面向对象编程语言最实用的特性之一是继承。
根据现有类定义新类。也就是说,我们可以从现有基类派生新类并添加新功能。我们不必从头开始编写。因此,继承提供了代码的可重用性。
继承形成一个类的层次结构,就像家谱一样。需要注意的是,为基类定义的属性将自动存在于派生类中。
此外,基类的方法也将适用于派生类。
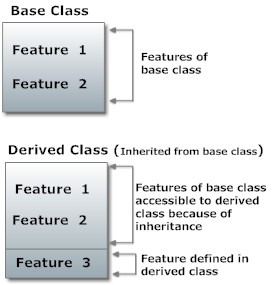
下面,我们将讨论 R 编程语言中的三个不同类系统是如何实现继承的。
S3 类中的继承
S3 类没有固定的定义。因此,S3 对象的属性可以是任意的。
然而,派生类会继承为基类定义的方法。让我们假设我们有一个函数,它创建了类 student 的新对象,如下所示。
student <- function(n,a,g) {
value <- list(name=n, age=a, GPA=g)
attr(value, "class") <- "student"
value
}
此外,我们为泛型函数 print() 定义了一个方法,如下所示。
print.student <- function(obj) {
cat(obj$name, "\n")
cat(obj$age, "years old\n")
cat("GPA:", obj$GPA, "\n")
}
现在我们想创建一个类 InternationalStudent 的对象,它继承自 student。
这可以通过分配一个类名字符向量来完成,例如 class(obj) <- c(child, parent)。
> # create a list
> s <- list(name="John", age=21, GPA=3.5, country="France")
> # make it of the class InternationalStudent which is derived from the class student
> class(s) <- c("InternationalStudent","student")
> # print it out
> s
John
21 years old
GPA: 3.5
从上面的代码可以看到,由于我们没有定义任何形式为 print.InternationalStudent() 的方法,因此调用了 print.student() 方法。这是继承自 student 类的方法。
现在让我们定义 print.InternationalStudent()。
print.InternationalStudent <- function(obj) {
cat(obj$name, "is from", obj$country, "\n")
}
这将覆盖为类 student 定义的方法,如下所示。
> s
John is from France
我们可以使用 inherits() 或 is() 等函数来检查继承。
> inherits(s,"student")
[1] TRUE
> is(s,"student")
[1] TRUE
S4 类中的继承
由于S4 类有正确的定义,派生类将继承父类的属性和方法。
让我们定义一个类 student,并为泛型函数 show() 定义一个方法。
# define a class called student
setClass("student",
slots=list(name="character", age="numeric", GPA="numeric")
)
# define class method for the show() generic function
setMethod("show",
"student",
function(object) {
cat(object@name, "\n")
cat(object@age, "years old\n")
cat("GPA:", object@GPA, "\n")
}
)
继承在派生类定义期间通过 contains 参数完成,如下所示。
# inherit from student
setClass("InternationalStudent",
slots=list(country="character"),
contains="student"
)
这里我们添加了一个属性 country,其余的将从父类继承。
> s <- new("InternationalStudent",name="John", age=21, GPA=3.5, country="France")
> show(s)
John
21 years old
GPA: 3.5
我们看到,当我们执行 show(s) 时,调用了为 student 类定义的方法。
与 S3 系统一样,我们可以为派生类定义方法,这些方法将覆盖基类的方法。
引用类中的继承
引用类中的继承与 S4 类非常相似。我们在 contains 参数中定义要从中派生的基类。
下面是一个 student 引用类的示例,它有两个方法 inc_age() 和 dec_age()。
student <- setRefClass("student",
fields=list(name="character", age="numeric", GPA="numeric"),
methods=list(
inc_age = function(x) {
age <<- age + x
},
dec_age = function(x) {
age <<- age - x
}
)
)
现在我们将从这个类继承。我们还将覆盖 dec_age() 方法以添加一个完整性检查,以确保 age 永远不会为负。
InternationalStudent <- setRefClass("InternationalStudent",
fields=list(country="character"),
contains="student",
methods=list(
dec_age = function(x) {
if((age - x)<0) stop("Age cannot be negative")
age <<- age - x
}
)
)
让我们来测试一下。
> s <- InternationalStudent(name="John", age=21, GPA=3.5, country="France")
> s$dec_age(5)
> s$age
[1] 16
> s$dec_age(20)
Error in s$dec_age(20) : Age cannot be negative
> s$age
[1] 16
通过这种方式,我们能够从父类继承。