在计算机编程中,continue 语句用于跳过循环的当前迭代,并将程序的控制权转移到下一个迭代。
continue 语句的语法是
continue;在学习 continue 语句之前,请确保您了解:
C++ continue 语句的工作原理
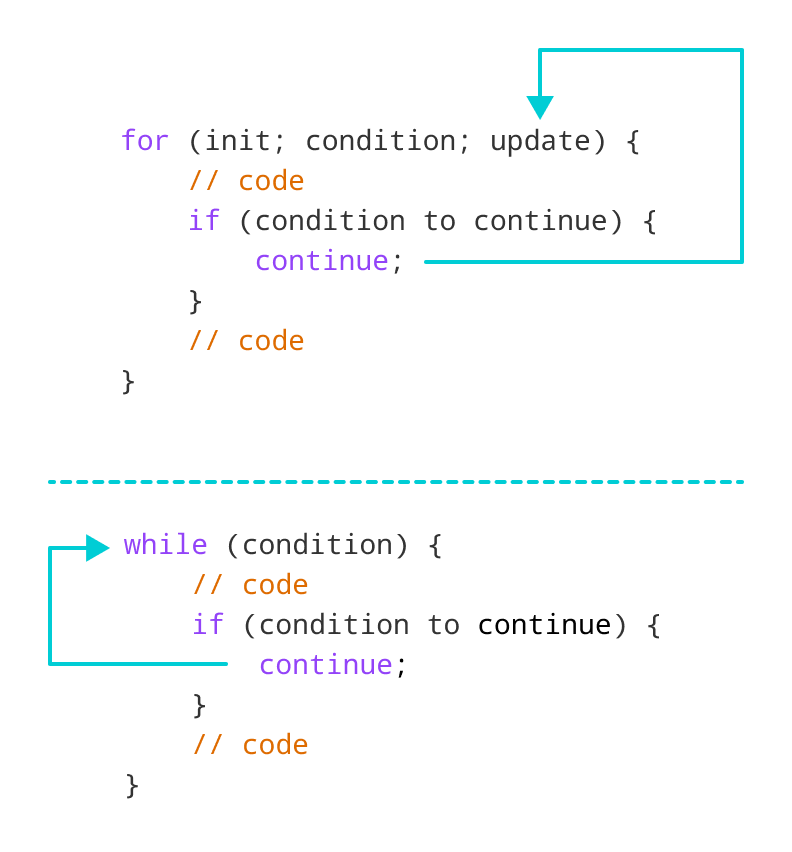
示例 1:for 循环中的 continue
在 `for` 循环中,`continue` 会跳过当前迭代,控制流会跳转到 `update` 表达式。
// program to print the value of i
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
// condition to continue
if (i == 3) {
continue;
}
cout << i << endl;
}
return 0;
}输出
1 2 4 5
在上面的程序中,我们使用 `for` 循环来打印每次迭代中 `i` 的值。请注意以下代码:
if (i == 3) {
continue;
}这意味着
- 当 `i` 等于 `3` 时,`continue` 语句会跳过当前迭代并开始下一次迭代。
- 然后,`i` 变为 `4`,`condition` 被再次评估。
- 因此,在接下来的两次迭代中会打印 `4` 和 `5`。
注意:`continue` 语句几乎总是与决策语句一起使用。
示例 2:while 循环中的 continue
在 `while` 循环中,`continue` 会跳过当前迭代,程序的控制流会跳转回 `while` 循环的 `condition`。
// program to calculate positive numbers till 50 only
// if the user enters a negative number,
// that number is skipped from the calculation
// negative number -> loop terminate
// numbers above 50 -> skip iteration
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int sum = 0;
int number = 0;
while (number >= 0) {
// add all positive numbers
sum += number;
// take input from the user
cout << "Enter a number: ";
cin >> number;
// continue condition
if (number > 50) {
cout << "The number is greater than 50 and won't be calculated." << endl;
number = 0; // the value of number is made 0 again
continue;
}
}
// display the sum
cout << "The sum is " << sum << endl;
return 0;
}输出
Enter a number: 12 Enter a number: 0 Enter a number: 2 Enter a number: 30 Enter a number: 50 Enter a number: 56 The number is greater than 50 and won't be calculated. Enter a number: 5 Enter a number: -3 The sum is 99
在上面的程序中,用户输入一个数字。`while` 循环用于打印用户输入的正数的总和,只要输入的数字不大于 `50`。
请注意 `continue` 语句的使用。
if (number > 50){
continue;
}- 当用户输入的数字大于 `50` 时,`continue` 语句会跳过当前迭代。然后程序的控制流会转到 `while` 循环的 `condition`。
- 当用户输入的数字小于 `0` 时,循环终止。
注意:`continue` 语句在 `do...while` 循环中的工作方式相同。
嵌套循环中的 continue
当 `continue` 与嵌套循环一起使用时,它会跳过内部循环的当前迭代。例如:
// using continue statement inside
// nested for loop
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number;
int sum = 0;
// nested for loops
// first loop
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
// second loop
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (j == 2) {
continue;
}
cout << "i = " << i << ", j = " << j << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}输出
i = 1, j = 1 i = 1, j = 3 i = 2, j = 1 i = 2, j = 3 i = 3, j = 1 i = 3, j = 3
在上面的程序中,当 `continue` 语句执行时,它会跳过内部循环的当前迭代。程序的控制权会转移到内部循环的**更新表达式**。
因此,`j = 2` 的值永远不会在输出中显示。
注意:break 语句会完全终止循环。然而,`continue` 语句只跳过当前迭代。