AS 关键字用于为列或表指定临时名称,该名称可在以后用于标识该列或表。
示例
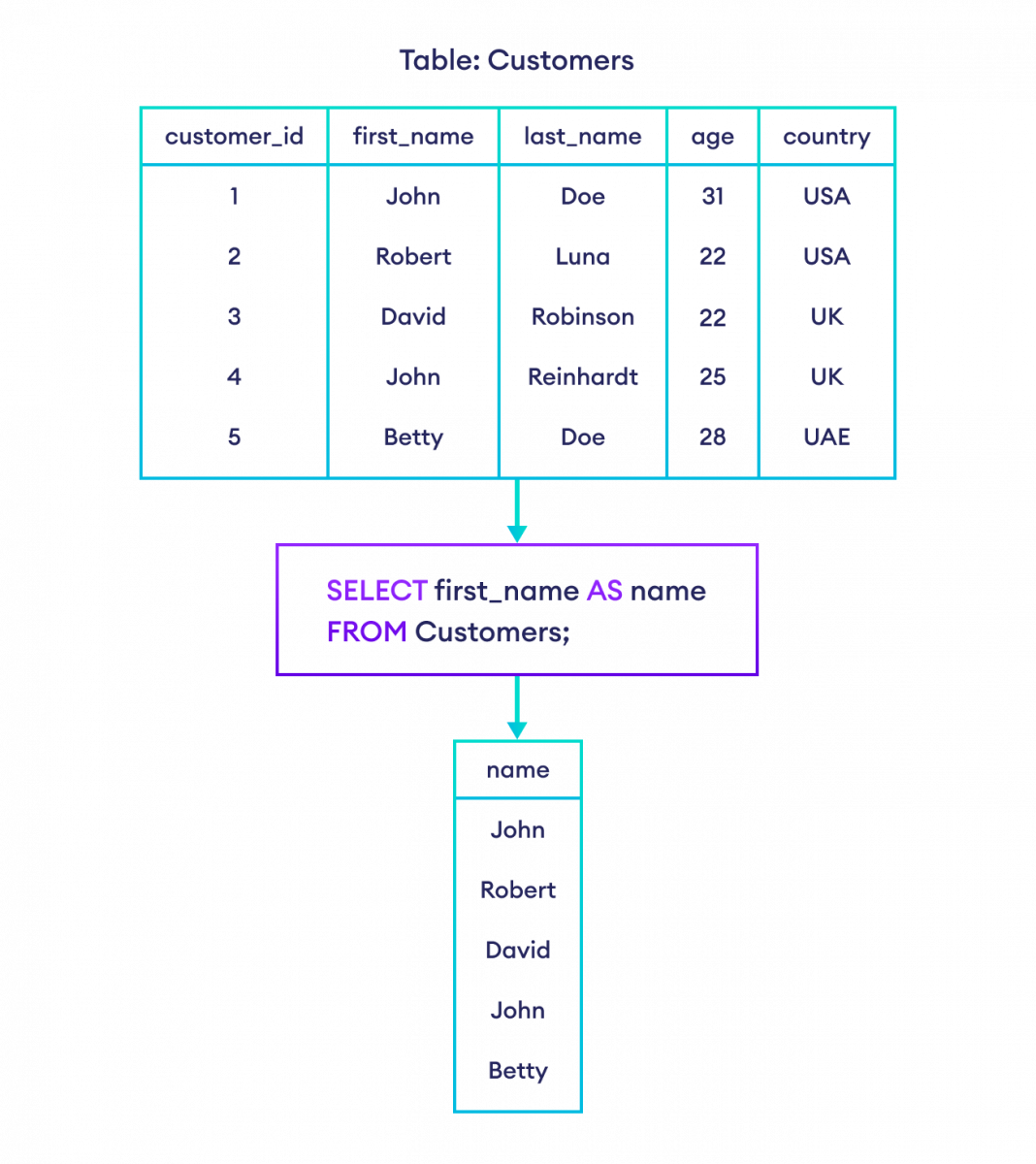
SELECT first_name AS name
FROM Customers;在这里,SQL 命令从 Customers 表中选择 first_name 列。但是,结果集中的列名被更改为 name。
SQL AS 别名语法
SQL AS 命令的语法是
SELECT column_1 AS alias_1,
column_2 AS alias_2,
... ...column_n AS alias_n
FROM table_name;这里,
column_1, column_2,...column_n是表列alias_1, alias_2,...alias_n是表列的别名
例如,
SELECT first_name AS name
FROM Customers;在这里,SQL 命令选择 Customers 的 first_name 列。但是,结果集中的列名将更改为 name。
SQL AS 包含多个列
我们还可以将别名与多个列一起使用。
例如,
SELECT customer_id AS cid, first_name AS name
FROM Customers;在这里,SQL 命令选择 customer_id 作为 cid,first_name 作为 name。
SQL AS 包含表达式
我们可以使用 CONCAT() 函数将多个列的数据合并并表示在单个列中。例如,
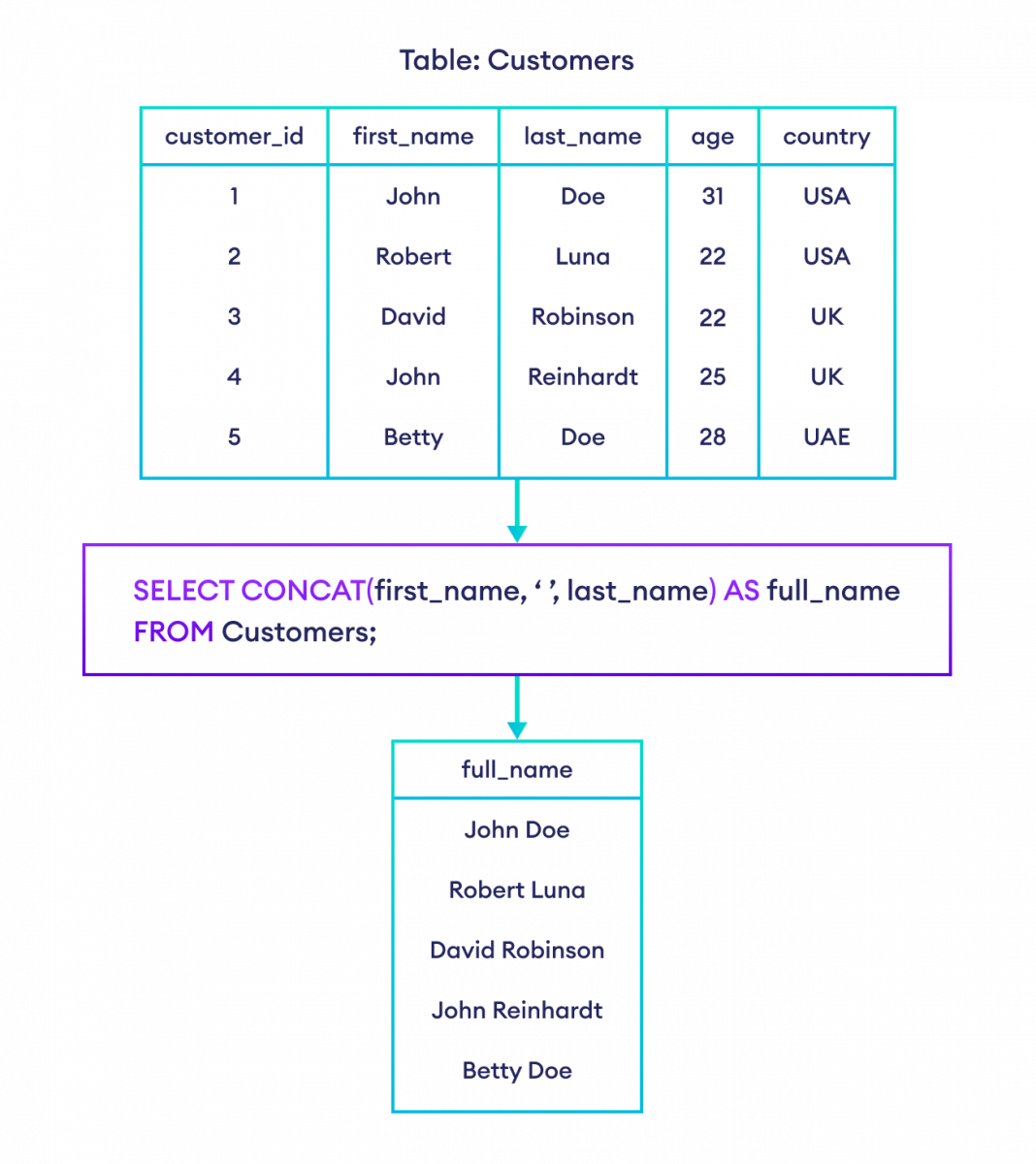
SELECT CONCAT(first_name, ' ', last_name) AS full_name
FROM Customers;在这里,SQL 命令选择 first_name 和 last_name。并且,结果集中的列名将是 full_name。
但是,由于我们的在线 SQL 编辑器使用 SQLite 数据库,因此不支持 CONCAT() 函数。在 SQLite 中,我们需要使用 || 运算符进行连接。
例如,这是一个等效的代码,它将在我们的 SQL 编辑器中运行。
-- concatenate first_name, empty space, and last_name
-- into a single column named full_name in the result set
SELECT first_name || ' ' || last_name AS full_name
FROM Customers;在这里,SQL 命令将在结果集中将 first_name 和 last_name 列连接为 full_name。
请注意,我们还在 first_name 和 last_name 之间连接了一个空字符串 ' '。这确保了这些列中的数据在结果集中用空格分隔。
更多 SQL AS 示例
在使用函数时,使用 AS 创建别名是一种常见做法。例如,
-- AS with functions
SELECT COUNT(*) AS total_customers
FROM Customers;在这里,SQL 命令计算总行数并将该值表示为 total_customers 属性。
此命令的结果集将有一个 total_customers 列。
AS 关键字也可以用于为表指定临时名称。例如,
-- AS table alias
SELECT cu.first_name, cu.last_name
FROM Customers AS cu;在这里,SQL 命令暂时将 Customers 表命名为 cu,并从 cu 中选择 first_name 和 last_name。
此命令的结果集将包含 first_name 和 last_name 作为列。
在使用 JOIN 时,我们可以使用 AS 别名与表名一起,使我们的代码段更短更整洁。例如,
SELECT C.customer_id AS cid, C.first_name AS name, O.amount
FROM Customers AS C
JOIN Orders AS O
ON C.customer_id = O.customer_id;在这里,SQL 命令暂时将 Customers 表命名为 C,将 Orders 表命名为 O,并从 C 中选择 customer_id,从 C 中选择 first_name,以及从 O 中选择 amount。
此命令的结果集将包含 cid、name 和 amount 列。
要了解更多信息,请访问 SQL JOIN。
另请阅读