3.4)` 时,函数行为不符合预期,因为不传递第一个参数就无法传递第二个参数。
因此,`3.4` 被作为第一个参数传递。由于第一个参数被定义为 `int`,实际传递的值是 `3`。
示例:默认参数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// defining the default arguments
void display(char = '*', int = 3);
int main() {
int count = 5;
cout << "No argument passed: ";
// *, 3 will be parameters
display();
cout << "First argument passed: ";
// #, 3 will be parameters
display('#');
cout << "Both arguments passed: ";
// $, 5 will be parameters
display('$', count);
return 0;
}
void display(char c, int count) {
for(int i = 1; i <= count; ++i)
{
cout << c;
}
cout << endl;
}输出
No argument passed: *** First argument passed: ### Both arguments passed: $$$$$
这个程序的工作原理如下:
- 调用 `display()` 时没有传递任何参数。在这种情况下,`display()` 使用两个默认参数 `c = '*'` 和 `n = 1`。
- 调用 `display('#')` 时只传递了一个参数。在这种情况下,第一个参数变为 `'#'`。第二个默认参数 `n = 1` 被保留。
- 调用 `display('#', count)` 时传递了两个参数。在这种情况下,不使用默认参数。
我们也可以在函数定义本身中定义默认参数。下面的程序与上面的程序等效。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// defining the default arguments
void display(char c = '*', int count = 3) {
for(int i = 1; i <= count; ++i) {
cout << c;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
int count = 5;
cout << "No argument passed: ";
// *, 3 will be parameters
display();
cout << "First argument passed: ";
// #, 3 will be parameters
display('#');
cout << "Both argument passed: ";
// $, 5 will be parameters
display('$', count);
return 0;
}注意事项
- 一旦我们为某个参数提供了默认值,所有后续参数也必须具有默认值。例如,
// Invalid void add(int a, int b = 3, int c, int d); // Invalid void add(int a, int b = 3, int c, int d = 4); // Valid void add(int a, int c, int b = 3, int d = 4); - 如果我们在函数定义中而不是在函数原型中提供默认参数,那么函数必须在函数调用之前定义。
// Invalid code int main() { // function call display(); } void display(char c = '*', int count = 5) { // code }
另请阅读