在编程中,循环用于重复执行一段代码,直到满足指定的条件。
C 编程有三种类型的循环:
- for 循环
- while 循环
- do...while 循环
在本教程中,我们将学习 `for` 循环。在下一篇教程中,我们将学习 `while` 和 `do...while` 循环。
for 循环
for 循环的语法是:
for (initializationStatement; testExpression; updateStatement)
{
// statements inside the body of loop
}for 循环如何工作?
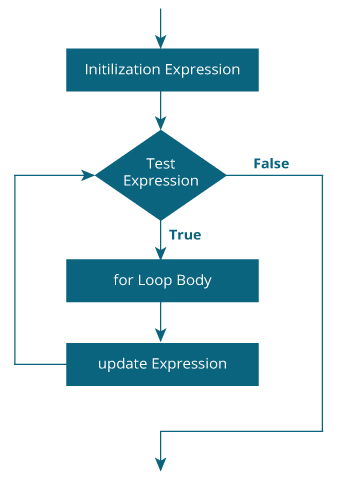
- 初始化语句只执行一次。
- 然后,对测试表达式进行求值。如果测试表达式求值为 false,则终止 `for` 循环。
- 但是,如果测试表达式求值为 true,则执行 `for` 循环体内的语句,并更新更新语句。
- 再次对测试表达式进行求值。
这个过程一直持续到测试表达式为 false。当测试表达式为 false 时,循环终止。
要了解更多关于测试表达式(测试表达式何时为 true 和 false)的信息,请查看 关系 和 逻辑运算符。
for 循环流程图
示例 1:for 循环
// Print numbers from 1 to 10
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i;
for (i = 1; i < 11; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", i);
}
return 0;
}
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
- `i` 被初始化为 1。
- 对测试表达式 `i < 11` 进行求值。由于 1 小于 11 为 true,将执行 `for` 循环体。这将在屏幕上打印 **1**(`i` 的值)。
- 执行更新语句 `++i`。现在,`i` 的值将是 2。再次对测试表达式进行求值。由于为 true,将执行 `for` 循环体。这将在屏幕上打印 **2**(`i` 的值)。
- 再次执行更新语句 `++i` 并对测试表达式 `i < 11` 进行求值。这个过程一直持续到 `i` 变为 11。
- 当 `i` 变为 11 时,`i < 11` 将为 false,`for` 循环终止。
示例 2:for 循环
// Program to calculate the sum of first n natural numbers
// Positive integers 1,2,3...n are known as natural numbers
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num, count, sum = 0;
printf("Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
// for loop terminates when count exceeds num
for(count = 1; count <= num; ++count)
{
sum += count;
}
printf("Sum = %d", sum);
return 0;
}输出
Enter a positive integer: 10 Sum = 55
用户输入的值存储在变量 `num` 中。假设用户输入了 10。
将 `count` 初始化为 1 并对测试表达式进行求值。由于测试表达式 `count <= num`(1 小于等于 10)为 true,将执行 `for` 循环体,`sum` 的值将等于 1。
然后,执行更新语句 `++count`,`count` 将等于 2。再次对测试表达式进行求值。由于 2 也小于 10,测试表达式求值为 true,将执行 `for` 循环体。现在,`sum` 将等于 3。
这个过程一直持续,直到 `count` 达到 11,计算出总和。
当 `count` 为 11 时,对测试表达式求值为 0(false),循环终止。
然后,在屏幕上打印 `sum` 的值。
我们将在下一篇教程中学习 `while` 循环和 `do...while` 循环。
