在 SQL 中,一个 SELECT 语句可以包含另一个 SQL 语句,这被称为子查询或嵌套查询。
示例
-- use a subquery to select the first name of customer
-- with the highest age
SELECT first_name
FROM Customers
WHERE age= (
-- subquery
SELECT MAX(age)
FROM CUSTOMERS
);这里,查询分为两部分
- 子查询从 Customers 表中选择最大 age
- 外部查询选择具有最大 id(由子查询返回)的客户的 first_name
SQL 子查询语法
SELECT column FROM table
WHERE column OPERATOR (
SELECT column FROM table
);这里,
column是要过滤的列名OPERATOR是用于连接两个查询的任何 SQL 运算符table是从中获取列的表的名称
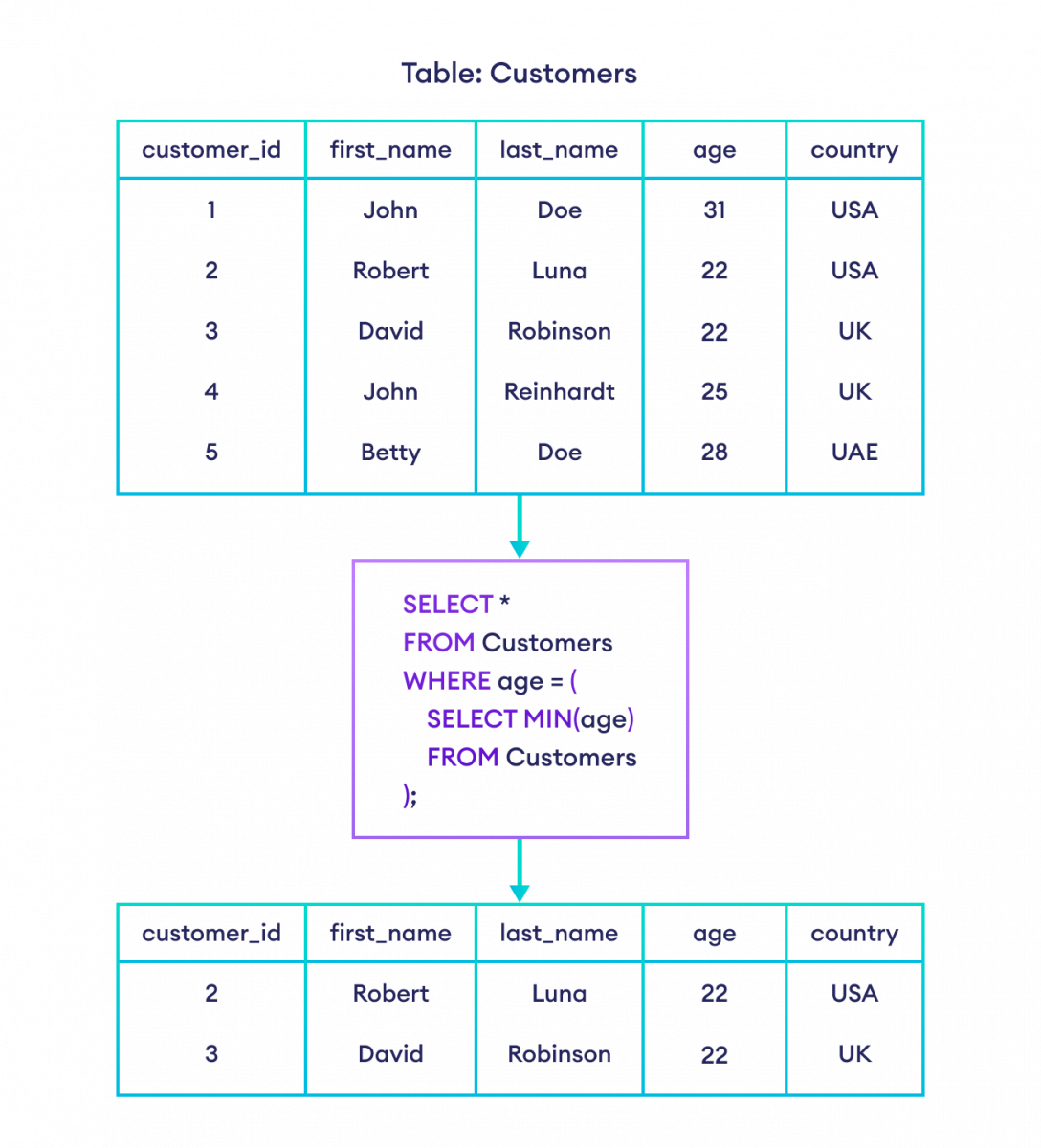
示例:使用子查询选择年龄最小的客户
-- select all the rows from the Customers table
-- with the minimum age
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE age = (
SELECT MIN(age)
FROM Customers
);
下面是查询如何过滤表格。
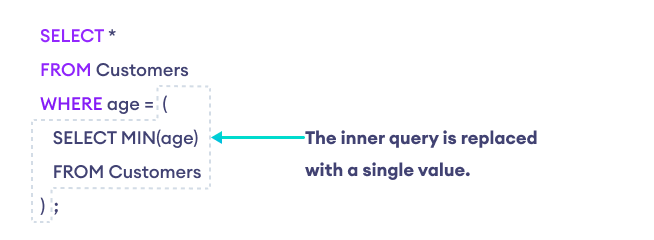
在子查询中,外部查询的结果取决于内部子查询的结果集。这就是为什么子查询也被称为嵌套查询。
此代码的工作原理如下
- 首先执行子查询(内部查询),并返回最小年龄 22
- 执行外部查询,并选择年龄为 22 的客户
更多关于 SQL 子查询
SQL 子查询与 IN 运算符
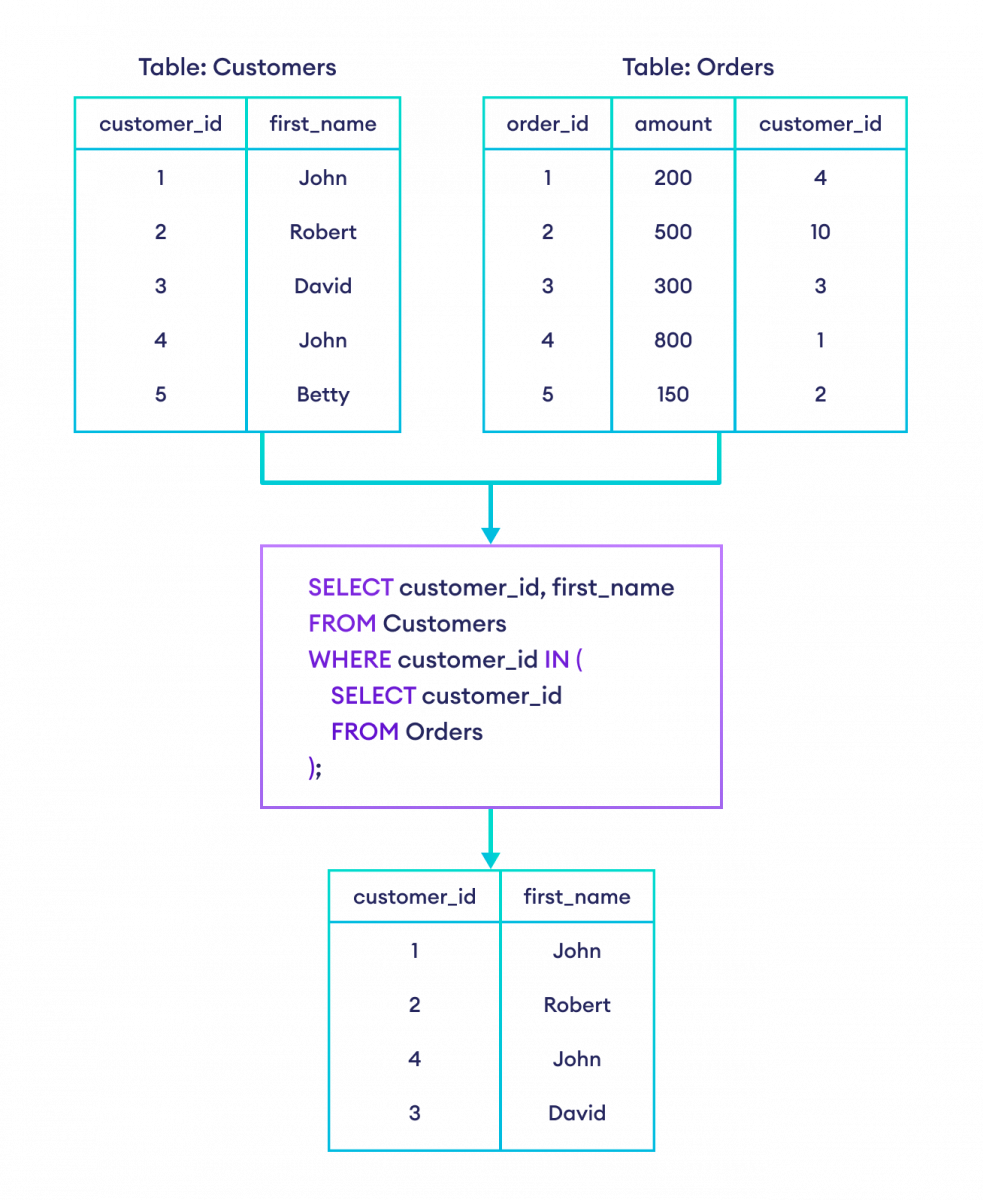
假设我们想要已下订单的客户的详细信息。我们可以通过使用子查询来实现。
-- select the customers who have made orders
SELECT customer_id, first_name
FROM Customers
WHERE customer_id IN (
SELECT customer_id
FROM Orders
);这里,SQL 命令
- 从 Orders 表中选择 customer_id 和 first_name
- 从 Customers 表中选择 customer_id 在子查询结果集中的行
要了解更多信息,请访问SQL IN。
SQL 子查询和 JOIN
在某些情况下,我们可以使用子查询和 JOIN 子句获得相同的结果集。例如,
-- SELECT DISTINCT only selects the unique combination of customer_id and first_name
-- join the Customers and Orders tables and select the rows where their customer_id values match
-- result set contains customer_id and first_name of customers who made an order
SELECT DISTINCT Customers.customer_id, Customers.first_name
FROM Customers
INNER JOIN Orders
ON Customers.customer_id = Orders.customer_id
ORDER BY Customers.customer_id;上述查询的结果集将与下面的查询结果集相同
-- display the distinct customer ids and first names
-- of customers who made an order using a subquery
SELECT customer_id, first_name
FROM Customers
WHERE customer_id IN (
SELECT customer_id
FROM Orders
);注意: 只要可能,我们都应该使用 JOIN 子句而不是子查询。这是因为 JOIN 的执行速度比子查询更优化。
另请阅读