SQL COUNT() 函数返回查询返回的记录数。
示例
-- returns the count of rows in the Orders table
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM Orders;这里,上面的 SQL 命令返回 Orders 表中的行数。
COUNT() 语法
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM table;这里,
COUNT()是计算表中行数的函数。table是表的名称。
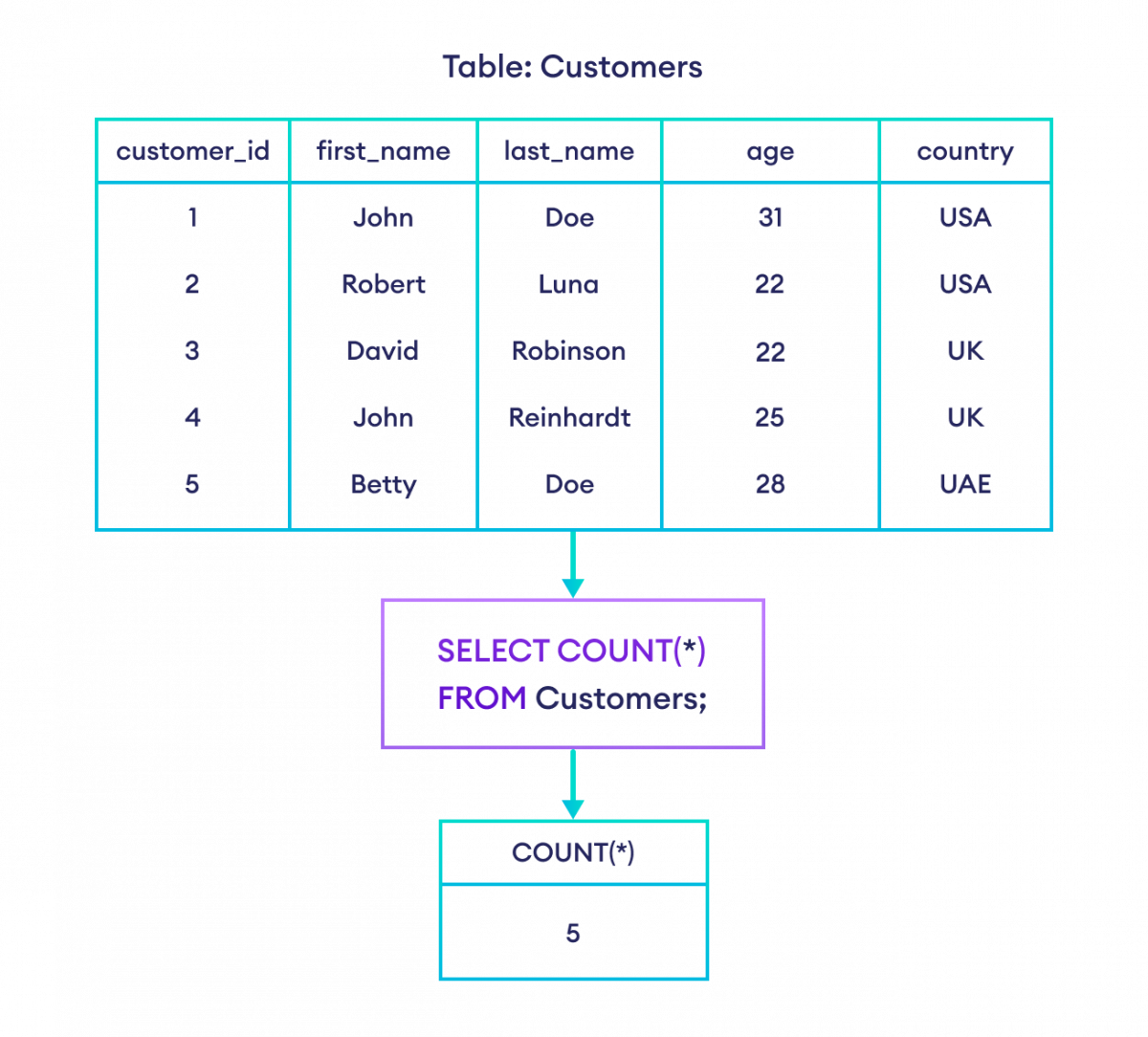
示例:SQL COUNT()
--returns the number of rows in the Customers table
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM Customers;这里,上面的 SQL 命令计算并返回 Customers 表中的行数。
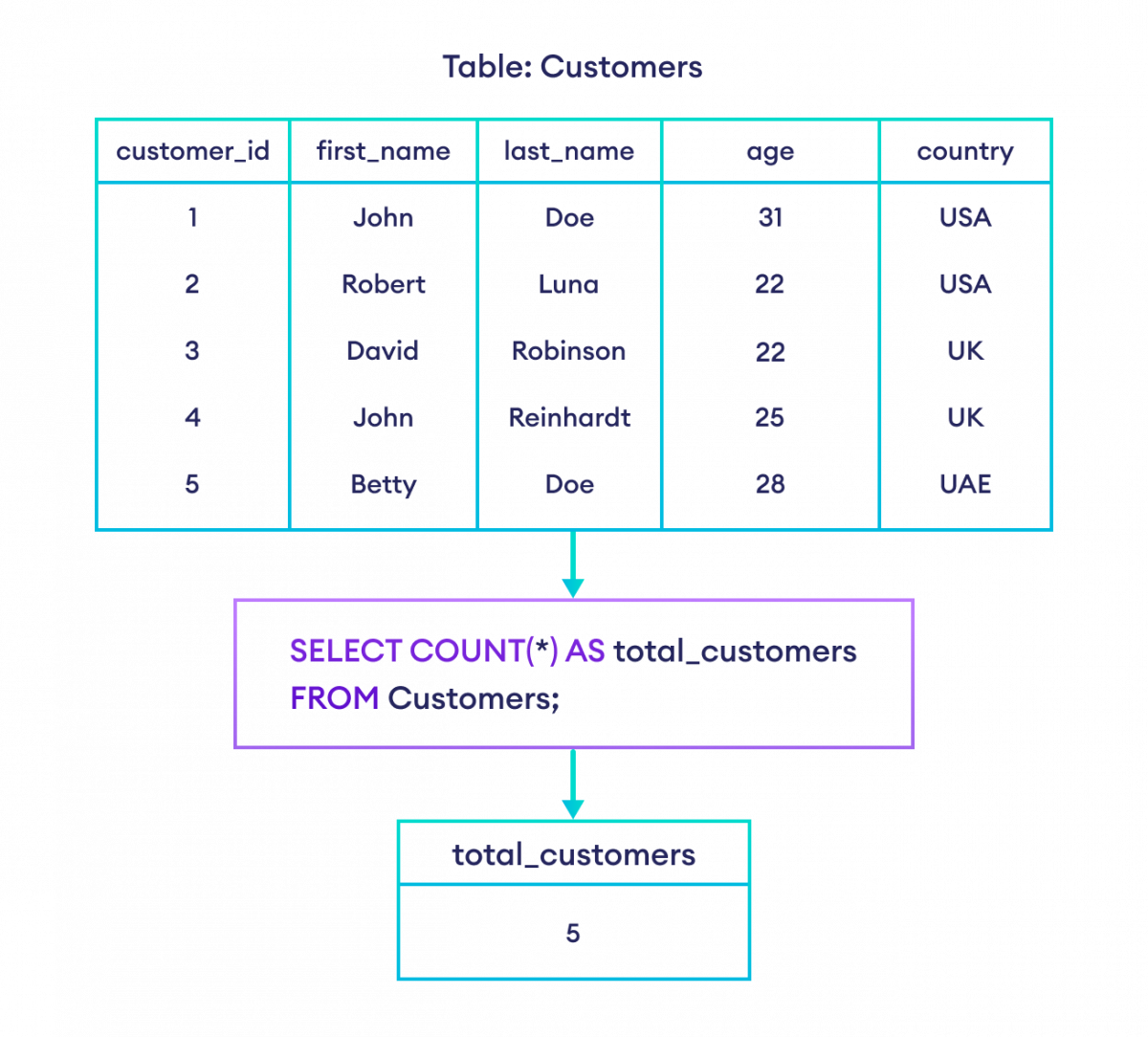
可以使用 AS 关键字为输出字段指定自定义名称。例如,
--return the count of rows from the customers table as total_customers
SELECT COUNT(*) AS total_customers
FROM Customers;这里,结果集中字段名 COUNT(*) 被 total_customers 替换。
示例:指定要计数的列
我们也可以在 COUNT() 中指定列名,只计算该特定列中的行。
让我们看一个例子。
--returns the count of non-null values in the age column
SELECT COUNT(age)
FROM Customers;这里,上面的 SQL 查询返回 age 列中非空值的数量。
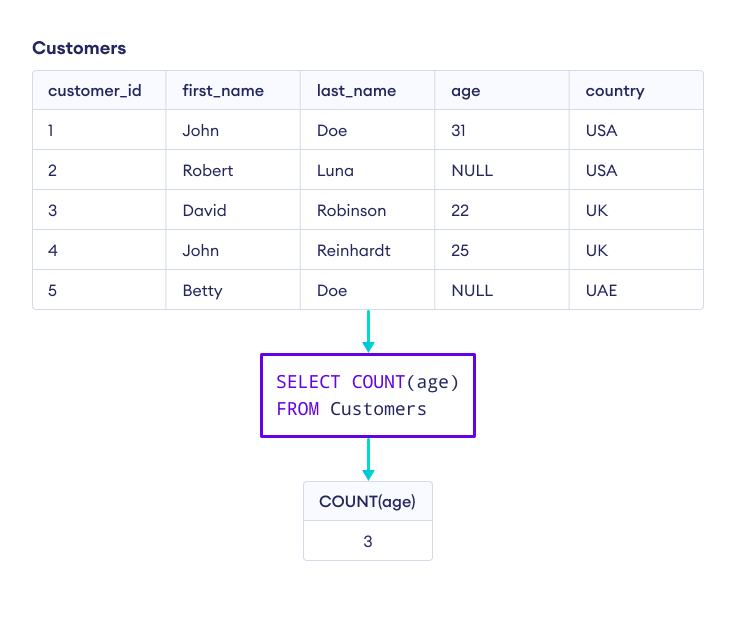
这里,当我们指定列名而不是 * 时,NULL 值不包含在计数中。
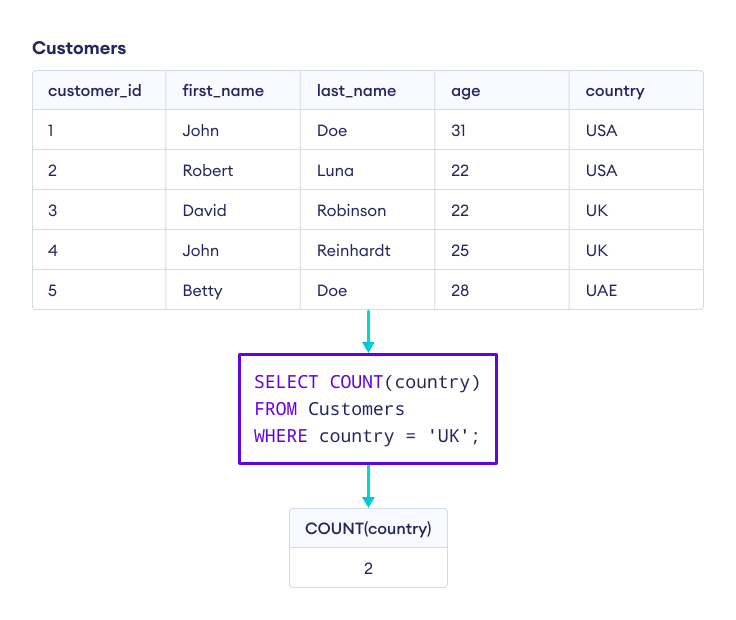
带 WHERE 的 COUNT()
我们可以使用带 WHERE 的 COUNT() 来计算匹配给定值的行。
-- count of customers who live in the UK
SELECT COUNT(country)
FROM Customers
WHERE country = 'UK';这里,SQL 命令返回国家为 UK 的客户数量。
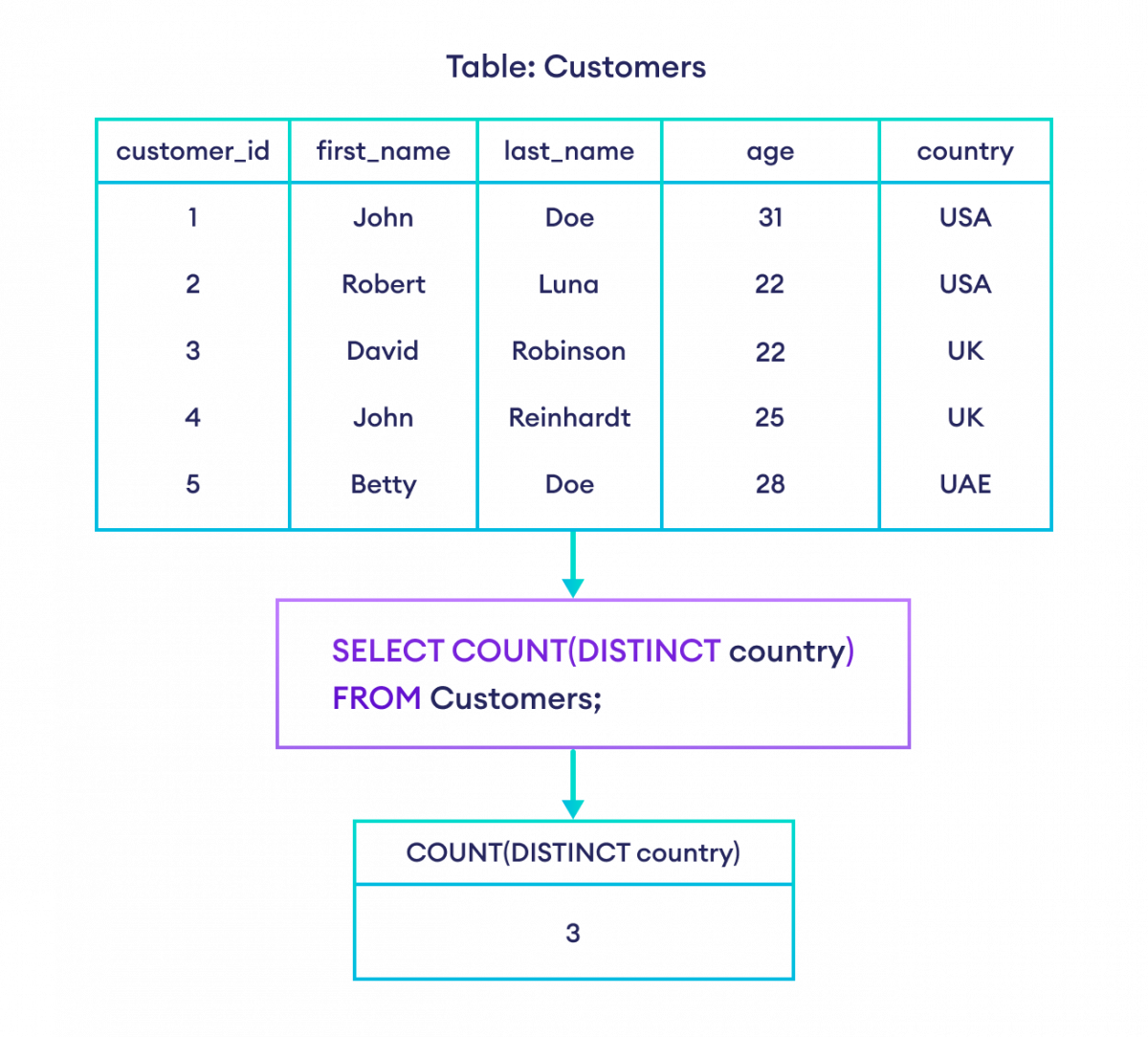
带 DISTINCT 的 COUNT()
如果我们需要计算唯一行的数量,可以使用带 DISTINCT 子句的 COUNT() 函数。例如,
-- count the unique countries in Customers table
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT country)
FROM Customers;这里,SQL 命令返回唯一国家的数量。
更多关于 SQL COUNT() 的信息
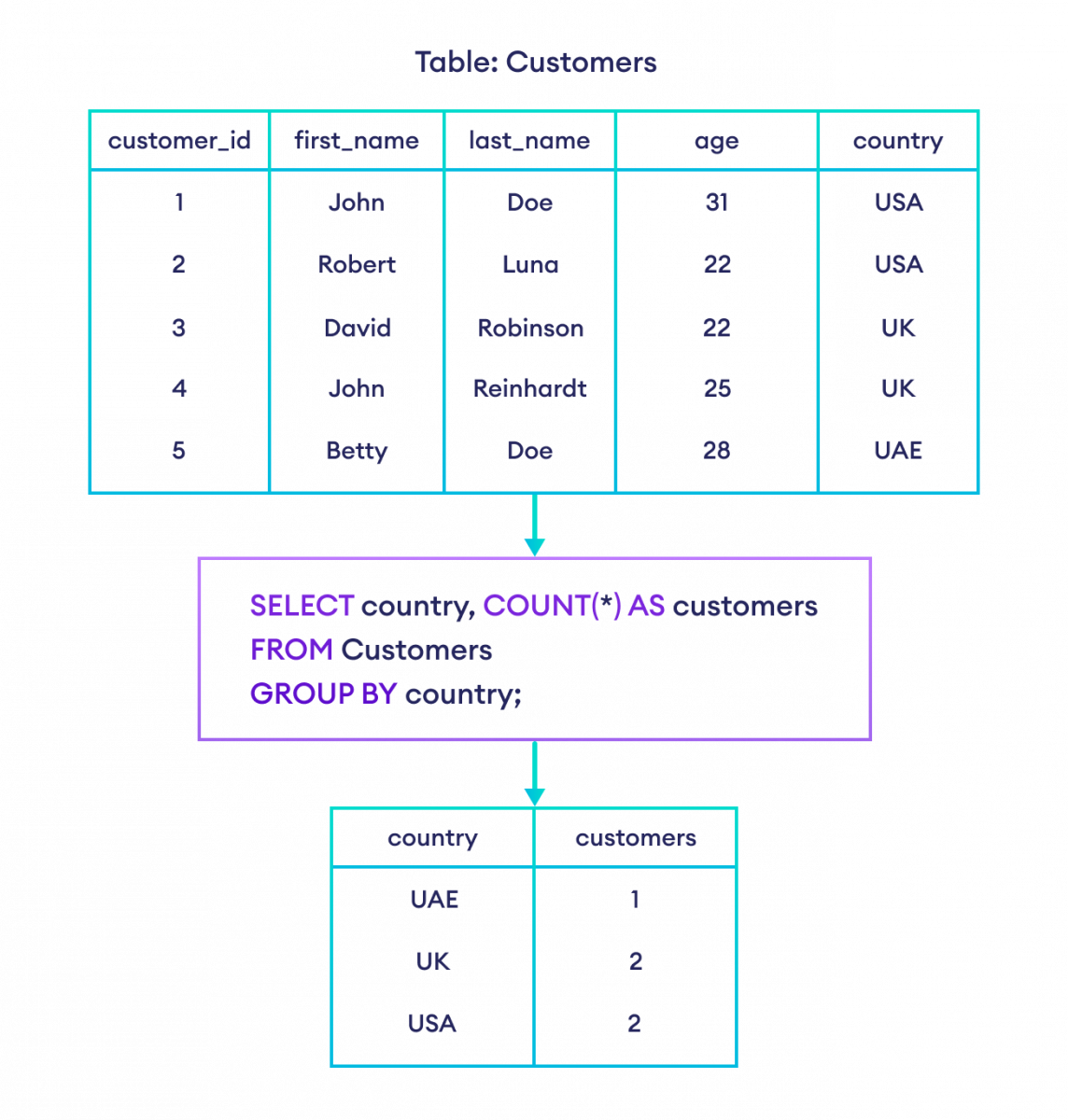
COUNT() 函数可以与 GROUP BY 子句一起使用,以计算具有相似值的行。例如,
-- count the number of customers in each country
SELECT country, COUNT(*) AS customers
FROM Customers
GROUP BY country;这里,SQL 命令返回每个国家/地区的客户数量。
我们可以像这样使用带 HAVING 子句的 COUNT()
--count the number of rows by country and return the results for count greater than one
SELECT COUNT(customer_id), country
FROM Customers
GROUP BY country
HAVING COUNT(customer_id) > 1;这里,SQL 命令
- 按 country 分组计算行数
- 如果它们的计数大于1,则返回结果集
另请阅读