CSS position 属性用于定义元素在网页上的位置。
定位元素的位置由四个属性设置:top、left、right 和 bottom。这些属性仅在设置了 position 属性时才起作用,并且具有不同的定位行为。
position 属性有以下五个值
- static (默认值)
- relative
- absolute
- fixed
- sticky
我们将逐一介绍它们。
CSS static 定位
position 属性的 static 值允许元素根据文档的正常流进行定位。static 定位不受 top、right、bottom 和 left 值的影响。
让我们看一个例子,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>CSS position</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p class="main">This paragraph is positioned using the static value.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>p {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 4px;
}
p.main {
position: static;
top: 50px; /* doesn't work */
right: 50px; /* doesn't work */
bottom: 50px; /* doesn't work */
left: 50%; /* doesn't work */
background-color: greenyellow;
}浏览器输出

注意:static 值是 position 属性的默认值。
CSS Relative 定位
relative 值将元素相对于文档中的原始位置进行定位。元素通过 top、right、bottom 和 left 值进行定位。
让我们看一个例子,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>CSS position</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p class="main">
This paragraph is positioned with a relative value of top 50px and
left 40px.
</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>p {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 4px;
}
p.main {
position: relative;
/* positions 90px from the top */
top: 90px;
/* positions 40px from the left */
left: 40px;
background-color: greenyellow;
}浏览器输出

在上面的示例中,第二个段落相对于其正常流进行了定位,即距离原始位置顶部 90px,距离左侧 40px。
元素原始位置的空间会被保留。
CSS Absolute 定位
absolute 值将元素完全从文档的正常流中移除。
元素相对于其最近的已定位父元素(祖先元素,其 position 值为 static 以外的值)进行定位。
如果没有已定位的祖先元素,则它们相对于文档本身进行定位。
让我们看一个例子,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>CSS position</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p class="main">
This is an absolutely positioned paragraph at 40px top and 60px left.
</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>p {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 4px;
}
p.main {
position: absolute;
top: 70px;
left: 60px;
background-color: greenyellow;
}浏览器输出
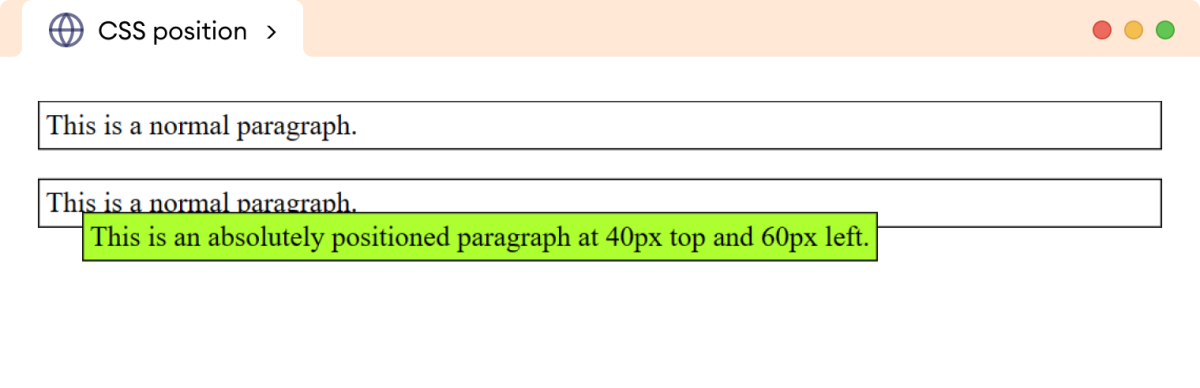
在上面的示例中,第二个段落没有已定位的父元素,因此它相对于视口(浏览器可见区域)进行定位。
让我们看一个例子,了解 absolute 定位如何与已定位的父元素一起工作
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>CSS position</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p class="main">
This is an absolutely positioned paragraph at 40px top and 60px
left.
</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<!-- Creating an container -->
<div class="parent">
<p>This paragraph is inside the div element.</p>
<p class="main">
This is an absolutely positioned paragraph inside the div
element at 40px top and 60px left.
</p>
<p>This paragraph is inside the div element.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>p {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 4px;
}
p.main {
position: absolute;
top: 70px;
left: 60px;
background-color: greenyellow;
}
div.parent {
position: relative;
background-color: orange;
border: 4px solid red;
}浏览器输出
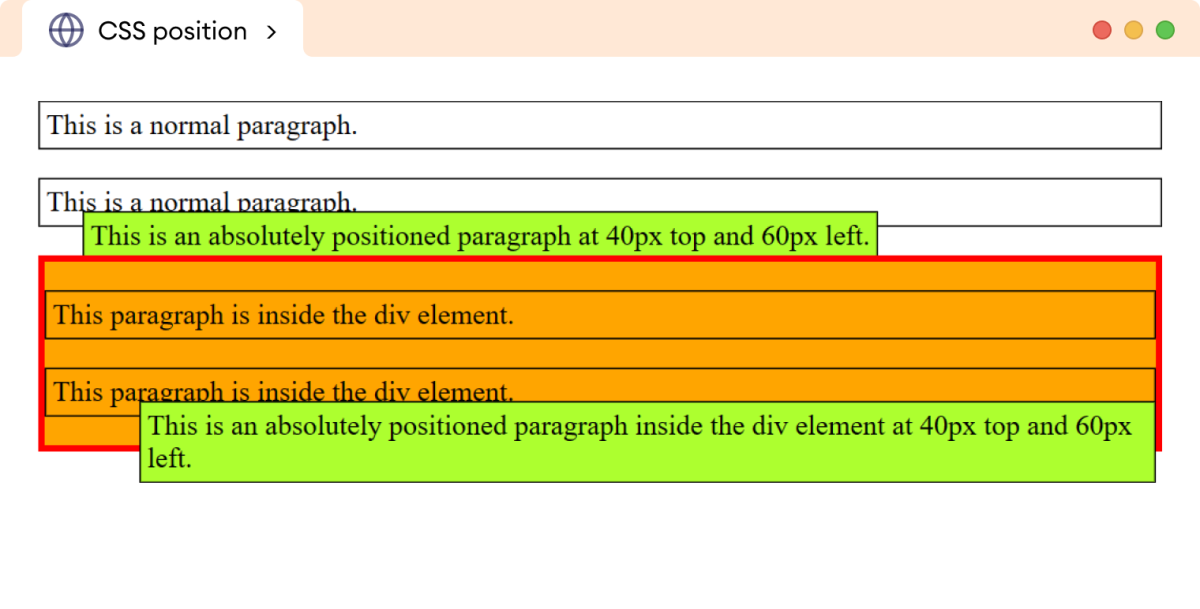
在这里,尽管 main 类下的两个段落具有相同的样式,但它们的位置却不同。这是因为第一个段落没有已定位的父元素,因此它相对于文档(视口)进行定位。
另一方面,第二个段落有一个具有 relative 定位值的父 div 元素,因此它相对于该 div 元素进行定位。
注意:绝对定位的元素会失去其在文档流中的大小和原始空间。
CSS fixed 定位
fixed 值将元素定位在相同位置,即使页面滚动也不会改变。它类似于 absolute 值,但它始终相对于视口。
让我们看一个例子,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>CSS position</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="main">
This paragraph has a fixed position value at 10px top.
</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>p {
border: 2px solid black;
padding: 4px;
}
p.main {
position: fixed;
top: 10px;
background-color: greenyellow;
}浏览器输出
此段落的 fixed 定位值为距离顶部 10px。
这是一个普通段落。
这是一个普通段落。
这是一个普通段落。
这是一个普通段落。
这是一个普通段落。
这是一个普通段落。
这是一个普通段落。
在上面的例子中:
position: fixed;
top: 10px;将段落固定在网页的 top 距离 10px 处。该段落不会随文档中的其他内容一起滚动。
CSS sticky 定位
sticky 值将元素定位为 relative 和 fixed 值的组合。
sticky 定位在元素到达屏幕上的某个滚动点之前,表现得像 relative 定位。之后,元素会像 fixed 元素一样固定在视口顶部。
让我们看一个例子,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>CSS position</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="main">
This paragraph has a fixed position value at 10px top.
</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
<p>This is a normal paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>p {
border: 2px solid black;
padding: 4px;
}
p.main {
position: fixed;
top: 10px;
background-color: greenyellow;
}浏览器输出
这是一个普通段落。
此段落的 sticky 定位值为距离顶部 10px。
这是一个普通段落。
在上面的示例中,段落会滚动,直到距离视口 top 10px。之后,它会保持 sticky 定位。