SQL SELECT 语句用于从数据库表中选择(检索)数据。
示例
-- select first_name from Customers table
SELECT first_name
FROM Customers;上述 SQL 查询从 `Customers` 表中选择所有客户的 `first_name`。
SQL SELECT 语法
SQL `SELECT` 语句的语法是
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table;这里,
- `column1, column2, ...` 是表中的列
- `table` 是我们从中选择数据的表名
例如,
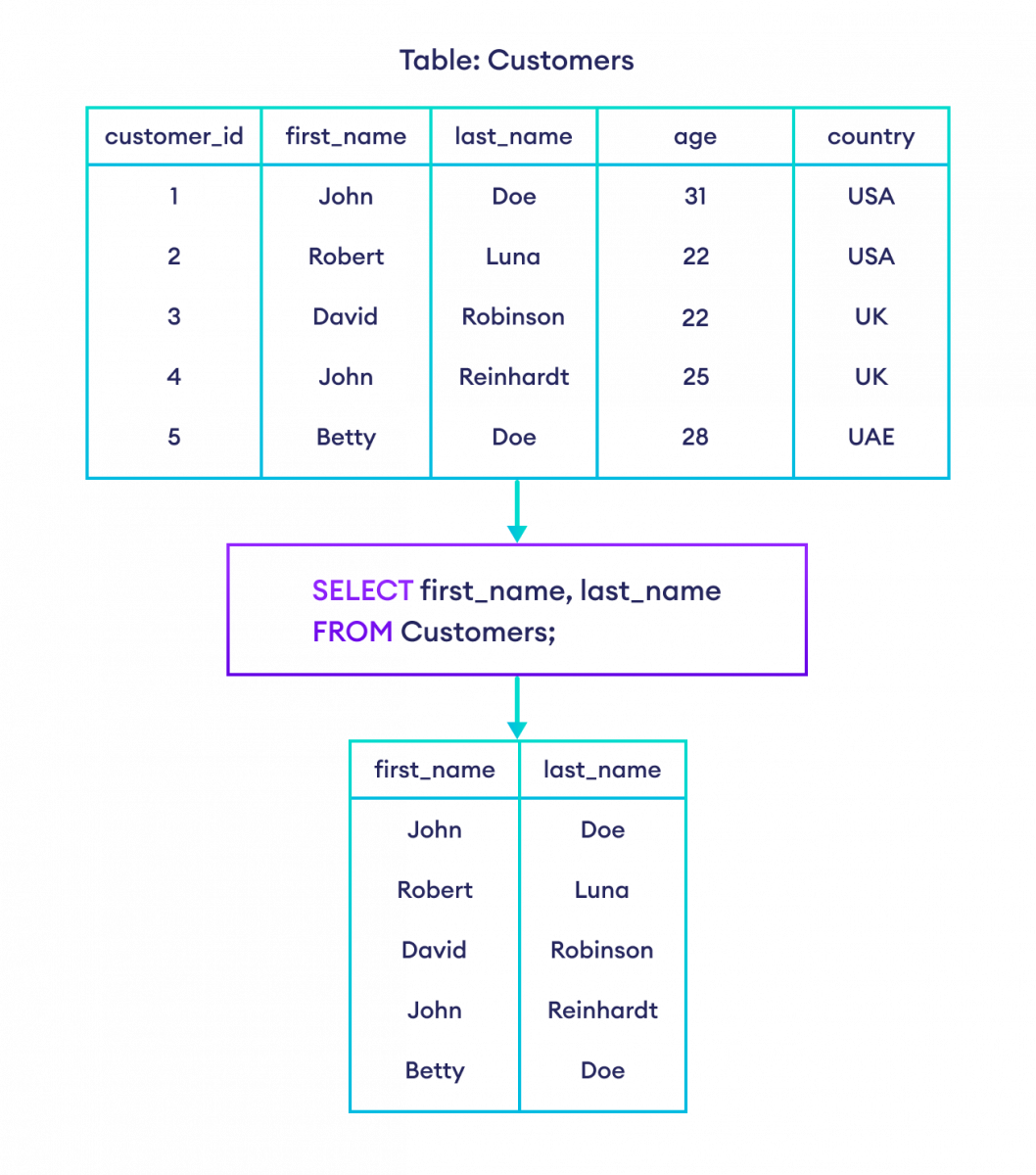
-- select first_name and last_name columns from Customers table
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM Customers;这里,SQL 命令选择 `Customers` 表中所有客户的 first_name 和 last_name。
SQL SELECT ALL
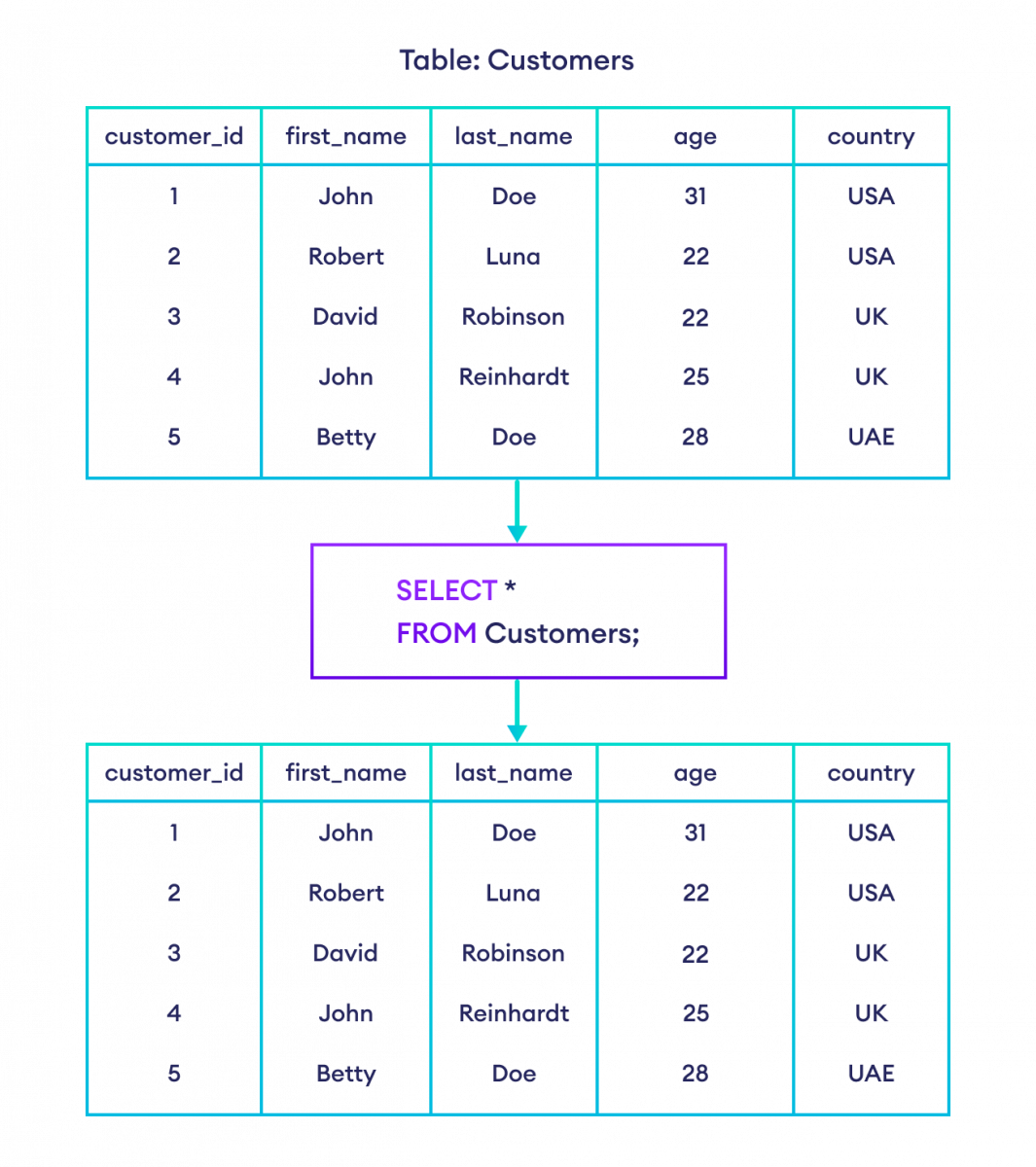
要选择数据库表中的所有列,我们使用 `*` 字符。例如,
-- select all columns from Customers table
SELECT *
FROM Customers;这里,SQL 命令选择 Customers 表中的所有列。
SQL SELECT WHERE 子句
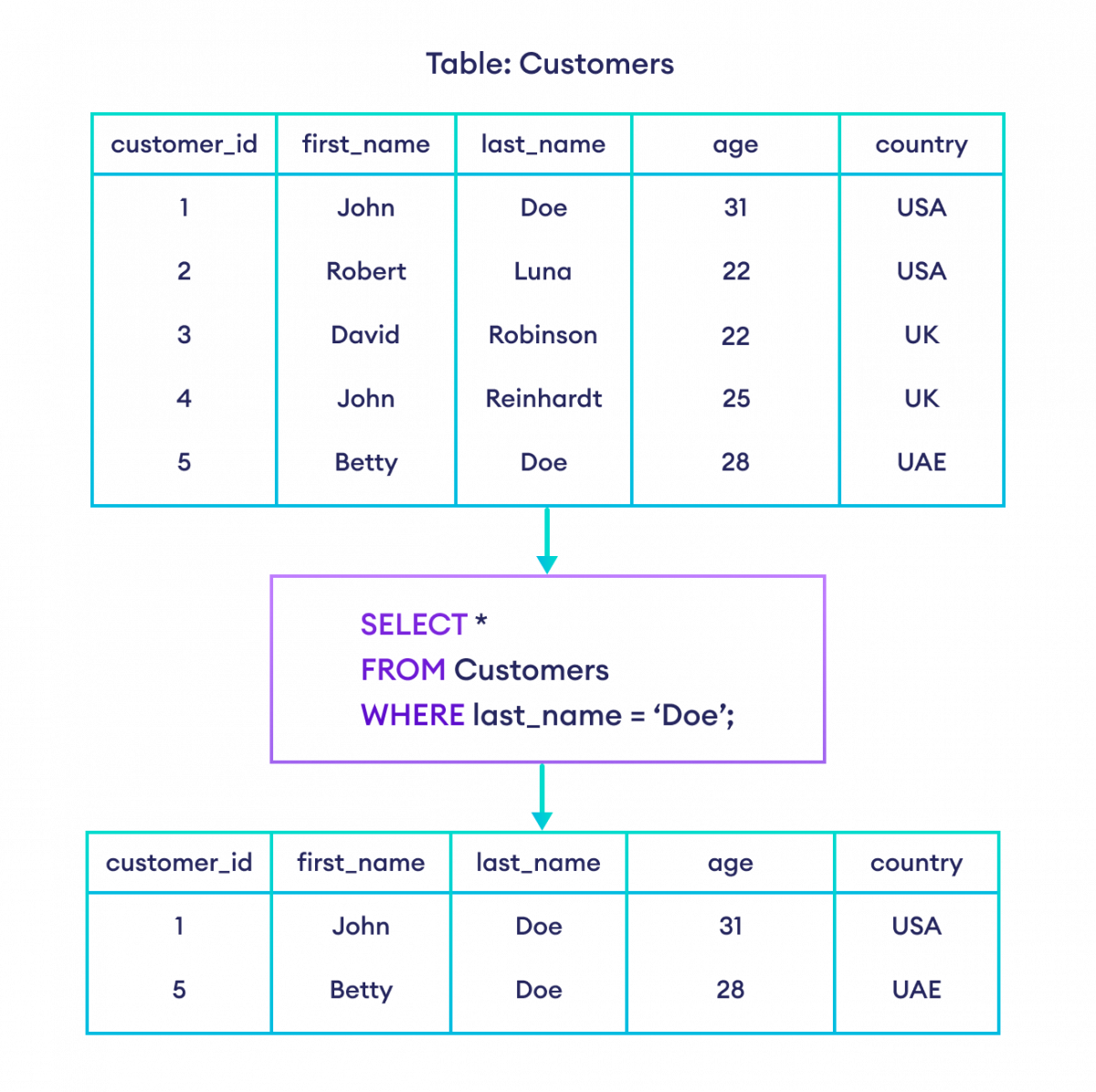
一个 `SELECT` 语句可以包含一个可选的 `WHERE` 子句。`WHERE` 子句允许我们从数据库表中获取符合指定条件(或多个条件)的记录。例如,
-- select all columns from the customers table with last_name 'Doe'
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE last_name = 'Doe';这里,SQL 命令从 Customers 表中选择所有 last_name 为 **Doe** 的客户。
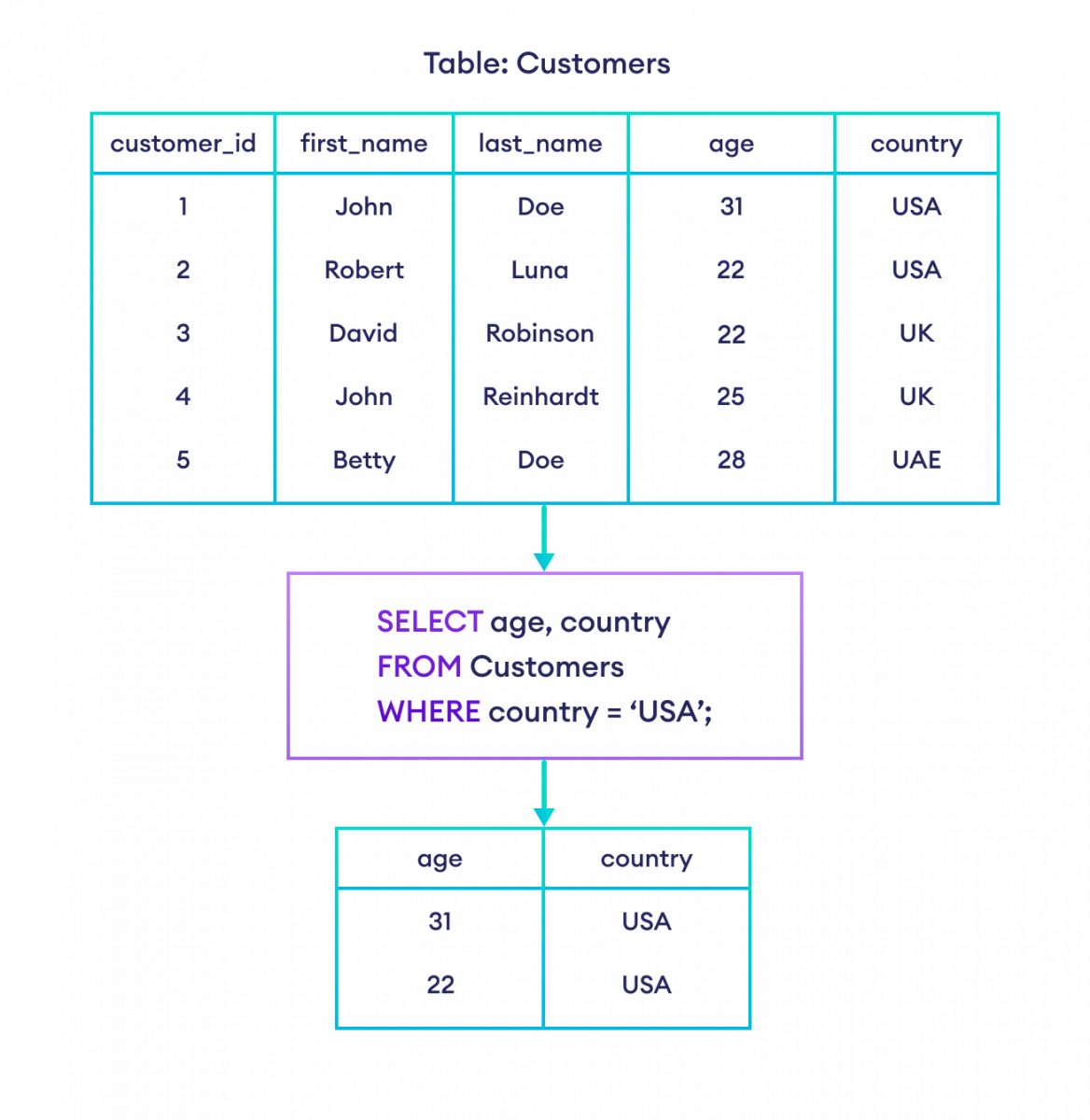
让我们看另一个例子。
-- select age and country columns from customers table where the country is 'USA'
SELECT age, country
FROM Customers
WHERE country = 'USA';这里,SQL 命令选择所有 `country` 为 **USA** 的客户的 `age` 和 `country` 列。
我们还可以将 `WHERE` 子句与 UPDATE 语句一起使用,以编辑数据库表中现有的行。
**注意:** 在 SQL 中,文本数据必须用单引号或双引号括起来,例如 ` 'USA' `。
SQL 运算符
`WHERE` 子句使用运算符来构建条件。一些常用的运算符是
1. 等于运算符 (=)
-- select all columns from Customers table with first name 'John'
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE first_name = 'John';上述 SQL 命令从 Customers 表中选择所有 first_name 为 **John** 的客户。
2. 大于 (>)
-- select all columns from Customers table with age greater than 25
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE age > 25;上述 SQL 命令从 Customers 表中选择所有 age **大于 25** 的客户。
3. AND 运算符 (AND)
-- select all columns from Customers table with last_name 'Doe' and country 'USA'
SELECT *
FROM Customers
WHERE last_name = 'Doe' AND country = 'USA';上述 SQL 命令从 Customers 表中选择所有 last_name 为 **Doe** 且 `country` 为 **USA** 的客户。
**注意:** 如果没有行满足 `WHERE` 子句条件,则返回一个空结果集。
要详细了解所有 SQL 运算符,请访问 SQL 运算符。
另请阅读