xlsx 文件是 Microsoft Excel 电子表格使用的文件格式。Excel 可用于存储表格数据。
R 具有内置功能,可以轻松读取和写入 xlsx 文件。
示例 xlsx 文件
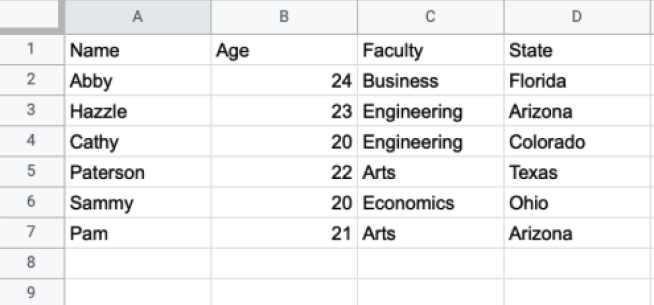
为了演示我们在 R 中如何读取 xlsx 文件,让我们假设我们有一个名为 studentinfo.xlsx 的 Excel 文件,其中包含以下数据:
我们将借助 R 的内置函数来读取这些数据。
安装和加载 xlsx 包
为了在 R 中读取、写入和格式化 Excel 文件,我们首先需要安装和加载 xlsx 包,如下所示:
# install xlsx package
install.package("xlsx")
# load xlsx file
library("xlsx")在这里,我们已成功安装并加载了 xlsx 包。
现在,我们可以从 xlsx 文件读取数据了。
在 R 中读取 xlsx 文件
在 R 中,我们使用 read.xlsx() 函数读取当前目录中存在的 xlsx 文件。例如:
# install xlsx package
install.package("xlsx")
# load xlsx file
library("xlsx")
# read studentinfo.xlsx file from our current directory
read_data <- read.xlsx("studentinfo.xlsx", sheetIndex = 1)
# display xlsx file
print(read_data)输出
Name Age Faculty State 1 Abby 24 Business Florida 2 Hazzle 23 Engineering Arizona 3 Cathy 20 Engineering Colorado 4 Paterson 22 Arts Texas 5 Sammy 20 Economics Ohio 6 Pam 2 Arts Arizona
在上面的示例中,我们读取了当前目录中存在的 studentinfo.xlsx 文件。请注意代码:
read_data <- read.xlsx("studentinfo.xlsx", sheetIndex = 1)这里,
read.xlsx()- 读取 xlsx 文件studentinfo.xlsx并创建一个数据框,该数据框存储在 read_data 变量中。sheetIndex = 1- 读取指定的А善,即 **1**
注意:
- 如果文件位于其他位置,我们需要指定路径和文件名,如下所示:
read.xlsx("D:/folder1/studentinfo.xlsx", sheetIndex = 1)。 - 如果我们要处理的数据集较大,我们也可以使用
read.xlsx2()函数。
R 中的 xlsx rowIndex 和 colIndex 参数
在 R 中,我们也可以从 Excel 文件中读取特定范围的数据。我们可以将 rowIndex 和 colIndex 参数传递给 read.xlsx() 来读取特定范围。
rowIndex- 读取特定范围的行colIndex- 读取特定范围的列
示例:读取行范围
# install xlsx package
install.package("xlsx")
# load xlsx file
library("xlsx")
# read first five rows of xlsx file
read_data <- read.xlsx("studentinfo.xlsx",
sheetIndex = 1,
rowIndex = 1:5
)
# display xlsx file
print(read_data)输出
Name Age Faculty State 1 Abby 24 Business Florida 2 Hazzle 23 Engineering Arizona 3 Cathy 20 Engineering Colorado 4 Paterson 22 Arts Texas
在上面的示例中,我们在 read.xlsx() 中传递了 rowIndex = 1:5,因此该函数仅从 studentinfo.xlsx 文件中读取前五行。
示例:读取列范围
# install xlsx package
install.package("xlsx")
# load xlsx file
library("xlsx")
# read first three columns of xlsx file
read_data <- read.xlsx("studentinfo.xlsx",
sheetIndex = 1,
colIndex = 1:3
)
# display xlsx file
print(read_data)输出
Name Age Faculty 1 Abby 24 Business 2 Hazzle 23 Engineering 3 Cathy 20 Engineering 4 Paterson 22 Arts 5 Sammy 20 Economics 6 Pam 21 Arts
在这里,read.xlsx() 中的 colIndex = 1:3 仅从 studentinfo.xlsx 文件中读取前三列。
R 中的 xlsx startRow 参数
有时 Excel 文件开头可能包含我们不想包含的标题。例如:
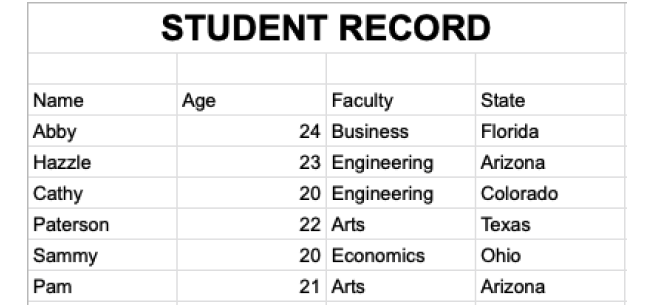
在这里,Excel 文件的 **第 1** 行包含标题,**第 2** 行是空的。因此,我们不想包含这两行。
要开始从 Excel 工作表中的特定行读取数据,我们将 startRow 参数传递给 read.xlsx()。
让我们看一个例子,
# install xlsx package
install.package("xlsx")
# load xlsx file
library("xlsx")
# start reading from 3rd row
read_data <- read.xlsx("studentinfo.xlsx",
sheetIndex = 1,
startRow = 3
)
# display xlsx file
print(read_data)输出
Name Age Faculty State 1 Abby 24 Business Florida 2 Hazzle 23 Engineering Arizona 3 Cathy 20 Engineering Colorado 4 Paterson 22 Arts Texas 5 Sammy 20 Economics Ohio 6 Pam 21 Arts Arizona
在上面的示例中,我们在 read.xlsx() 函数中使用 startRow 参数从指定行开始读取。
startRow = 3 表示忽略前两行,read.xlsx() 从第 3 行开始读取数据。
在 R 中写入 xlsx 文件
在 R 中,我们使用 write.xlsx() 函数将数据写入 xlsx 文件。我们将数据以 数据框 的形式传递。例如:
# install xlsx package
install.package("xlsx")
# load xlsx file
library("xlsx")
# create a data frame
dataframe1 <- data.frame (
Name = c("Juan", "Alcaraz", "Simantha"),
Age = c(22, 15, 19),
Vote = c(TRUE, FALSE, TRUE))
# write dataframe1 into file1 xlsx file
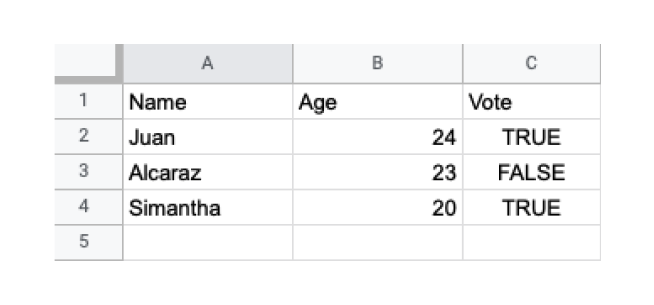
write.xlsx(dataframe1, "file1.xlsx")在上面的示例中,我们使用 write.xlsx() 函数将名为 dataframe1 的数据框导出到 xlsx 文件。请注意传递给 write.xlsx() 的参数:
write.xlsx(dataframe1, "file1.xlsx")这里,
dataframe1- 要导出的数据框的名称file1.xlsx- xlsx 文件的名称
最后,file1.xlsx 文件在我们的目录中将如下所示:
重命名当前工作表
我们可以使用 write.xlsx() 函数中的 sheetName 参数来重命名当前工作表。例如:
# install xlsx package
install.package("xlsx")
# load xlsx file
library("xlsx")
# create a data frame
dataframe1 <- data.frame (
Name = c("Juan", "Alcaraz", "Simantha"),
Age = c(22, 15, 19),
Vote = c(TRUE, FALSE, TRUE))
# name current worksheet
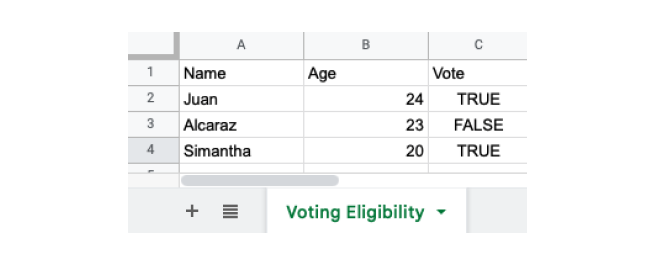
write.xlsx(dataframe1, "file1.xlsx",
sheetName = "Voting Eligibility"
)在这里,我们在 write.xlsx() 中传递了 sheetname = "Voting Eligibility",因此工作表的名称将更改为 "Voting Eligibility"。
因此,file1.xlsx 将如下所示: