CSS font-weight 用于调整网页中文本的轻重或粗细。例如,
span {
font-weight: bold;
}浏览器输出

这里,font-weight: bold 将 span 元素的文本设置为 粗体。
CSS 字体粗细语法
font-weight 属性具有以下语法,
font-weight: normal|bold|bolder|lighter|number|initial|inherit;font-weight 的可能值如下,
| 字体粗细值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
normal |
设置正常字体粗细,是默认值,等同于数字值 400 |
bold |
将文本设置为粗体,等同于数字值 700 |
bolder |
将文本设置为比其父元素更粗一个级别的粗细 |
lighter |
将文本设置为比其父元素更细一个级别的粗细 |
100 |
设置文本为细体 |
200 |
设置文本为特细体 |
300 |
设置文本为细体 |
400 |
设置文本为正常 |
500 |
设置文本为中等 |
600 |
设置文本为半粗 |
700 |
设置文本为粗体 |
800 |
设置文本为特粗 |
900 |
设置文本为超粗 |
initial |
将文本设置为默认值 |
inherit |
继承父元素的样式 |
font-weight 示例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>CSS font weight</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="normal">This is normal font weight.</p>
<p class="bold">This is bold font weight.</p>
<p class="weight-100">This is 100 font weight.</p>
<p class="weight-200">This is 200 font weight.</p>
<p class="weight-300">This is 300 font weight.</p>
<p class="weight-400">This is 400 font weight.</p>
<p class="weight-500">This is 500 font weight.</p>
<p class="weight-600">This is 600 font weight.</p>
<p class="weight-700">This is 700 font weight.</p>
<p class="weight-800">This is 800 font weight.</p>
<p class="weight-900">This is 900 font weight.</p>
</body>
</html>@import url("https://fonts.googleapis.ac.cn/css2?family=Roboto:wght@100;300;400;500;700;900&display=swap");
body {
font-family: "Roboto", sans-serif;
}
p.normal {
font-weight: normal;
}
p.bold {
font-weight: bold;
}
p.weight-100 {
font-weight: 100;
}
p.weight-200 {
font-weight: 200;
}
p.weight-300 {
font-weight: 300;
}
p.weight-400 {
font-weight: 400;
}
p.weight-500 {
font-weight: 500;
}
p.weight-600 {
font-weight: 600;
}
p.weight-700 {
font-weight: 700;
}
p.weight-800 {
font-weight: 800;
}
p.weight-900 {
font-weight: 900;
}浏览器输出
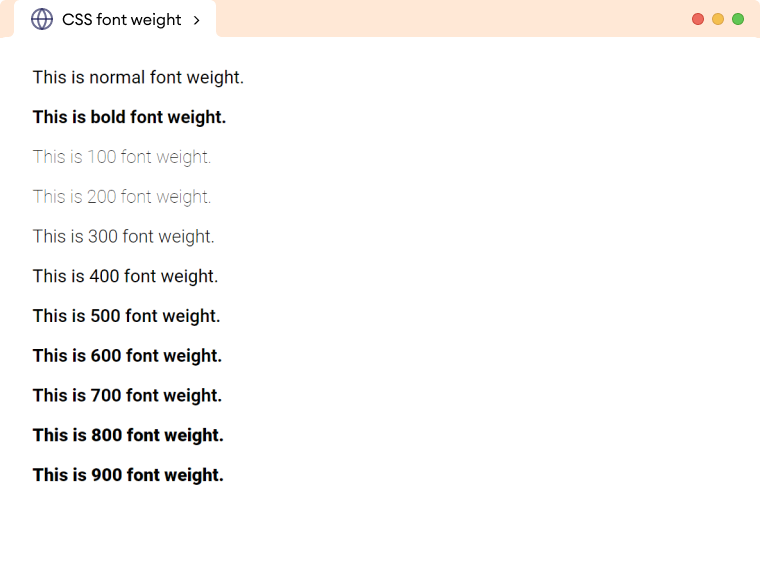
上面的示例演示了 font-weight 的不同值如何工作。
相对字体粗细
相对字体粗细用于指定字体的粗细相对于父字体的粗细。
CSS 中有两种相对字体粗细:lighter 和 bolder。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>CSS font weight</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="bold">This <span>statement</span> is set to the bold.</p>
<p class="normal">This <span>statement</span> is set to the normal.</p>
</body>
</html>@import url("https://fonts.googleapis.ac.cn/css2?family=Roboto:wght@100;300;400;500;700;900&display=swap");
body {
font-family: "Roboto", sans-serif;
}
p.bold {
/* sets font-weight to bold */
font-weight: bold;
}
p.normal {
/* sets font-weight to normal */
font-weight: normal;
}
p.bold span {
/* sets font-weight to lighter */
font-weight: lighter;
}
p.normal span {
/* sets font-weight to lighter */
font-weight: lighter;
}浏览器输出

在上面的示例中,尽管我们对两个 span 元素都使用了 font-weight: lighter,但浏览器输出略有不同。这是因为在第一个段落中,lighter 是相对于 bold 的,而在第二个段落中,lighter 是相对于 normal 的。
注意:font-weight 属性并非对所有 font-family 都有效。但是,在大多数情况下,浏览器会模拟一种能够近似给定 font-weight 的粗细。