在 NumPy 中,数组中的每个元素都与一个数字相关联。这个数字被称为数组索引。
让我们来看一个示例来演示 NumPy 数组索引。
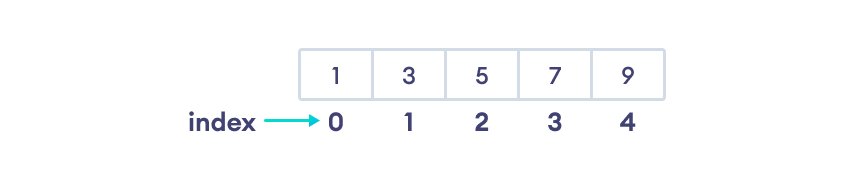
在上面的数组中,5 是第 3 个元素。但是,它的索引是 2。
这是因为数组索引从 0 开始,也就是说,数组的第一个元素的索引是 0,第二个元素的索引是 1,依此类推。
现在,我们将看到如何使用索引号从数组中访问单个元素。
使用索引访问数组元素
我们可以使用索引来访问 NumPy 数组的单个元素。
假设我们有一个 NumPy 数组
array1 = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])现在,我们可以使用索引号来访问数组元素,如下所示:
array1[0]- 访问第一个元素,即1array1[2]- 访问第三个元素,即5array1[4]- 访问第五个元素,即9
示例:使用索引访问数组元素
import numpy as np
array1 = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
# access numpy elements using index
print(array1[0]) # prints 1
print(array1[2]) # prints 5
print(array1[4]) # prints 9注意:由于 array1 的最后一个元素的索引是4,如果我们尝试访问超出该范围的元素,例如索引5,我们将收到一个索引错误:IndexError: index 5 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 5
使用索引修改数组元素
我们可以使用索引来更改 NumPy 数组中元素的值。例如,
import numpy as np
# create a numpy array
numbers = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
# change the value of the first element
numbers[0] = 12
print("After modifying first element:",numbers) # prints [12 4 6 8 10]
# change the value of the third element
numbers[2] = 14
print("After modifying third element:",numbers) # prints [12 4 14 8 10]输出
After modifying first element: [12 4 6 8 10] After modifying third element: [12 4 14 8 10]
在上面的示例中,我们使用数组索引修改了 numbers 数组的元素。
numbers[0] = 12- 修改 numbers 的第一个元素并将其值设置为12numbers[2] = 14- 修改 numbers 的第三个元素并将其值设置为14
NumPy 负数数组索引
NumPy 允许对其数组进行负数索引。索引-1指向最后一个项目,-2指向倒数第二个项目,依此类推。
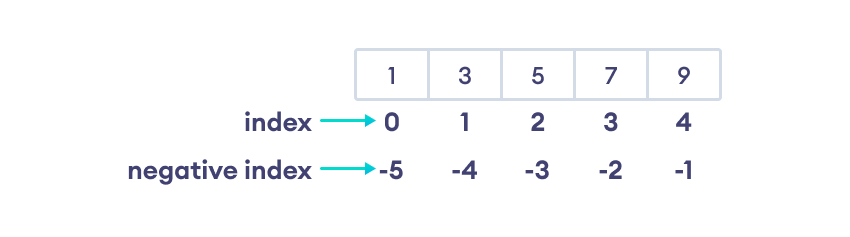
让我们看一个例子。
import numpy as np
# create a numpy array
numbers = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
# access the last element
print(numbers[-1]) # prints 9
# access the second-to-last element
print(numbers[-2]) # prints 7输出
9 7
使用负数索引修改数组元素
与常规索引类似,我们也可以使用负数索引修改数组元素。例如,
import numpy as np
# create a numpy array
numbers = np.array([2, 3, 5, 7, 11])
# modify the last element
numbers[-1] = 13
print(numbers) # Output: [2 3 5 7 13]
# modify the second-to-last element
numbers[-2] = 17
print(numbers) # Output: [2 3 5 17 13]在这里,numbers[-1] = 13 将最后一个元素修改为13,numbers[-2] = 17 将倒数第二个元素修改为17。
注意:与常规索引不同,负数索引从-1(而不是0)开始,并从数组末尾开始计数。
2-D NumPy 数组索引
NumPy 中的数组索引允许我们访问和操作 2-D 数组中的元素。
要访问 array1 中的元素,我们需要指定该元素的行索引和列索引。假设我们有以下 2-D 数组,
array1 = np.array([[1, 3, 5],
[7, 9, 2],
[4, 6, 8]])现在,假设我们要访问第三行第二列的元素,我们指定索引为
array1[2, 1] # returns 6由于我们知道索引从0开始。因此,要访问第三行第二列的元素,我们需要分别使用索引2表示第三行,使用索引1表示第二列。
示例:2-D NumPy 数组索引
import numpy as np
# create a 2D array
array1 = np.array([[1, 3, 5, 7],
[9, 11, 13, 15],
[2, 4, 6, 8]])
# access the element at the second row and fourth column
element1 = array1[1, 3] # returns 15
print("4th Element at 2nd Row:",element1)
# access the element at the first row and second column
element2 = array1[0, 1] # returns 3
print("2nd Element at First Row:",element2) 输出
4th Element at 2nd Row: 15 2nd Element at First Row: 3
使用索引访问 2D 数组的行或列
在 NumPy 中,我们可以使用数组索引来访问 2-D 数组的特定行或列。
让我们看一个例子。
import numpy as np
# create a 2D array
array1 = np.array([[1, 3, 5],
[7, 9, 2],
[4, 6, 8]])
# access the second row of the array
second_row = array1[1, :]
print("Second Row:", second_row) # Output: [7 9 2]
# access the third column of the array
third_col = array1[:, 2]
print("Third Column:", third_col) # Output: [5 2 8]输出
Second Row: [7 9 2] Third Column: [5 2 8]
这里,
array1[1, :]- 访问 array1 的第二行array1[:, 2]- 访问 array1 的第三列
3-D NumPy 数组索引
我们已经学习了如何访问 2D 数组中的元素。我们也可以访问更高维度数组中的元素。
要访问 3D 数组中的元素,我们使用三个索引,用逗号分隔。
- 第一个索引指向切片
- 第二个索引指向行
- 第三个索引指向列。
注意:在 3D 数组中,切片是通过获取其中一个维度的元素子集而得到的 2D 数组。
让我们看一个例子。
import numpy as np
# create a 3D array with shape (2, 3, 4)
array1 = np.array([[[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9, 10, 11, 12]],
[[13, 14, 15, 16],
[17, 18, 19, 20],
[21, 22, 23, 24]]])
# access a specific element of the array
element = array1[1, 2, 1]
# print the value of the element
print(element)
# Output: 22在这里,我们创建了一个名为 array1 的 3D 数组,其形状为(2, 3, 4)。该数组包含2个 2D 数组,每个 2D 数组有3行和4列。
然后,我们使用索引来访问 array1 的特定元素。请注意代码,
array1[1, 2, 1]这里,
array1[1, , ,]- 访问第二个 2D 数组,即
[13, 14, 15, 16],
[17, 18, 19, 20],
[21, 22, 23, 24]array1[ ,2, ]- 访问 2D 数组的第三行,即
[21, 22, 23, 24]array1[ , ,1]- 访问第三行的第二个元素,即
[22]相关阅读:NumPy Fancy Indexing
