在计算机编程中,我们使用if...else语句根据某些条件执行一段代码,在其他条件下执行另一段代码。
例如,根据学生获得的分数分配等级(A、B、C)。
- 如果百分比高于 90,则分配成绩 A
- 如果百分比高于 75,则分配成绩 B
- 如果百分比高于 65,则分配成绩 C
C++ if语句
语法
if (condition) {
// body of if statement
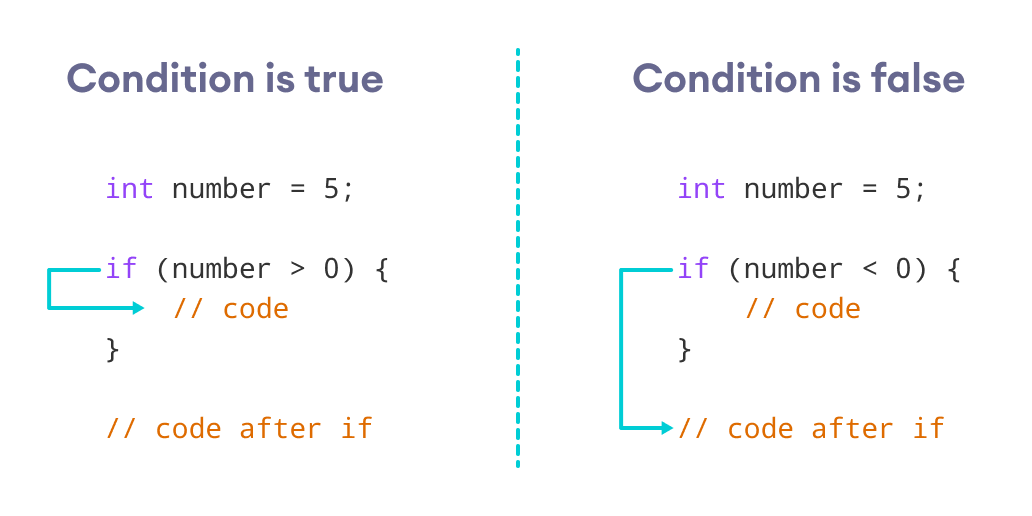
}if语句会评估括号( )中的条件。
- 如果条件评估为true,则执行
if主体内的代码。 - 如果条件评估为false,则跳过
if主体内的代码。
注意:{ }内的代码是if语句的主体。
示例 1:C++ if语句
// Program to print positive number entered by the user
// If the user enters a negative number, it is skipped
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number;
cout << "Enter an integer: ";
cin >> number;
// checks if the number is positive
if (number > 0) {
cout << "You entered a positive integer: " << number << endl;
}
cout << "This statement is always executed.";
return 0;
}输出 1
Enter an integer: 5 You entered a positive number: 5 This statement is always executed.
当用户输入5时,条件number > 0被评估为true,并执行if主体内的语句。
输出 2
Enter a number: -5 This statement is always executed.
当用户输入-5时,条件number > 0被评估为false,并且不执行if主体内的语句。
C++ if...else
if语句可以有一个可选的else子句。
语法
if (condition) {
// block of code if condition is true
}
else {
// block of code if condition is false
}if..else语句会评估括号内的条件。
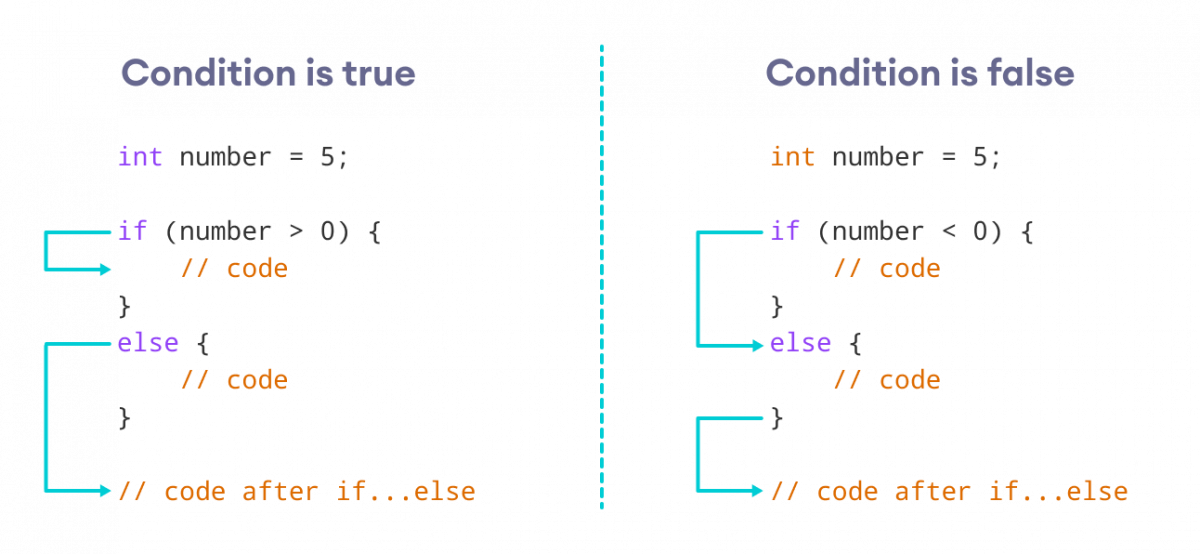
如果条件评估为true,
- 则执行
if主体内的代码 - 则跳过
else主体内的代码的执行
如果条件评估为false,
- 则执行
else主体内的代码 - 则跳过
if主体内的代码的执行
示例 2:C++ if...else语句
// Program to check whether an integer is positive or negative
// This program considers 0 as a positive number
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number;
cout << "Enter an integer: ";
cin >> number;
if (number >= 0) {
cout << "You entered a positive integer: " << number << endl;
}
else {
cout << "You entered a negative integer: " << number << endl;
}
cout << "This line is always printed.";
return 0;
}输出 1
Enter an integer: 4 You entered a positive integer: 4. This line is always printed.
在上面的程序中,我们有条件number >= 0。如果我们输入的数字大于或等于0,则条件评估为true。
这里,我们输入4。因此,条件为true。因此,执行if主体内的语句。
输出 2
Enter an integer: -4 You entered a negative integer: -4. This line is always printed.
这里,我们输入-4。因此,条件为false。因此,执行else主体内的语句。
C++ if...else...else if语句
if...else语句用于在两个选择中执行一个代码块。但是,如果我们需要在两个以上选择之间做出选择,我们使用if...else if...else语句。
语法
if (condition1) {
// code block 1
}
else if (condition2){
// code block 2
}
else {
// code block 3
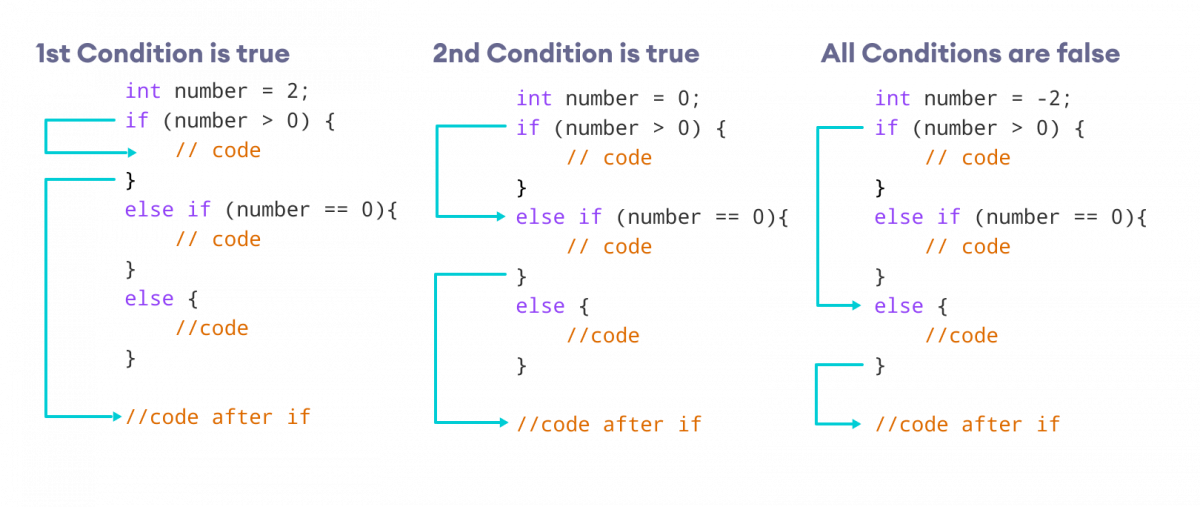
}这里,
- 如果condition1评估为true,则执行
code block 1。 - 如果condition1评估为false,则评估condition2。
- 如果condition2为true,则执行
code block 2。 - 如果condition2为false,则执行
code block 3。
注意:可以有多个else if语句,但只有一个if和else语句。
示例 3:C++ if...else...else if
// Program to check whether an integer is positive, negative or zero
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number;
cout << "Enter an integer: ";
cin >> number;
if (number > 0) {
cout << "You entered a positive integer: " << number << endl;
}
else if (number < 0) {
cout << "You entered a negative integer: " << number << endl;
}
else {
cout << "You entered 0." << endl;
}
cout << "This line is always printed.";
return 0;
}输出 1
Enter an integer: 1 You entered a positive integer: 1. This line is always printed.
输出 2
Enter an integer: -2 You entered a negative integer: -2. This line is always printed.
输出 3
Enter an integer: 0 You entered 0. This line is always printed.
在此程序中,我们从用户那里获取一个数字。然后,我们使用if...else if...else梯形来检查该数字是正数、负数还是零。
如果数字大于0,则执行if块内的代码。如果数字小于0,则执行else if块内的代码。否则,执行else块内的代码。
C++嵌套if...else
有时,我们需要在另一个if语句中使用if语句。这就是所谓的嵌套if语句。
可以将其视为多个if语句层。有一个第一个(外部)if语句,其内部是另一个(内部)if语句。
语法
// outer if statement
if (condition1) {
// statements
// inner if statement
if (condition2) {
// statements
}
}注意事项
- 我们可以根据需要向内部
if语句添加else和else if语句。 - 内部
if语句也可以插入到外部else或else if语句(如果存在)中。 - 我们可以嵌套多层
if语句。
示例 4:C++嵌套if
// C++ program to find if an integer is positive, negative or zero
// using nested if statements
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int num;
cout << "Enter an integer: ";
cin >> num;
// outer if condition
if (num != 0) {
// inner if condition
if (num > 0) {
cout << "The number is positive." << endl;
}
// inner else condition
else {
cout << "The number is negative." << endl;
}
}
// outer else condition
else {
cout << "The number is 0 and it is neither positive nor negative." << endl;
}
cout << "This line is always printed." << endl;
return 0;
}输出 1
Enter an integer: 35 The number is positive. This line is always printed.
输出 2
Enter an integer: -35 The number is negative. This line is always printed.
输出 3
Enter an integer: 0 The number is 0 and it is neither positive nor negative. This line is always printed.
在上面的例子中:
- 我们从用户那里获取一个整数并将其存储在变量num中。
- 然后,我们使用
if...else语句检查num是否不等于0。- 如果为true,则执行**内部**
if...else语句。 - 如果为false,则执行**外部**
else条件内的代码,该代码打印"The number is 0 and it is neither positive nor negative."
- 如果为true,则执行**内部**
- **内部**
if...else语句检查输入的数字是否为正数,即num是否大于0。- 如果为true,则打印一条语句说明该数字是正数。
- 如果为false,则打印该数字是负数。
注意:正如你所见,嵌套的if...else会使你的逻辑复杂化。如果可能,你应该始终尽量避免嵌套if...else。
只有一个语句的if...else主体
如果if...else的主体只有一个语句,则可以省略程序中的{ }。例如,你可以将
int number = 5;
if (number > 0) {
cout << "The number is positive." << endl;
}
else {
cout << "The number is negative." << endl;
}替换为
int number = 5;
if (number > 0)
cout << "The number is positive." << endl;
else
cout << "The number is negative." << endl;两个程序的输出将相同。
注意:尽管如果if...else的主体只有一个语句,使用{ }不是必需的,但使用{ }可以使你的代码更具可读性。
关于决策的更多信息
**三元运算符**是一种简洁的内联方法,用于根据条件执行两个表达式中的一个。要了解更多信息,请访问C++三元运算符。
如果我们想根据给定的测试条件在多个选择之间做出选择,可以使用switch语句。要了解更多信息,请访问C++ switch。
另请阅读