C++ List 是一个 STL 容器,它将元素随机存储在不相关的内存位置。为了保持顺序,列表中的每个元素都包含两个链接
- 一个指向前一个元素
- 另一个指向后一个元素
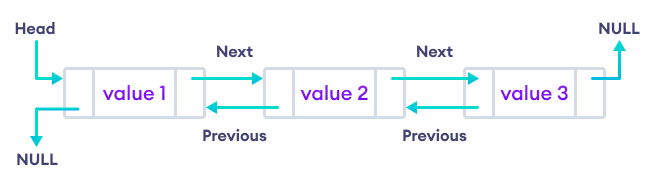
在 C++ 中,STL list 实现的是 双向链表数据结构。因此,我们可以向前和向后迭代。
创建 C++ STL List
要创建 list,我们需要在程序中包含 list 头文件。
#include<list>导入头文件后,我们就可以使用以下语法声明 list 了
std::list<Type> list_name = {value1, value2, ...};这里,
std::list- 声明一个类型为list的 STL 容器<Type>- 要存储在 list 中的值的 数据类型list_name- 为 list 指定的唯一名称value1, value2, ...- 要存储在 list 中的值
让我们看一个例子,
// create a list of integer type
std::list<int> numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// create a list of character type
std::list<char> vowels = {'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'};注意:我们也可以在不提及 赋值运算符 的情况下包含 list 元素。例如,
std::list<int> numbers {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};示例:C++ STL List
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create the list
list<int> numbers {1, 2, 3, 4};
// display the elements of the list
cout << "List Elements: ";
for(int number : numbers) {
cout << number <<", ";
}
return 0;
}输出
List Elements: 1, 2, 3, 4,
在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个名为 numbers 的 list,其元素为:1、2、3、4。然后我们使用 基于范围的 for 循环 来打印 list 元素。
注意:我们使用了 list 而不是 std::list,因为我们已经使用 using namespace std; 定义了 std 命名空间。
List 的基本操作
C++ STL 提供了各种 函数,我们可以使用它们对 list 执行不同的操作。让我们来看一些常用的 list 函数来执行以下操作
- 添加元素
- 访问元素
- 删除元素
1. 在 C++ List 中添加元素
我们可以使用以下函数向 list 添加值
push_front()- 将元素插入 list 的开头push_back()- 将元素添加到 list 的末尾
让我们看一个例子,
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a list
list<int> numbers = {1, 2, 3};
// display the original list
cout << "Initial List: ";
for(int number: numbers) {
cout << number << ", ";
}
// add element at the beginning
numbers.push_front(0);
// add element at the end
numbers.push_back(4);
// display the modified list
cout << endl << "Final List: ";
for(int number : numbers) {
cout << number << ", ";
}
return 0;
}输出
Initial List: 1, 2, 3, Final List: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,
2. 访问 List 元素
我们可以使用以下函数访问 list 元素
front()- 返回 list 的第一个元素back()- 返回 list 的最后一个元素
让我们看一个例子,
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a list
list<int> numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// display the first element
cout << "First Element: " << numbers.front() << endl;
// display the last element
cout << "Last Element: " << numbers.back();
return 0;
}输出
First Element: 1 Last Element: 5
3. 删除 List 元素
我们可以使用以下函数删除 list 元素
pop_front()- 删除 list 开头的元素pop_back()- 删除 list 末尾的元素
这是一个例子,
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a list
list<int> numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// display the original list
cout << "Inital List: ";
for(int number : numbers) {
cout << number << ", ";
}
// remove the first element of the list
numbers.pop_front();
// remove the last element of the list
numbers.pop_back();
// display the modified list
cout << endl << "Final List: ";
for(int number : numbers) {
cout << number << ", ";
}
return 0;
}输出
Inital List: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, Final List: 2, 3, 4,
C++ 中的其他 List 函数
虽然有许多函数可以与 list 一起使用,但我们将在下表中仅介绍其中一些函数
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
reverse() |
反转元素的顺序。 |
sort() |
按特定顺序对 list 元素进行排序。 |
unique() |
删除连续的重复元素。 |
empty() |
检查 list 是否为空。 |
size() |
返回 list 中的元素数量。 |
clear() |
清除 list 中的所有值 |
merge() |
合并两个已排序的 list。 |
使用迭代器访问元素
我们可以使用 迭代器 来访问指定位置的 list 元素。例如,
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a list
list<int> numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// create an iterator to point to the first element of the list
list<int>::iterator itr = numbers.begin();
// increment itr to point to the 2nd element
++itr;
//display the 2nd element
cout << "Second Element: " << *itr << endl;
// increment itr to point to the 4th element
++itr;
++itr;
// display the 4th element
cout << "Fourth Element: " << *itr;
return 0;
}输出
Second Element: 2 Fourth Element: 4
在上面的例子中:
list<int>::iterator- 定义了一个int类型 list 的迭代器numbers.begin()- 将迭代器设置为指向 list 的开头
请注意,我们反复使用了 ++itr; 而不是像 itr+3; 这样将整数添加到 itr。
这是因为迭代器不像常规整数那样是简单的数值。它们指向容器中的特定内存位置。
使用 ++ 运算符递增迭代器会使其指向容器中的下一个元素。
要了解有关迭代器的更多信息,请访问 C++ STL Iterators。
常见问题
我们使用 insert() 函数将元素添加到指定位置。
list 的 insert() 函数的语法是
list_name.insert(iterator, value);这里,
iterator- 指向要插入值的目标位置value- 需要插入到迭代器指定位置的实际值
让我们看一个例子,
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a list
list<int> numbers {1, 2, 3};
// display the original list
cout<<"Initial List: ";
for(int number : numbers) {
cout << number << ", ";
}
// create an iterator to point to the 1st position
list<int>::iterator itr = numbers.begin();
// increment the iterator to point to the 3rd position
++itr;
++itr;
// insert 0 at the 3rd position of list
numbers.insert(itr, 0);
// display the modified list
cout<<endl<<"Final List: ";
for(int number : numbers) {
cout << number << ", ";
}
return 0;
}输出
Initial List: 1, 2, 3, Final List: 1, 2, 0, 3,
我们使用 remove() 函数从指定位置移除元素。remove() 函数的语法是
list_name.remove(element);remove() 函数可以用于以下两种方式
- 使用值
- 使用迭代器
1. 使用值进行 remove()
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a list
list<int> numbers {1, 2, 1, 3, 4, 1};
// display the original list
cout << "Initial List: ";
for(int number : numbers) {
cout << number << ", ";
}
// remove all the elements with value 1
numbers.remove(1);
// display the modified list
cout << endl << "Final List: ";
for(int number : numbers) {
cout << number << ", ";
}
return 0;
}输出
Initial List: 1, 2, 1, 3, 4, 1, Final List: 2, 3, 4,
2. 使用迭代器进行 remove()
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a list and an iterator
list<int> numbers {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 3};
list<int>::iterator itr = numbers.begin();
// display the original list
cout<<"Initial List: ";
for(int number : numbers) {
cout << number << ", ";
}
// point iterator to the 4th element
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
++itr;
}
// remove the 4th element
numbers.remove(*itr);
// display the modified list
cout << endl << "Final List: ";
for(int number : numbers) {
cout << number << ", ";
}
return 0;
}输出
Initial List: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 3, Final List: 0, 1, 2, 4, 5,
这里,值为 3 的两个元素都被删除了,尽管我们只对第四个元素使用了 remove() 函数。
这是因为 remove() 函数会删除所有具有与迭代器指向的元素相同的值的元素。
另请阅读