exp() 函数用于计算数组元素的指数值。
示例
import numpy as np
array1 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
# use of exp() to calculate the exponential values of each elements in array1
result = np.exp(array1)
print(result)
# Output : [ 2.71828183 7.3890561 20.08553692 54.59815003 148.4131591 ]exp() 语法
exp() 的语法是:
numpy.exp(array)exp() 参数
exp() 函数接受一个参数:
array- 输入数组
exp() 返回值
exp() 函数返回一个包含输入数组元素指数值的数组。
示例 1:使用 exp() 计算自然对数
import numpy as np
# create a 2-D array
array1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
# use exp() to calculate the exponential values each element in array1
result = np.exp(array1)
print(result)输出
[[ 2.71828183 7.3890561 20.08553692] [ 54.59815003 148.4131591 403.42879349]]
在这里,我们使用 np.exp() 函数计算名为 array1 的二维数组中每个元素的指数值。
结果数组 result 包含指数值。
示例 2:exp() 的图形表示
为了提供指数函数的图形表示,让我们使用 Python 中流行的可视化库 matplotlib 来绘制指数曲线。
要使用 matplotlib,我们首先将其导入为 plt。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# generate x values from -5 to 5 with a step of 0.1
x = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1)
# compute the exponential values of x
y = np.exp(x)
# Plot the exponential curve
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('exp(x)')
plt.title('Exponential Function')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()输出
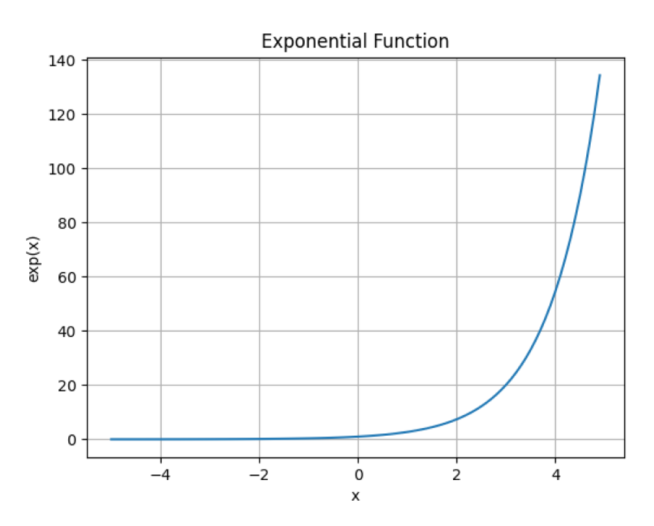
在上面的示例中,我们使用 plt.plot(x, y) 将 x 绘制在 x 轴上,将包含指数值的 y 绘制在 y 轴上。
