文件处理是C++中用于创建文件和执行读写操作的机制。
我们可以通过导入 <fstream> 类来访问C++中的各种文件处理方法。
#include <fstream><fstream> 包含两个用于文件处理的类:
ifstream- 用于从文件读取。ofstream- 用于创建/打开和写入文件。
注意:我们目前的在线编译器无法处理文件操作。因此,请在您的计算机上安装IDE或文本编辑器来运行此处提供的程序。
打开和关闭文件
为了处理文件,我们首先需要打开它们。在C++中,我们可以使用 ofstream 和 ifstream 类来打开文件。
例如,这是我们如何使用 ofstream 打开文件:
std::ofstream my_file("example.txt"); 这里,
my_file-ofstream类对象的名称。example.txt- 我们想要打开的文件的名称和扩展名。
注意:我们也可以使用 open() 函数来打开文件。例如:
std::ofstream my_file.open("example.txt");关闭文件
完成文件操作后,我们需要使用 close() 函数将其关闭。
my_file.close();让我们通过一个示例程序来了解这些操作。
示例1:打开和关闭文件
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// opening a text file for writing
ofstream my_file("example.txt");
// close the file
my_file.close();
return 0;
}此代码将打开和关闭文件 example.txt。
注意:如果不存在要打开的文件,ofstream my_file("example.txt"); 将会创建一个名为 example.txt 的新文件。
检查文件错误
在文件处理中,在进行任何进一步操作之前,确保文件已成功打开非常重要。有三种常见的方法可以检查文件错误:
1. 通过检查文件对象
ofstream my_file("example.txt");
// check if the file has been opened properly
if (!my_file) {
// print error message
cout << "Error opening the file." << endl;
// terminate the main() function
return 1;
}注意 if 语句中的条件:
if (!my_file) {...}此方法通过评估文件对象本身来检查文件是否处于错误状态。
- 如果文件已成功打开,则条件评估为
true。 - 如果存在错误,则评估为
false,您可以相应地处理错误。
2. 使用 is_open() 函数
is_open() 函数返回:
- true - 如果文件已成功打开。
- false - 如果文件打开失败或处于错误状态。
例如,
ofstream my_file("example.txt");
if (!my_file.is_open()) {
cout << "Error opening the file." << endl;
return 1;
}3. 使用 fail() 函数
fail() 函数返回:
- true - 如果文件打开失败或处于错误状态。
- false - 如果文件已成功打开。
ofstream my_file("example.txt");
if (my_file.fail()) {
cout << "Error opening the file." << endl;
return 1;
}注意:为了简单起见,我们建议使用第一种方法。
从文件读取
从文本文件中读取是通过使用 ifstream 类打开文件来完成的。例如:
ifstream my_file("example.txt");然后,我们需要逐行读取文件。要做到这一点,我们需要循环遍历文件的每一行,直到所有行都被读取,即直到我们到达文件末尾。
为此,我们使用 eof() 函数,该函数返回:
- true - 如果文件指针指向文件末尾
- false - 如果文件指针未指向文件末尾
例如,
// variable to store file content
string line;
// loop until the end of the file
while (!my_file.eof()) {
// store the current line of the file
// in the "line" variable
getline(my_file, line);
// print the line variable
cout << line << endl;
}在这里,while 循环将一直运行到文件末尾。在循环的每次迭代中:
getline(my_file, line);读取文件的当前行并将其存储在 line 变量中。- 然后,它会打印 line 变量。
接下来,让我们通过一个实际示例来阐明这一点。
示例2:从文件读取
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// open a text file for reading
ifstream my_file("example.txt");
// check the file for errors
if(!my_file) {
cout << "Error: Unable to open the file." << endl;
return 1;
}
// store the contents of the file in "line" string
string line;
// loop until the end of the text file
while (!my_file.eof()) {
// store the current line of the file
// in the "line" variable
getline(my_file, line);
// print the line variable
cout << line << endl;
}
// close the file
my_file.close();
return 0;
}假设 example.txt 包含以下文本:
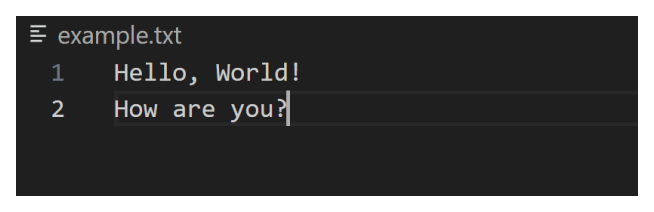
然后,我们的终端将打印以下输出:
Hello, World! How are you?
写入文件
我们使用 ofstream 类来写入文件。例如:
ofstream my_file("example.txt");然后,我们可以使用插入运算符 << 和 ofstream 对象 my_file 来写入文件。例如:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// open a text file for writing
ofstream my_file("example.txt");
// check the file for errors
if(!my_file) {
cout << "Error: Unable to open the file." << endl;
return 1;
}
// write multiple lines to the file
my_file << "Line 1" << endl;
my_file << "Line 2" << endl;
my_file << "Line 3" << endl;
// close the file
my_file.close();
return 0;
}请注意以下写入文件的代码:
my_file << "Line 1" << endl;
my_file << "Line 2" << endl;
my_file << "Line 3" << endl;这类似于将输出打印到屏幕
cout << "Line1" << endl;在文件处理中,我们只需将 cout 替换为文件对象即可将内容写入文件,而不是写入控制台。
我们的特定代码将以下文本写入 example.txt:
Line1 Line2 Line3
注意:写入现有文件将覆盖文件的现有内容。
追加到文本文件
要添加/追加到文件的现有内容,您需要以追加模式打开文件。
在C++中,您可以通过在打开文件时使用 ios::app 标志来实现这一点:
ofstream my_file("example.txt", ios::app);现在,让我们向 example.txt 的现有内容添加一些更多文本:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// open a text file for appending
ofstream my_file("example.txt", ios::app);
// if the file doesn't open successfully, print an error message
if(!my_file) {
cout << "Failed to open the file for appending." << endl;
return 1;
}
// append multiple lines to the file
my_file << "Line 4" << endl;
my_file << "Line 5" << endl;
my_file << "Line 6" << endl;
// close the file
my_file.close();
return 0;
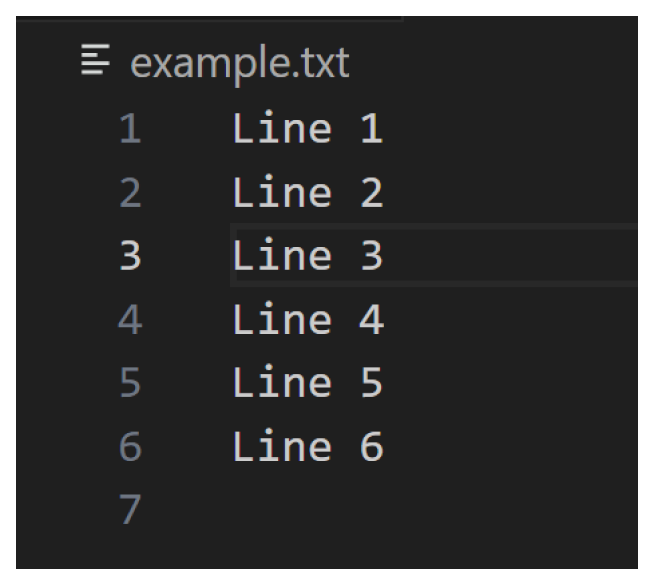
}这将向 example.txt 添加以下行:
Line 4 Line 5 Line 6
使用 fstream 进行文件处理
与使用 ifstream 从文件读取和使用 ofstream 写入文件不同,我们可以直接使用 fstream 类进行所有文件操作。
fstream 的构造函数允许您指定文件名和文件操作的模式。
| 模式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
ios::in |
打开文件进行读取(ifstream 的默认值)。 |
ios::out |
打开文件进行写入(ofstream 的默认值)。 |
ios::app |
打开文件并在末尾追加新内容。 |
我们来看一个例子
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 1. write to a text file
fstream my_file("example.txt", ios::out);
if (my_file) {
my_file << "This is a test line." << endl;
my_file.close();
}
else {
cout << "Unable to open file for writing." << endl;
return 1;
}
// 2. read from the same file
string line;
my_file.open("example.txt", ios::in);
if (my_file) {
while (!my_file.eof()) {
getline(my_file, line);
cout << "Read from file: " << line << endl;
}
my_file.close();
}
else {
cout << "Unable to open file for reading." << endl;
return 1;
}
// 3. append data to the end of the file
my_file.open("example.txt", ios::app);
if (my_file) {
my_file << "This is another test line, appended to the file." << endl;
my_file.close();
}
else {
cout << "Unable to open file for appending." << endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}输出
Read from file: This is a test line. Read from file:
运行程序后查看文件,我们将找到以下内容:
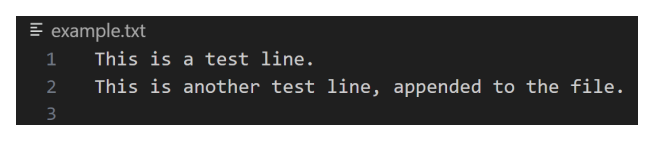
注意:明确使用 ifstream 和 ofstream 分别表示读取或写入的意图,这使得代码更具可读性,并且不易出错。如果不仔细处理,使用 fstream 进行两者操作可能会导致歧义或意外操作。