双向链表是一种 链表,其中每个节点包含 3 个部分
*prev- 前一个节点的地址data- 数据项*next- 下一个节点的地址
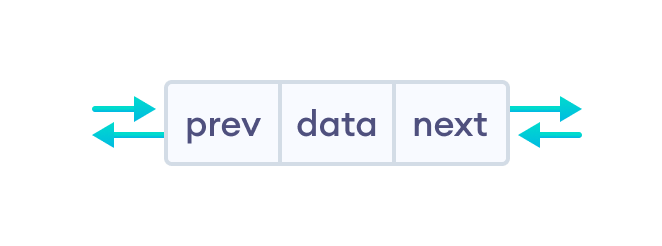
注意:在继续学习之前,请务必学习 指针和结构。
双向链表的表示
让我们看看如何在算法/代码中表示双向链表。假设我们有一个双向链表

这里,单个节点表示为
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
}每个结构节点都有一个数据项、一个指向前一个结构节点的指针和一个指向下一个结构节点的指针。
现在我们将创建一个包含三个简单双向链表以了解它是如何工作的。
/* Initialize nodes */
struct node *head;
struct node *one = NULL;
struct node *two = NULL;
struct node *three = NULL;
/* Allocate memory */
one = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
two = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
three = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* Assign data values */
one->data = 1;
two->data = 2;
three->data = 3;
/* Connect nodes */
one->next = two;
one->prev = NULL;
two->next = three;
two->prev = one;
three->next = NULL;
three->prev = two;
/* Save address of first node in head */
head = one;在上面的代码中,one、two 和 three 分别是数据项为 1、2 和 3 的节点。
- 对于节点 one:
next存储two的地址,prev存储null(它前面没有节点) - 对于节点 two:
next存储three的地址,prev存储one的地址 - 对于节点 three:
next存储null(它后面没有节点),prev存储two的地址。
注意:对于头节点,prev 指向 null;对于尾指针,next 指向 null。这里,one 是头节点,three 是尾节点。
双向链表的插入
将节点推入双向链表类似于将节点推入链表,但需要额外的工作来处理指向前一个节点的指针。
我们可以在双向链表的 3 个不同位置插入元素
假设我们有一个包含元素 1、2 和 3 的双向链表。

1. 在开头插入
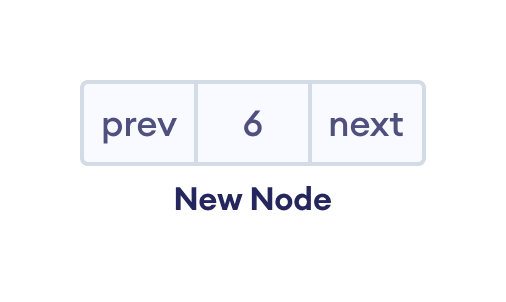
让我们在上面创建的双向链表开头添加一个值为 6 的节点。
1. 创建一个新节点
- 为
newNode分配内存 - 将数据分配给
newNode。
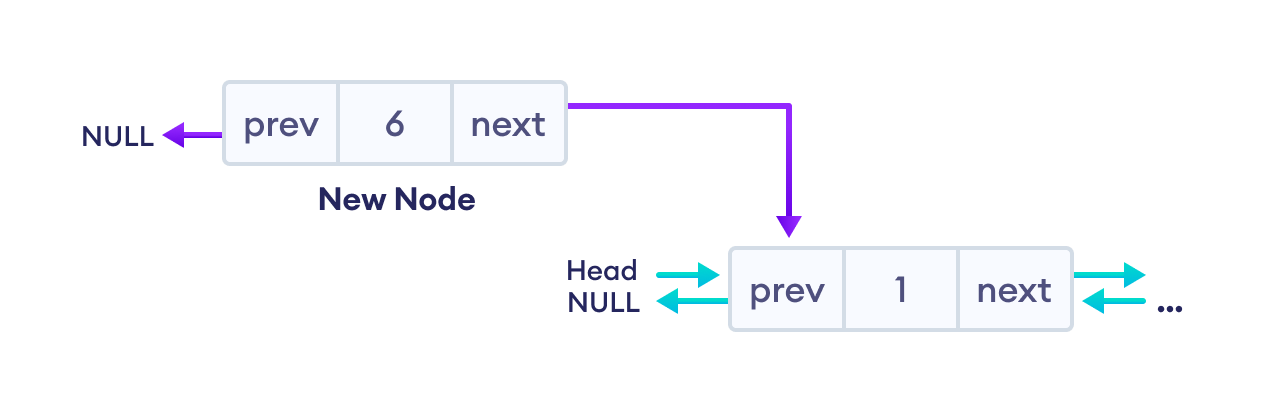
2. 设置新节点的 prev 和 next 指针
- 将
newNode的next指向双向链表的第一个节点 - 将
prev指向null
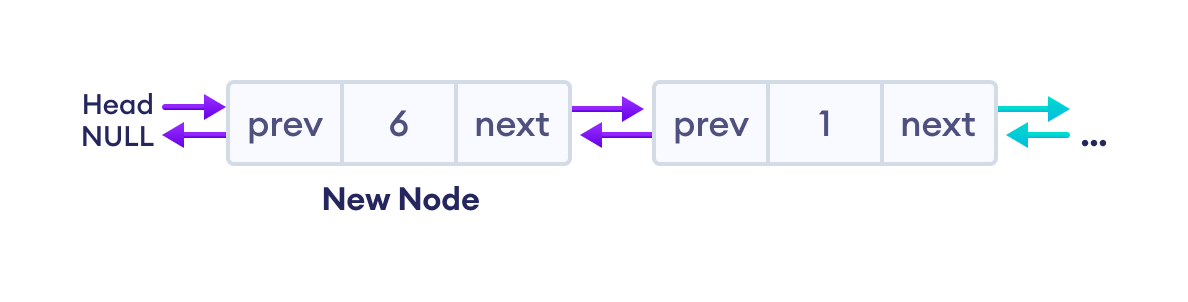
3. 将新节点设为头节点
- 将第一个节点的
prev指向newNode(现在原来的head是第二个节点) - 将
head指向newNode
在开头插入的代码
// insert node at the front
void insertFront(struct Node** head, int data) {
// allocate memory for newNode
struct Node* newNode = new Node;
// assign data to newNode
newNode->data = data;
// point next of newNode to the first node of the doubly linked list
newNode->next = (*head);
// point prev to NULL
newNode->prev = NULL;
// point previous of the first node (now first node is the second node) to newNode
if ((*head) != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// head points to newNode
(*head) = newNode;
}2. 在两个节点之间插入
让我们在双向链表中值为 1 的节点后面添加一个值为 6 的节点。
1. 创建一个新节点
- 为
newNode分配内存 - 将数据分配给
newNode。

2. 设置新节点和前一个节点的 next 指针
- 将前一个节点的
next值分配给newNode的next - 将
newNode的地址分配给前一个节点的next
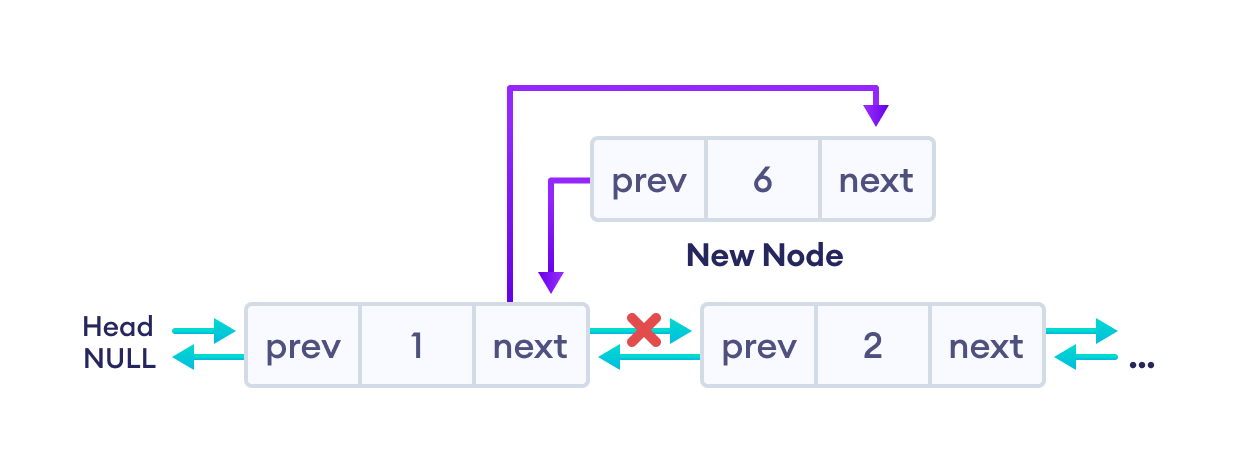
3. 设置新节点和下一个节点的 prev 指针
- 将下一个节点的
prev值分配给newNode的prev - 将
newNode的地址分配给下一个节点的prev
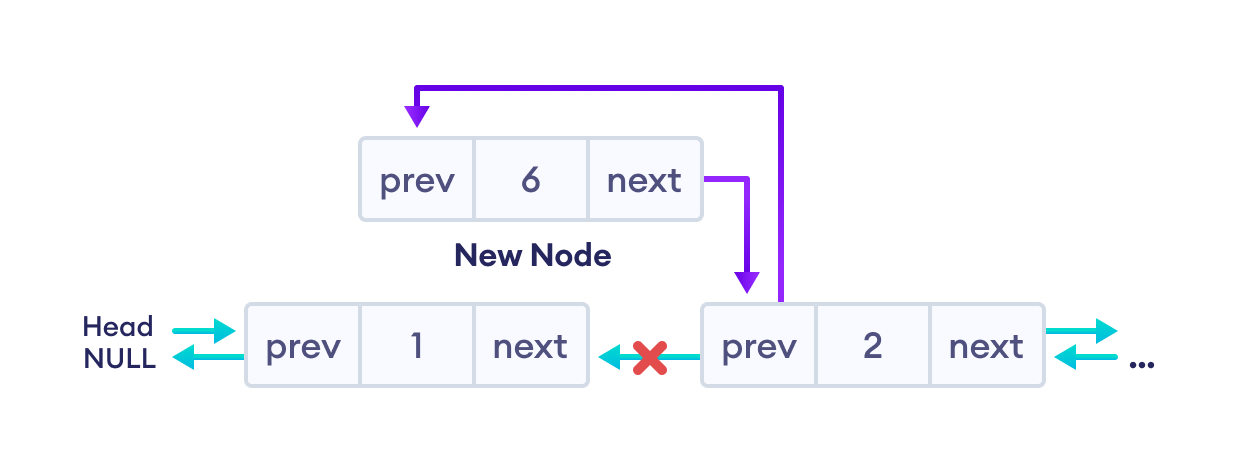
这次插入后,最终的双向链表是

在两个节点之间插入的代码
// insert a node after a specific node
void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node, int data) {
// check if previous node is NULL
if (prev_node == NULL) {
cout << "previous node cannot be NULL";
return;
}
// allocate memory for newNode
struct Node* newNode = new Node;
// assign data to newNode
newNode->data = data;
// set next of newNode to next of prev node
newNode->next = prev_node->next;
// set next of prev node to newNode
prev_node->next = newNode;
// set prev of newNode to the previous node
newNode->prev = prev_node;
// set prev of newNode's next to newNode
if (newNode->next != NULL)
newNode->next->prev = newNode;
}3. 在末尾插入
让我们在双向链表末尾添加一个值为 6 的节点。
1. 创建一个新节点
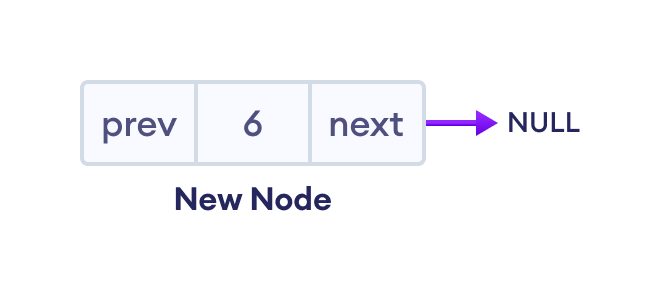
2. 设置新节点和前一个节点的 prev 和 next 指针
如果链表为空,则将 newNode 设置为头节点。否则,遍历双向链表的末尾,然后
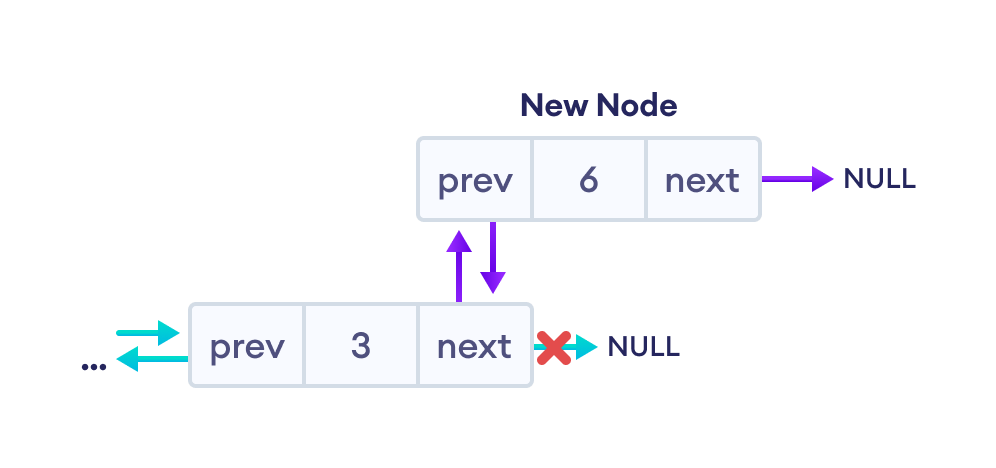
最终的双向链表如下所示。

在末尾插入的代码
// insert a newNode at the end of the list
void insertEnd(struct Node** head, int data) {
// allocate memory for node
struct Node* newNode = new Node;
// assign data to newNode
newNode->data = data;
// assign NULL to next of newNode
newNode->next = NULL;
// store the head node temporarily (for later use)
struct Node* temp = *head;
// if the linked list is empty, make the newNode as head node
if (*head == NULL) {
newNode->prev = NULL;
*head = newNode;
return;
}
// if the linked list is not empty, traverse to the end of the linked list
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
// now, the last node of the linked list is temp
// point the next of the last node (temp) to newNode.
temp->next = newNode;
// assign prev of newNode to temp
newNode->prev = temp;
}从双向链表中删除
与插入类似,我们也可以从双向链表的 3 个不同位置删除节点。
假设我们有一个包含元素 1、2 和 3 的双向链表。

1. 删除双向链表的第一个节点
如果待删除节点(即 del_node)在开头
重置 del_node 之后的节点(即第二个节点)的值
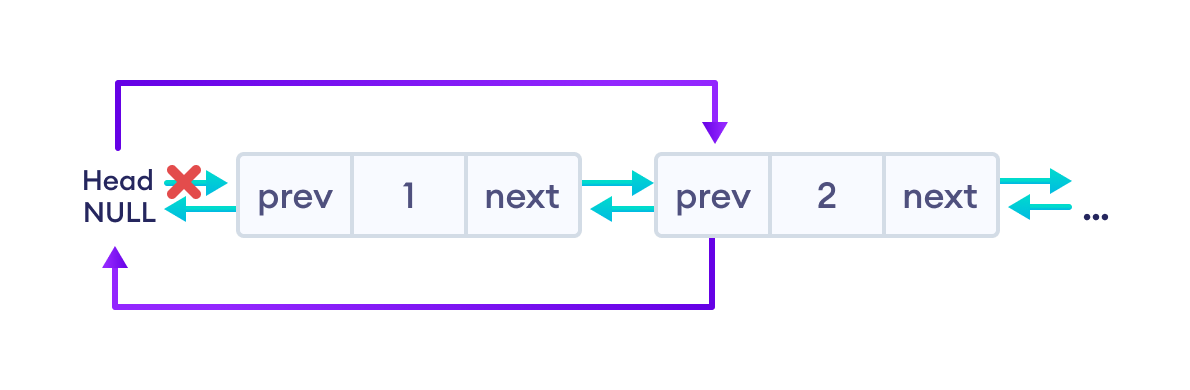
最后,释放 del_node 的内存。然后,链表将如下所示

删除第一个节点的代码
if (*head == del_node)
*head = del_node->next;
if (del_node->prev != NULL)
del_node->prev->next = del_node->next;
free(del);2. 删除中间节点
如果 del_node 是中间节点(第二个节点),我们必须重置 del_node 前后节点的 next 和 prev 的值。
对于 del_node 之前的节点(即第一个节点)
将 del_node 的 next 值分配给 first 节点的 next。
对于 del_node 之后的节点(即第三个节点)
将 del_node 的 prev 值分配给 third 节点的 prev。
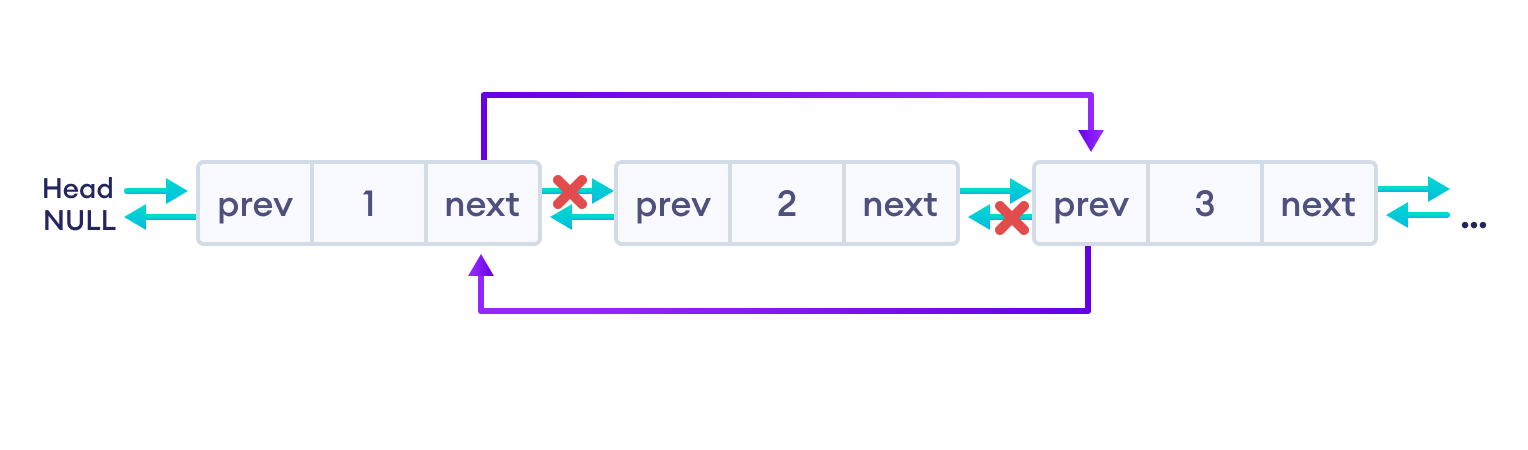
最后,我们将释放 del_node 的内存。然后,最终的双向链表如下所示。
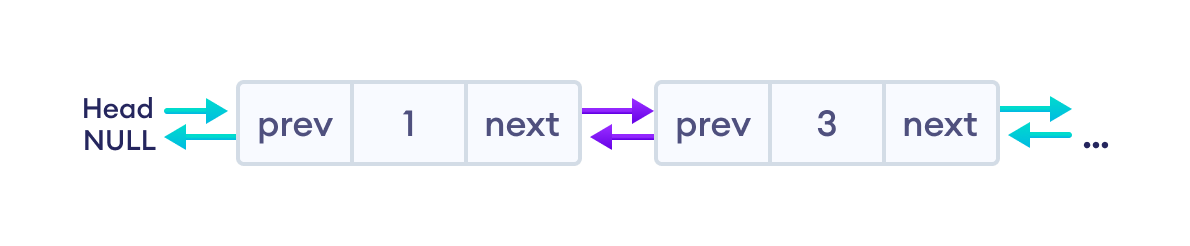
删除中间节点的代码
if (del_node->next != NULL)
del_node->next->prev = del_node->prev;
if (del_node->prev != NULL)
del_node->prev->next = del_node->next;3. 删除双向链表的最后一个节点
在这种情况下,我们将删除双向链表中值为 3 的最后一个节点。
在这里,我们可以简单地删除 del_node,并将 del_node 前一个节点的 next 指向 NULL。
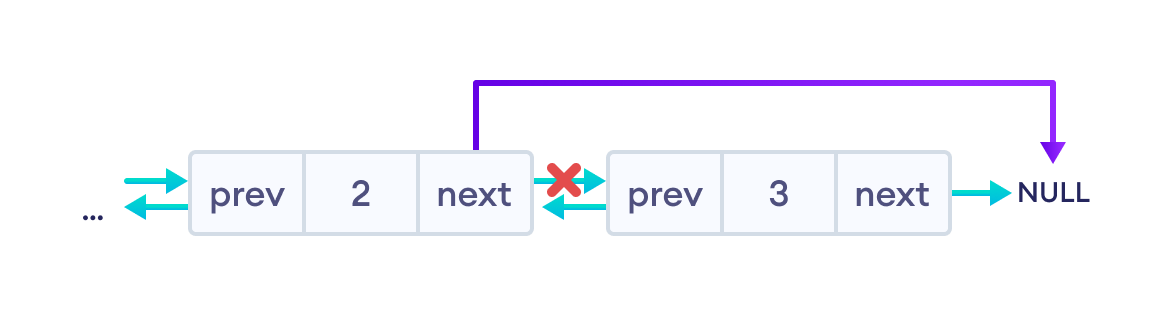
最终的双向链表如下所示。

删除最后一个节点的代码
if (del_node->prev != NULL)
del_node->prev->next = del_node->next;这里,del_node ->next 是 NULL,所以 del_node->prev->next = NULL。
注意:我们也可以使用第二个条件(删除中间节点)的第一个条件(对于 del_node 前的节点)来解决这个问题。
Python、Java、C 和 C++ 中的双向链表代码
import gc
# node creation
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# insert node at the front
def insert_front(self, data):
# allocate memory for newNode and assign data to newNode
new_node = Node(data)
# make newNode as a head
new_node.next = self.head
# assign null to prev (prev is already none in the constructore)
# previous of head (now head is the second node) is newNode
if self.head is not None:
self.head.prev = new_node
# head points to newNode
self.head = new_node
# insert a node after a specific node
def insert_after(self, prev_node, data):
# check if previous node is null
if prev_node is None:
print("previous node cannot be null")
return
# allocate memory for newNode and assign data to newNode
new_node = Node(data)
# set next of newNode to next of prev node
new_node.next = prev_node.next
# set next of prev node to newNode
prev_node.next = new_node
# set prev of newNode to the previous node
new_node.prev = prev_node
# set prev of newNode's next to newNode
if new_node.next:
new_node.next.prev = new_node
# insert a newNode at the end of the list
def insert_end(self, data):
# allocate memory for newNode and assign data to newNode
new_node = Node(data)
# assign null to next of newNode (already done in constructor)
# if the linked list is empty, make the newNode as head node
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
# store the head node temporarily (for later use)
temp = self.head
# if the linked list is not empty, traverse to the end of the linked list
while temp.next:
temp = temp.next
# now, the last node of the linked list is temp
# assign next of the last node (temp) to newNode
temp.next = new_node
# assign prev of newNode to temp
new_node.prev = temp
return
# delete a node from the doubly linked list
def deleteNode(self, dele):
# if head or del is null, deletion is not possible
if self.head is None or dele is None:
return
# if del_node is the head node, point the head pointer to the next of del_node
if self.head == dele:
self.head = dele.next
# if del_node is not at the last node, point the prev of node next to del_node to the previous of del_node
if dele.next is not None:
dele.next.prev = dele.prev
# if del_node is not the first node, point the next of the previous node to the next node of del_node
if dele.prev is not None:
dele.prev.next = dele.next
# free the memory of del_node
gc.collect()
# print the doubly linked list
def display_list(self, node):
while node:
print(node.data, end="->")
last = node
node = node.next
# initialize an empty node
d_linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
d_linked_list.insert_end(5)
d_linked_list.insert_front(1)
d_linked_list.insert_front(6)
d_linked_list.insert_end(9)
# insert 11 after head
d_linked_list.insert_after(d_linked_list.head, 11)
# insert 15 after the seond node
d_linked_list.insert_after(d_linked_list.head.next, 15)
d_linked_list.display_list(d_linked_list.head)
# delete the last node
d_linked_list.deleteNode(d_linked_list.head.next.next.next.next.next)
print()
d_linked_list.display_list(d_linked_list.head)public class DoublyLinkedList {
// node creation
Node head;
class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
}
}
// insert node at the front
public void insertFront(int data) {
// allocate memory for newNode and assign data to newNode
Node newNode = new Node(data);
// make newNode as a head
newNode.next = head;
// assign null to prev of newNode
newNode.prev = null;
// previous of head (now head is the second node) is newNode
if (head != null)
head.prev = newNode;
// head points to newNode
head = newNode;
}
// insert a node after a specific node
public void insertAfter(Node prev_node, int data) {
// check if previous node is null
if (prev_node == null) {
System.out.println("previous node cannot be null");
return;
}
// allocate memory for newNode and assign data to newNode
Node new_node = new Node(data);
// set next of newNode to next of prev node
new_node.next = prev_node.next;
// set next of prev node to newNode
prev_node.next = new_node;
// set prev of newNode to the previous node
new_node.prev = prev_node;
// set prev of newNode's next to newNode
if (new_node.next != null)
new_node.next.prev = new_node;
}
// insert a newNode at the end of the list
void insertEnd(int data) {
// allocate memory for newNode and assign data to newNode
Node new_node = new Node(data);
// store the head node temporarily (for later use)
Node temp = head;
// assign null to next of newNode
new_node.next = null;
// if the linked list is empty, make the newNode as head node
if (head == null) {
new_node.prev = null;
head = new_node;
return;
}
// if the linked list is not empty, traverse to the end of the linked list
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
// assign next of the last node (temp) to newNode
temp.next = new_node;
// assign prev of newNode to temp
new_node.prev = temp;
}
// delete a node from the doubly linked list
void deleteNode(Node del_node) {
// if head or del is null, deletion is not possible
if (head == null || del_node == null) {
return;
}
// if del_node is the head node, point the head pointer to the next of del_node
if (head == del_node) {
head = del_node.next;
}
// if del_node is not at the last node, point the prev of node next to del_node
// to the previous of del_node
if (del_node.next != null) {
del_node.next.prev = del_node.prev;
}
// if del_node is not the first node, point the next of the previous node to the
// next node of del_node
if (del_node.prev != null) {
del_node.prev.next = del_node.next;
}
}
// print the doubly linked list
public void printlist(Node node) {
Node last = null;
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + "->");
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList doubly_ll = new DoublyLinkedList();
doubly_ll.insertEnd(5);
doubly_ll.insertFront(1);
doubly_ll.insertFront(6);
doubly_ll.insertEnd(9);
// insert 11 after head
doubly_ll.insertAfter(doubly_ll.head, 11);
// insert 15 after the seond node
doubly_ll.insertAfter(doubly_ll.head.next, 11);
doubly_ll.printlist(doubly_ll.head);
// delete the last node
doubly_ll.deleteNode(doubly_ll.head.next.next.next.next.next);
doubly_ll.printlist(doubly_ll.head);
}
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// node creation
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
// insert node at the front
void insertFront(struct Node** head, int data) {
// allocate memory for newNode
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// assign data to newNode
newNode->data = data;
// make newNode as a head
newNode->next = (*head);
// assign null to prev
newNode->prev = NULL;
// previous of head (now head is the second node) is newNode
if ((*head) != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// head points to newNode
(*head) = newNode;
}
// insert a node after a specific node
void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node, int data) {
// check if previous node is null
if (prev_node == NULL) {
printf("previous node cannot be null");
return;
}
// allocate memory for newNode
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// assign data to newNode
newNode->data = data;
// set next of newNode to next of prev node
newNode->next = prev_node->next;
// set next of prev node to newNode
prev_node->next = newNode;
// set prev of newNode to the previous node
newNode->prev = prev_node;
// set prev of newNode's next to newNode
if (newNode->next != NULL)
newNode->next->prev = newNode;
}
// insert a newNode at the end of the list
void insertEnd(struct Node** head, int data) {
// allocate memory for node
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// assign data to newNode
newNode->data = data;
// assign null to next of newNode
newNode->next = NULL;
// store the head node temporarily (for later use)
struct Node* temp = *head;
// if the linked list is empty, make the newNode as head node
if (*head == NULL) {
newNode->prev = NULL;
*head = newNode;
return;
}
// if the linked list is not empty, traverse to the end of the linked list
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
// now, the last node of the linked list is temp
// assign next of the last node (temp) to newNode
temp->next = newNode;
// assign prev of newNode to temp
newNode->prev = temp;
}
// delete a node from the doubly linked list
void deleteNode(struct Node** head, struct Node* del_node) {
// if head or del is null, deletion is not possible
if (*head == NULL || del_node == NULL)
return;
// if del_node is the head node, point the head pointer to the next of del_node
if (*head == del_node)
*head = del_node->next;
// if del_node is not at the last node, point the prev of node next to del_node to the previous of del_node
if (del_node->next != NULL)
del_node->next->prev = del_node->prev;
// if del_node is not the first node, point the next of the previous node to the next node of del_node
if (del_node->prev != NULL)
del_node->prev->next = del_node->next;
// free the memory of del_node
free(del_node);
}
// print the doubly linked list
void displayList(struct Node* node) {
struct Node* last;
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d->", node->data);
last = node;
node = node->next;
}
if (node == NULL)
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main() {
// initialize an empty node
struct Node* head = NULL;
insertEnd(&head, 5);
insertFront(&head, 1);
insertFront(&head, 6);
insertEnd(&head, 9);
// insert 11 after head
insertAfter(head, 11);
// insert 15 after the seond node
insertAfter(head->next, 15);
displayList(head);
// delete the last node
deleteNode(&head, head->next->next->next->next->next);
displayList(head);
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// node creation
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
// insert node at the front
void insertFront(struct Node** head, int data) {
// allocate memory for newNode
struct Node* newNode = new Node;
// assign data to newNode
newNode->data = data;
// make newNode as a head
newNode->next = (*head);
// assign null to prev
newNode->prev = NULL;
// previous of head (now head is the second node) is newNode
if ((*head) != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// head points to newNode
(*head) = newNode;
}
// insert a node after a specific node
void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node, int data) {
// check if previous node is null
if (prev_node == NULL) {
cout << "previous node cannot be null";
return;
}
// allocate memory for newNode
struct Node* newNode = new Node;
// assign data to newNode
newNode->data = data;
// set next of newNode to next of prev node
newNode->next = prev_node->next;
// set next of prev node to newNode
prev_node->next = newNode;
// set prev of newNode to the previous node
newNode->prev = prev_node;
// set prev of newNode's next to newNode
if (newNode->next != NULL)
newNode->next->prev = newNode;
}
// insert a newNode at the end of the list
void insertEnd(struct Node** head, int data) {
// allocate memory for node
struct Node* newNode = new Node;
// assign data to newNode
newNode->data = data;
// assign null to next of newNode
newNode->next = NULL;
// store the head node temporarily (for later use)
struct Node* temp = *head;
// if the linked list is empty, make the newNode as head node
if (*head == NULL) {
newNode->prev = NULL;
*head = newNode;
return;
}
// if the linked list is not empty, traverse to the end of the linked list
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
// now, the last node of the linked list is temp
// assign next of the last node (temp) to newNode
temp->next = newNode;
// assign prev of newNode to temp
newNode->prev = temp;
}
// delete a node from the doubly linked list
void deleteNode(struct Node** head, struct Node* del_node) {
// if head or del is null, deletion is not possible
if (*head == NULL || del_node == NULL)
return;
// if del_node is the head node, point the head pointer to the next of del_node
if (*head == del_node)
*head = del_node->next;
// if del_node is not at the last node, point the prev of node next to del_node to the previous of del_node
if (del_node->next != NULL)
del_node->next->prev = del_node->prev;
// if del_node is not the first node, point the next of the previous node to the next node of del_node
if (del_node->prev != NULL)
del_node->prev->next = del_node->next;
// free the memory of del_node
free(del_node);
}
// print the doubly linked list
void displayList(struct Node* node) {
struct Node* last;
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << "->";
last = node;
node = node->next;
}
if (node == NULL)
cout << "NULL\n";
}
int main() {
// initialize an empty node
struct Node* head = NULL;
insertEnd(&head, 5);
insertFront(&head, 1);
insertFront(&head, 6);
insertEnd(&head, 9);
// insert 11 after head
insertAfter(head, 11);
// insert 15 after the seond node
insertAfter(head->next, 15);
displayList(head);
// delete the last node
deleteNode(&head, head->next->next->next->next->next);
displayList(head);
}双向链表复杂度
| 双向链表复杂度 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 |
| 插入操作 | O(1) 或 O(n) | O(1) |
| 删除操作 | O(1) | O(1) |
1. 插入操作的复杂度
- 不需要遍历的插入操作的时间复杂度为
O(1)。 - 而需要遍历的插入的时间复杂度为
O(n)。 - 空间复杂度为
O(1)。
2. 删除操作的复杂度
- 所有删除操作的时间复杂度均为
O(1)。 - 空间复杂度为
O(1)。
双向链表的应用
- 软件中的撤销和重做功能。
- 浏览器中的前进和后退导航。
- 用于需要前后导航的导航系统。
单向链表与双向链表
| 单向链表 | 双向链表 |
| 每个节点包含一个数据值和一个指向下一个节点的指针。 | 每个节点包含一个数据值、一个指向下一个节点的指针和一个指向前一个节点的指针。 |
| 遍历只能单向进行(向前)。 | 遍历可以双向进行。 |
| 它需要更少的空间。 | 由于多了一个指针,它需要更多的空间。 |
| 它可以在堆栈上实现。 | 它有多种用途。它可以在堆栈、堆和二叉树上实现。 |
