CSS @font-face 属性允许我们为网页指定自定义字体。例如,
@font-face {
font-family: "Roboto";
src: url("path/to/roboto-regular.woff2") format("woff2");
}这里,
@font-face:指允许自定义字体的 CSS 属性font-family:将字体系列设置为Robotosrc:指定自定义字体的路径和格式
现在我们可以在网页中使用自定义字体。
CSS @font-face 规则
CSS @font-face 规则允许我们在网页上加载自定义字体。自定义字体可以从远程服务器加载,也可以从用户计算机上的本地安装字体加载。例如,
@font-face {
font-family: "My Custom Font";
src: url("path/my-custom-font.woff") format("woff"),
url("path/my-custom-font.woff") format("woff");
}这里,
font-family:指要加载的font-familysrc:指定自定义字体的 URL 和格式url:指定远程或本地托管的字体路径format:指字体文件的格式
现在,我们可以在 HTML 页面上像使用普通字体一样使用 My Custom Font。
h1{
font-family: "My Custom Font", sans-serif;
}我们只有在使用 @font-face 规则定义了字体后,才可以在 font-family 属性中使用自定义字体。
在上面的示例中,我们为 @font-face 属性定义了多个 url。如果第一个 url 加载失败,则会渲染第二个 url。
@font-face 示例
现在,让我们看一个 @font-face 如何工作的示例,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>Custom font in CSS</title>
</head>
<body>
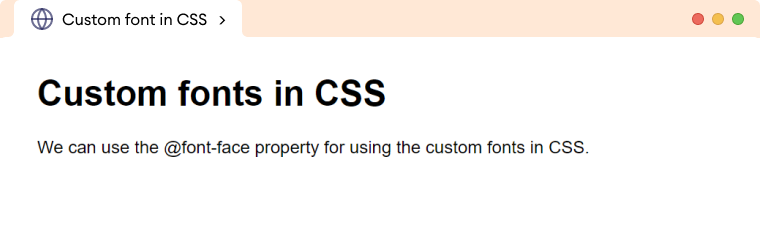
<h1>Custom fonts in CSS</h1>
<p>
We can use the @font-face property for using the custom fonts in
CSS.
</p>
</body>
</html>/* allows to set Helvetica font*/
@font-face {
font-family: "Helvetica";
src: url("https://fonts.gstatic.com/s/helvetica/v1/7Auop_0qiz-aVz7u3PJLcA.eot?#iefix")
format("embedded-opentype"),
url("https://fonts.gstatic.com/s/helvetica/v1/7Auop_0qiz-aVz7u3PJLcA.woff2")
format("woff2"),
url("https://fonts.gstatic.com/s/helvetica/v1/7Auop_0qiz-aVz7u3PJLcA.woff")
format("woff");
}
h1, p {
/* sets the text to Helvetica font */
font-family: Helvetica;
}浏览器输出
自定义字体的替代技术
我们还可以通过以下方式使用自定义字体
- 使用 CSS
@import规则 - 使用 HTML
<link>标签
使用 @import 规则
我们可以使用 CSS @import 规则来导入其他远程托管的字体。例如,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>Using import rule</title>
</head>
<body>
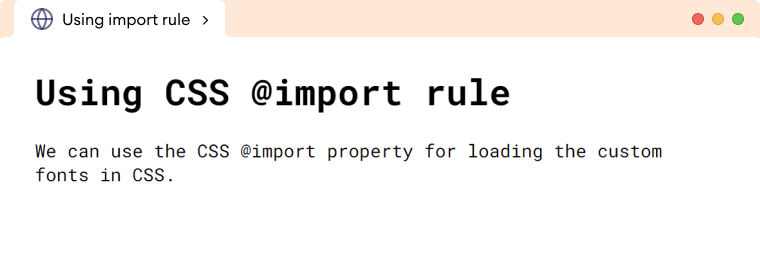
<h1>Using CSS @import rule</h1>
<p>
We can use the CSS @import property for loading the custom fonts in
CSS.
</p>
</body>
</html>@import url("https://fonts.googleapis.ac.cn/css2?family=Roboto+Mono:wght@400;700&display=swap");
h1, p {
font-family: "Roboto Mono", monospace;
}浏览器输出
在上面的示例中,我们使用 @import 从 Google Fonts 加载 Roboto Mono 字体。
使用 <link> 标签
我们可以使用 <link> 标签来加载字体,就像我们使用 @import 规则一样。例如,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.ac.cn/css2?family=Roboto+Mono:wght@400;700&display=swap"
rel="stylesheet"/>
<title>Using Link tag</title>
</head>
<body>
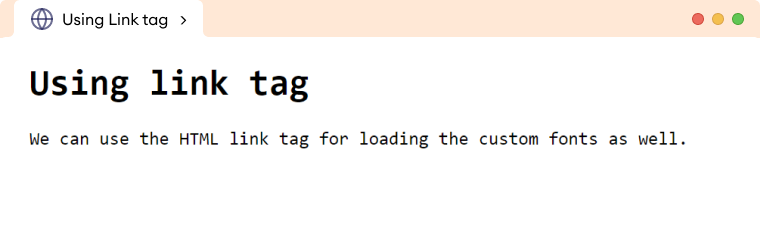
<h1>Using link tag</h1>
<p>
We can use the HTML link tag for loading the custom fonts as well.
</p>
</body>
</html>h1, p {
font-family: "Roboto Mono", monospace;
}浏览器输出
在上面的示例中,我们使用 <link> 标签在网页中加载 Roboto Mono 字体,并将其与 h1 和 p 元素一起使用。
不同的字体格式类型
我们有不同的字体格式类型,它们具有不同的功能和能力。
WOFF/ WOFF2 (Web 开放字体格式)
WOFF 是一种压缩字体格式,常用于网页。它提供更快的加载速度,并受大多数现代浏览器支持。
SVG/SVGZ (可伸缩矢量图形)
SVG 通常用于图形和徽标,可以轻松调整大小而不会损失质量。它可用于字体,但不建议使用,因为它缺少高级排版功能。SVG 字体目前不受主要现代浏览器的支持。
EOT (嵌入式 Open Type)
EOT 字体格式用作在网页上嵌入字体的方式。EOT 主要用于旧版本的 Internet Explorer,目前不受现代浏览器的支持。
OTF/TTF (OpenType 字体/ TrueType 字体)
OTF 和 TTF 字体是网页上最常用的字体,因为它们受大多数现代网络浏览器的支持。
注意:
- 自定义字体可能会影响网页性能,因为字体需要下载才能渲染,这可能会增加页面加载时间。
- 较大的字体大小也可能因下载和渲染时间较长而影响网页性能。