有时我们需要将两个或多个图形放在一个图中。
R par() 函数
我们可以通过使用 par() 函数设置一些图形参数,将多个图形放在一个图中。R 编程有许多图形参数,它们控制图形的显示方式。
par() 函数可以帮助我们设置或查询这些参数。例如,您可以通过在不带任何参数的情况下调用该函数来查看所有参数及其值。
>par()
$xlog
[1] FALSE
...
$yaxt
[1] "s"
$ylbias
[1] 0.2
您会看到一个很长的参数列表,要了解每个参数的作用,您可以查看帮助部分 ?par。在这里,我们将重点介绍有助于我们创建子图的参数。
图形参数 mfrow 可用于指定我们需要的子图数量。
它接受一个形式为 c(m, n) 的向量,将给定的图划分为 m*n 的子图阵列。例如,如果我们想并排放置两个图形,我们会设置 m=1 和 n=2。以下示例说明了这一点。
>max.temp # a vector used for plotting
Sun Mon Tue Wen Thu Fri Sat
22 27 26 24 23 26 28
par(mfrow=c(1,2)) # set the plotting area into a 1*2 array
barplot(max.temp, main="Barplot")
pie(max.temp, main="Piechart", radius=1)
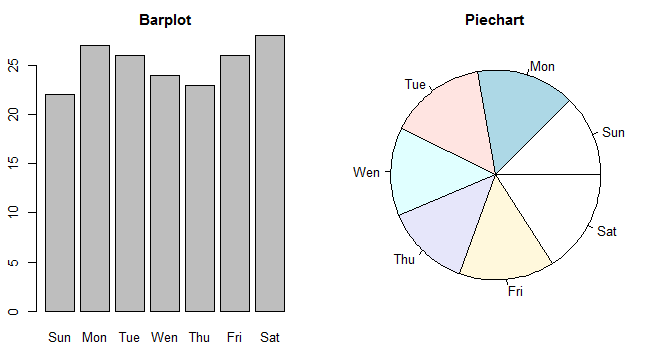
图形参数 mfcol 也可以实现相同的效果。
两者之间的唯一区别是,mfrow 按行填充子图区域,而 mfcol 按列填充。
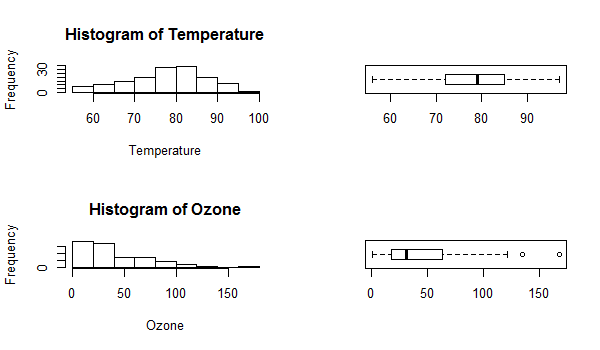
Temperature <- airquality$Temp
Ozone <- airquality$Ozone
par(mfrow=c(2,2))
hist(Temperature)
boxplot(Temperature, horizontal=TRUE)
hist(Ozone)
boxplot(Ozone, horizontal=TRUE)
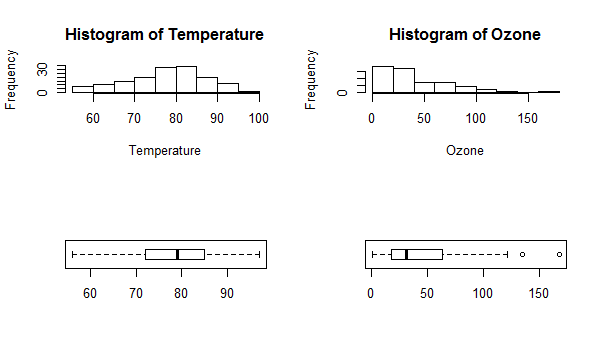
使用 par(mfcol = c(2, 2)) 相同的图形将如下所示。请注意,只有子图的排列顺序不同。
更精确的控制
图形参数 fig 允许我们精确地控制图形在一个图中的位置。
我们需要以标准化形式提供坐标,如 c(x1, x2, y1, y2)。例如,整个绘图区域将是 c(0, 1, 0, 1),其中 (x1, y1) = (0, 0) 是左下角,(x2, y2) = (1, 1) 是右上角。
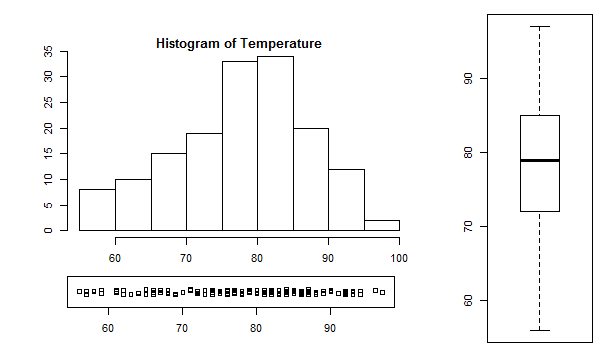
注意: 我们使用了参数 cex 来减小标签的大小,并使用了 mai 来定义边距。
# make labels and margins smaller
par(cex=0.7, mai=c(0.1,0.1,0.2,0.1))
Temperature <- airquality$Temp
# define area for the histogram
par(fig=c(0.1,0.7,0.3,0.9))
hist(Temperature)
# define area for the boxplot
par(fig=c(0.8,1,0,1), new=TRUE)
boxplot(Temperature)
# define area for the stripchart
par(fig=c(0.1,0.67,0.1,0.25), new=TRUE)
stripchart(Temperature, method="jitter")
分配给 fig 的数字是通过反复试验的方法得出的,以获得最佳的图形效果。