Java 中的 super 关键字用于子类中访问超类成员(属性、构造函数和方法)。
在学习 super 关键字之前,请确保了解 Java 继承。
super 关键字的用法
- 调用在子类中被重写(overridden)的超类方法。
- 如果子类和超类拥有同名属性,则访问超类的属性。
- 在子类构造函数中显式调用超类的无参(默认)或带参构造函数。
让我们逐一了解这些用法。
1. 访问超类的重写方法
如果在超类和子类中都定义了同名方法,子类中的方法会重写超类中的方法。这称为方法重写。
示例 1:方法重写
class Animal {
// overridden method
public void display(){
System.out.println("I am an animal");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
// overriding method
@Override
public void display(){
System.out.println("I am a dog");
}
public void printMessage(){
display();
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog1 = new Dog();
dog1.printMessage();
}
}输出
I am a dog
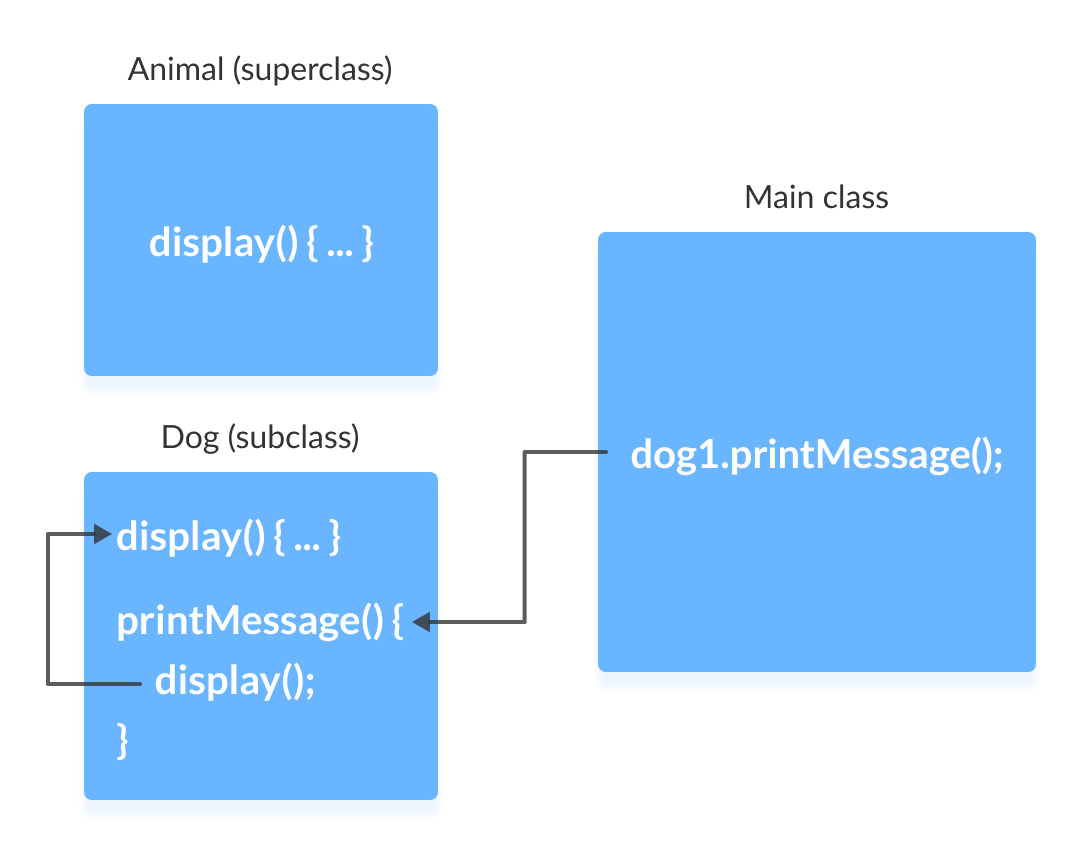
在这个示例中,通过创建 Dog 类的对象 dog1,我们可以调用其 printMessage() 方法,该方法随后执行 display() 语句。
由于 display() 在两个类中都已定义,子类 Dog 的方法会重写超类 Animal 的方法。因此,调用的是子类的 display()。
如果需要调用超类中被重写的方法怎么办?
如果我们想调用超类 Animal 中被重写的 display() 方法,可以使用 super.display()。
示例 2:使用 super 调用超类方法
class Animal {
// overridden method
public void display(){
System.out.println("I am an animal");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
// overriding method
@Override
public void display(){
System.out.println("I am a dog");
}
public void printMessage(){
// this calls overriding method
display();
// this calls overridden method
super.display();
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog1 = new Dog();
dog1.printMessage();
}
}输出
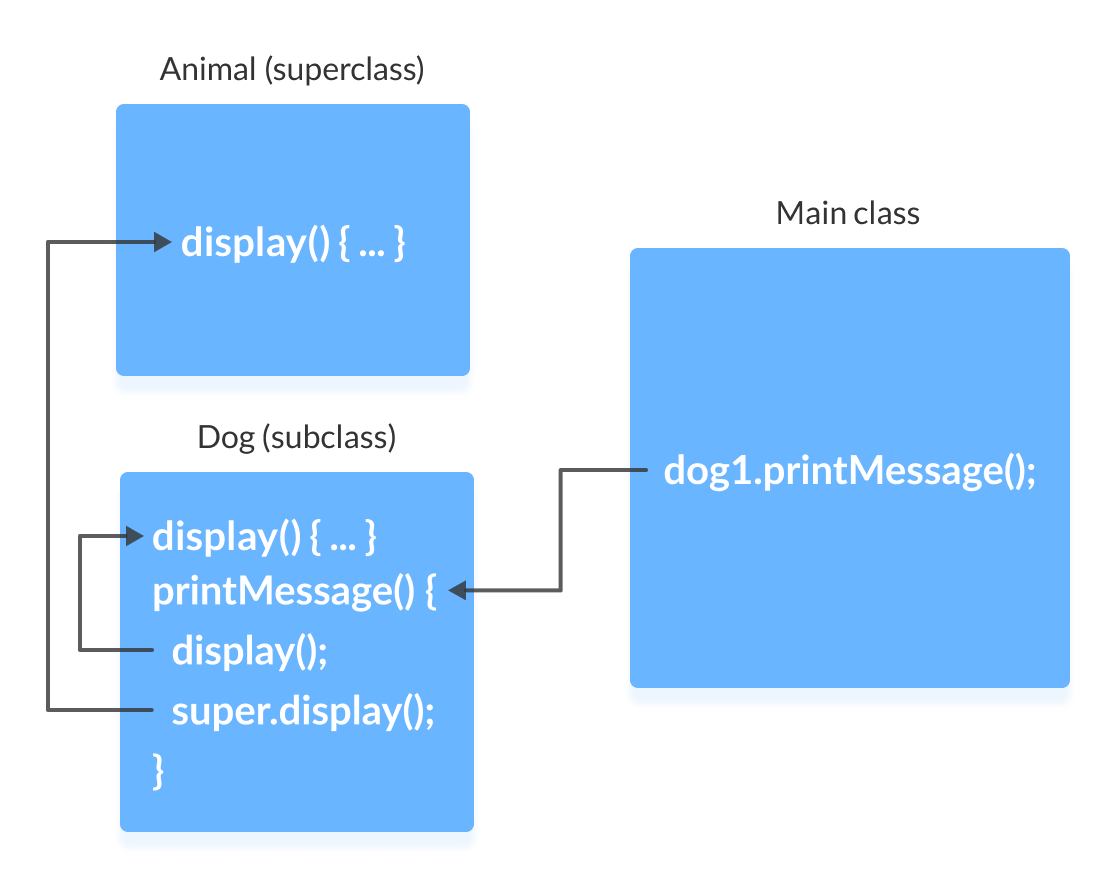
I am a dog I am an animal
下面是上述程序的工作原理。
2. 访问超类的属性
超类和子类可以拥有同名的属性。我们使用 super 关键字来访问超类的属性。
示例 3:访问超类属性
class Animal {
protected String type="animal";
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public String type="mammal";
public void printType() {
System.out.println("I am a " + type);
System.out.println("I am an " + super.type);
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog1 = new Dog();
dog1.printType();
}
}输出:
I am a mammal I am an animal
在这个示例中,我们在超类 Animal 和子类 Dog 中都定义了相同的实例字段 type。
然后,我们创建了 Dog 类的对象 dog1。接着,使用此对象调用 printType() 方法。
在 printType() 函数内部,
- type 指的是子类 Dog 的属性。
- super.type 指的是超类 Animal 的属性。
因此,System.out.println("I am a " + type); 打印 I am a mammal。而 System.out.println("I am an " + super.type); 打印 I am an animal。
3. 使用 super() 访问超类构造函数
我们知道,当创建一个类的对象时,它的默认构造函数会被自动调用。
为了在子类构造函数中显式调用超类构造函数,我们使用 super()。这是 super 关键字的一种特殊形式。
super() 只能在子类构造函数中使用,并且必须是第一条语句。
示例 4:使用 super()
class Animal {
// default or no-arg constructor of class Animal
Animal() {
System.out.println("I am an animal");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
// default or no-arg constructor of class Dog
Dog() {
// calling default constructor of the superclass
super();
System.out.println("I am a dog");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog1 = new Dog();
}
}输出
I am an animal I am a dog
在这里,当创建 Dog 类的对象 dog1 时,它会自动调用该类的默认构造函数或无参构造函数。
在子类构造函数中,super() 语句会调用超类的构造函数并执行其中的语句。因此,我们得到输出 I am an animal。
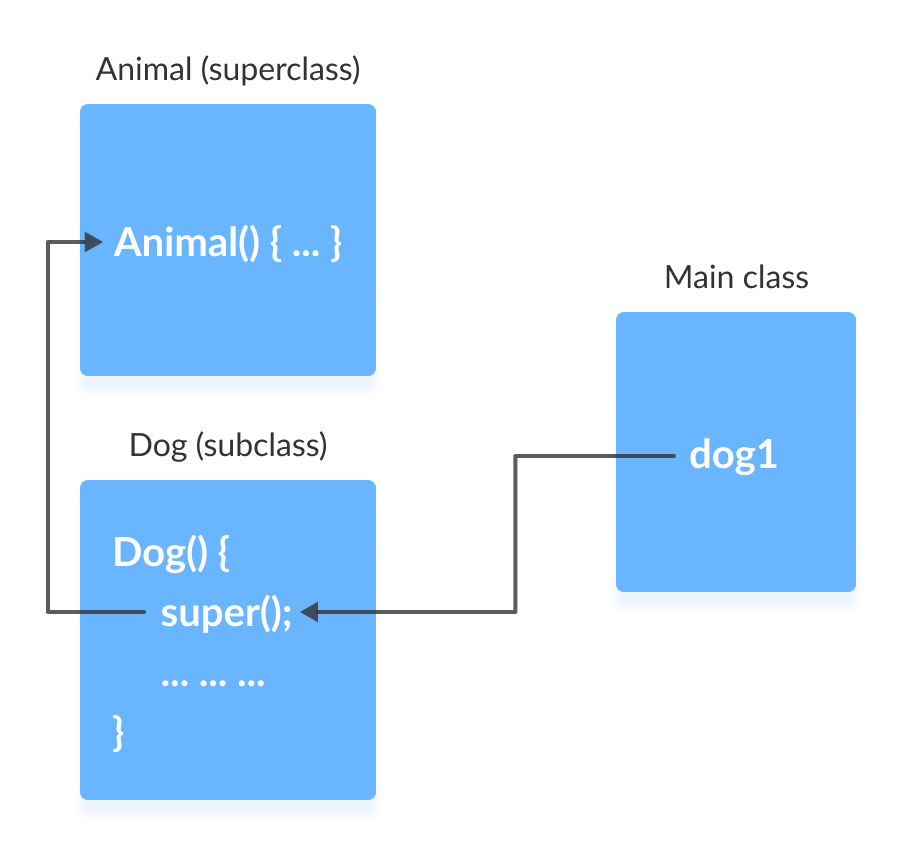
程序的流程然后返回到子类构造函数,并执行剩余的语句。因此,会打印 I am a dog。
然而,使用 super() 不是强制性的。即使在子类构造函数中没有使用 super(),编译器也会隐式调用超类的默认构造函数。
既然编译器会自动调用 super(),为什么还要编写冗余的代码呢?
如果需要从子类构造函数调用超类的带参构造函数(接受参数的构造函数),则必须使用 super()。
带参的 super() 必须始终是子类构造函数体中的第一条语句,否则会出现编译错误。
示例 5:使用 super() 调用带参构造函数
class Animal {
// default or no-arg constructor
Animal() {
System.out.println("I am an animal");
}
// parameterized constructor
Animal(String type) {
System.out.println("Type: "+type);
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
// default constructor
Dog() {
// calling parameterized constructor of the superclass
super("Animal");
System.out.println("I am a dog");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog1 = new Dog();
}
}输出
Type: Animal I am a dog
编译器可以自动调用无参构造函数。但是,它无法调用带参构造函数。
如果要调用带参构造函数,我们需要在子类构造函数中显式定义它。
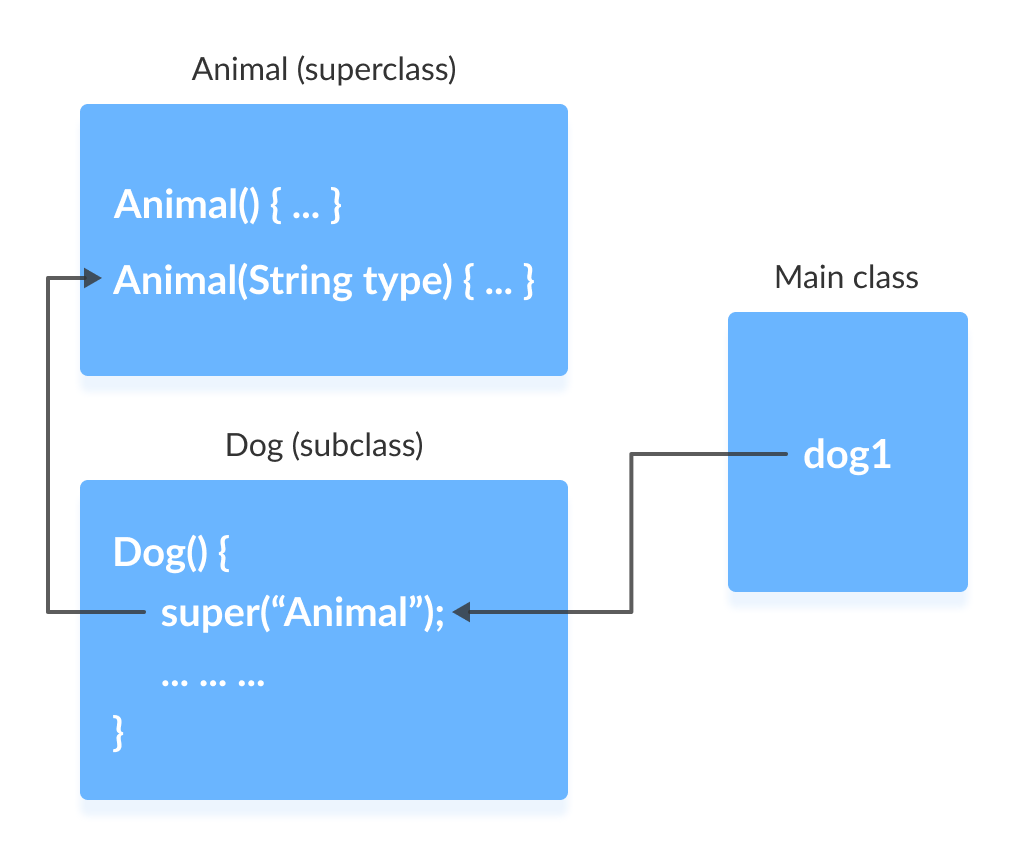
请注意,在上面的示例中,我们显式调用了带参构造函数 super("Animal")。在这种情况下,编译器不会调用超类的默认构造函数。