循环会多次执行一段代码。但是,有时我们需要通过终止循环的执行或跳过一次迭代来改变循环的流程。
在这种情况下,我们使用 Rust 的 break 和 continue 来改变循环的正常执行。例如:
break- 终止循环continue- 跳过当前迭代,继续下一次迭代
Rust break
在 Rust 中,我们使用 break 关键字来终止任何循环的执行。例如:
while n < 10 {
break;
}在这里,while 循环将在遇到 break 关键字时结束,而不管循环条件 (n < 10) 是什么。
示例:Rust break
fn main() {
let mut number = 0;
// loop starts here
loop {
number += 1;
// condition to exit the loop
if number > 5 {
break;
}
println!("{}", number);
}
}输出
1 2 3 4 5
此程序使用 loop 表达式和 break 关键字打印前五个自然数。请注意 break 关键字的用法。
if number > 5 {
break;
}当 number 变量(在每次迭代中加 1)达到 6 时,if 条件求值为 false,我们使用 break 关键字退出 loop。
注意:用户需要自行定义循环退出的条件,否则循环可能会永远运行。您可以以类似的方式将 break 关键字与 while 或 for 循环一起使用。
break 关键字在 Rust 中的工作原理
Rust break 与嵌套循环
fn main() {
let mut i = 1;
// start of outer loop
while i <= 5 {
let mut j = 1;
// start of inner loop
while j <= 5 {
print!("*");
// condition to exit the inner loop
if j == 3 {
// terminate the inner loop
break;
}
j += 1;
}
println!("");
i += 1;
}
}输出
*** *** *** *** ***
在上面的示例中,我们在内部 while 循环的身体中使用了 break 关键字。
if j == 3 {
// terminate the inner loop
break;
}当计数器变量 j 的值达到 3 时,内部 while 循环终止。因此,我们在屏幕的每一行上只看到三颗星 (***) 被打印出来。
Rust continue
在 Rust 中,我们使用 continue 语句来跳过循环的当前迭代,并进行下一次迭代。例如:
while n < 10 {
if n == 5 {
continue;
}
}在这里,while 循环将在遇到 continue 关键字时跳过当前迭代,而不管循环条件 (n<10) 是什么。
示例:Rust continue
fn main() {
let mut number = 0;
while number < 5 {
number += 1;
// condition to skip the iteration
if number == 3 {
continue;
}
println!("{}", number);
}
}输出
1 2 4 5
在此示例中,我们使用 while 表达式打印自然数。请注意 continue 关键字的用法。
if number == 3 {
continue;
}在这里,当 number 变量等于 3 时,我们跳过迭代。因此,我们在输出中看不到 3。
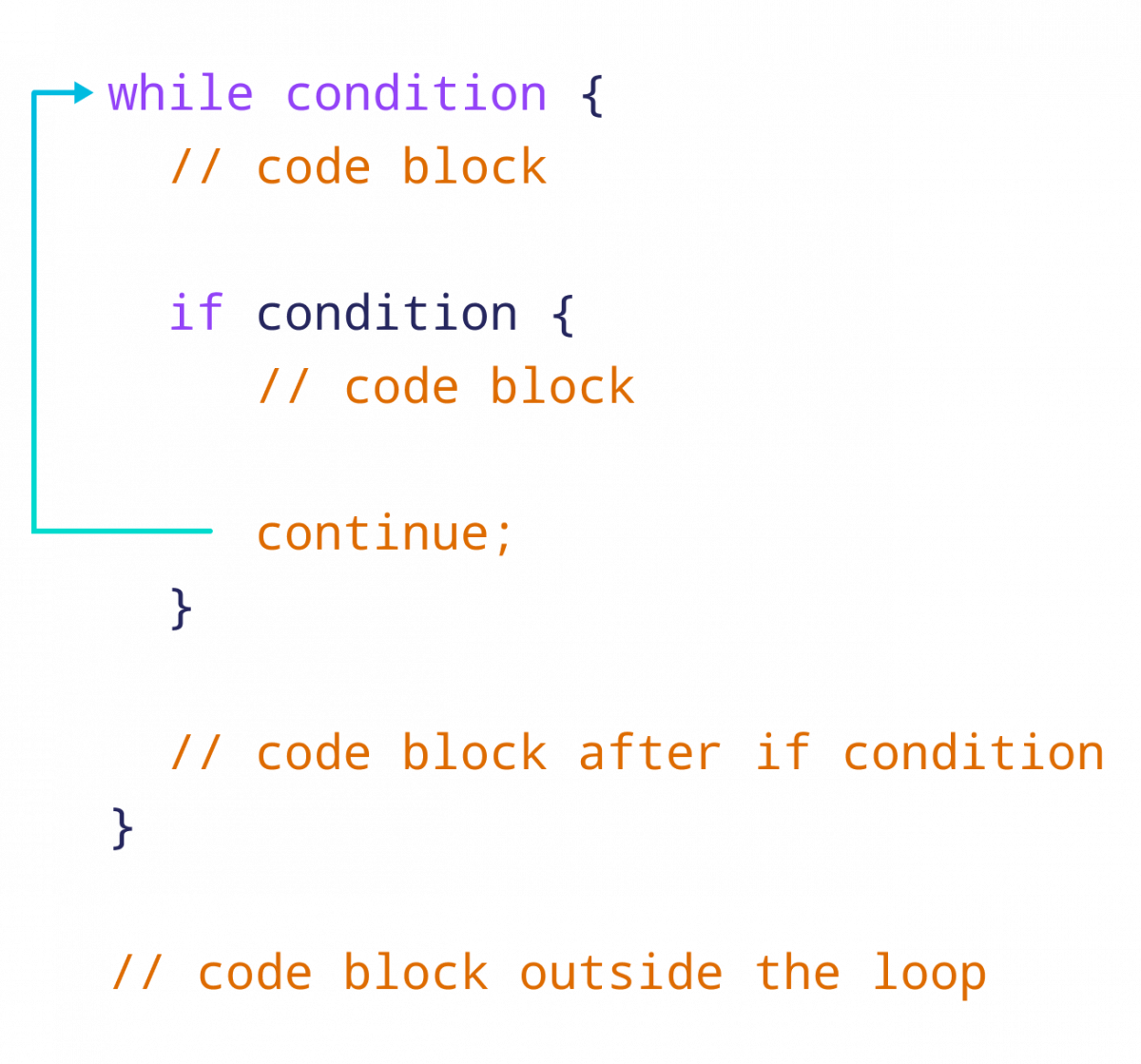
continue 关键字在 Rust 中的工作原理
Rust continue 与嵌套循环
fn main() {
let mut i = 1;
// start of outer loop
while i <= 5 {
let mut j = 1;
// start of inner loop
while j <= 5 {
j += 1;
// condition to skip iteration of the inner loop
if j == 3 {
// move to the next iteration of the inner loop
continue;
}
print!("*");
}
println!("");
i += 1;
}
}输出
**** **** **** **** ****
在这里,我们使用 continue 关键字跳过内部 while 循环的一次迭代。
if j == 3 {
// move to the next iteration of the inner loop
continue;
}当计数器变量 j 的值达到 3 时,我们跳过当前的内部 while 迭代,并且 print!("*") 语句被跳过。因此,我们在屏幕的每一行上只看到四颗星 (****) 被打印出来。
break 和 continue 与 loop
我们也可以一起使用 break 和 continue 来控制程序的流程。例如:
fn main() {
let mut number = 0;
loop {
number += 1;
// condition to skip the iteration
if number == 3 {
continue;
}
// condition to exit the loop
if number > 5 {
break;
}
println!("{}", number);
}
}输出
1 2 4 5
在这里,continue 关键字,
if number == 3 {
continue;
}当 number 变量的值为 3 时,跳过迭代。
同样,break 关键字,
if number > 5 {
break;
}如果 number 变量的值大于 5,则终止循环。