Java 集合框架中的 Set 接口提供了数学集合的特性。它扩展了 Collection 接口。
与 List 接口不同,集合不能包含重复的元素。
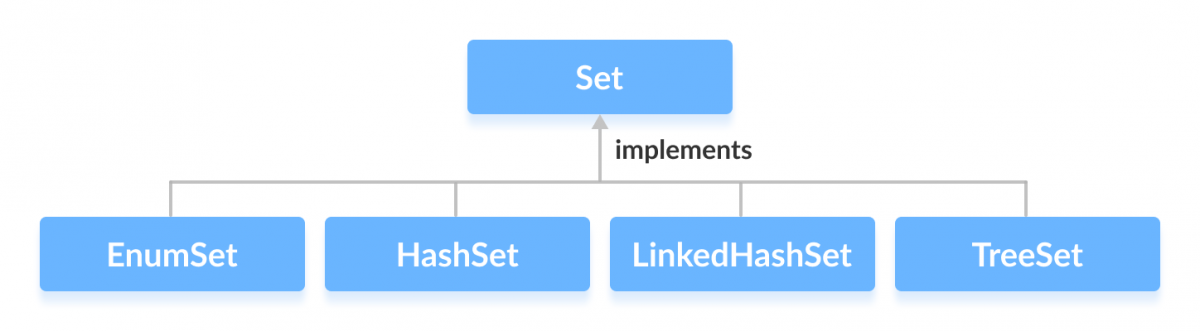
实现 Set 的类
由于 Set 是一个接口,我们无法从中创建对象。
为了使用 Set 接口的功能,我们可以使用这些类
这些类定义在 Collections 框架中,并实现 Set 接口。
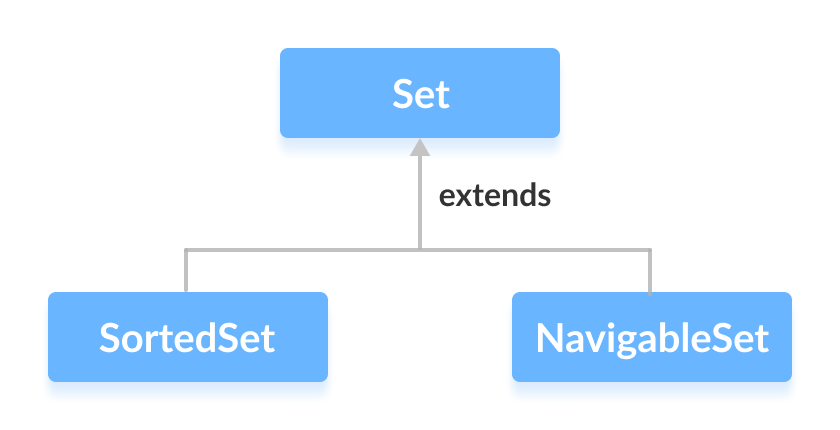
扩展 Set 的接口
Set 接口还被这些子接口扩展
如何使用 Set?
在 Java 中,我们必须导入 java.util.Set 包才能使用 Set。
// Set implementation using HashSet
Set<String> animals = new HashSet<>();在这里,我们创建了一个名为 animals 的 Set。我们使用 HashSet 类来实现 Set 接口。
Set 的方法
Set 接口包含 Collection 接口的所有方法。这是因为 Collection 是 Set 的父接口。
Set 接口中也包含一些常用的 Collection 接口方法,例如
- add() - 将指定元素添加到集合中
- addAll() - 将指定集合的所有元素添加到集合中
- iterator() - 返回一个迭代器,可用于按顺序访问集合中的元素
- remove() - 从集合中移除指定元素
- removeAll() - 移除集合中存在于另一个指定集合中的所有元素
- retainAll() - 保留集合中也存在于另一个指定集合中的所有元素
- clear() - 移除集合中的所有元素
- size() - 返回集合的长度(元素数量)
- toArray() - 返回一个包含集合中所有元素的数组
- contains() - 如果集合包含指定元素,则返回
true - containsAll() - 如果集合包含指定集合的所有元素,则返回
true - hashCode() - 返回一个哈希码值(集合中元素的地址)
要了解 Set 接口的更多方法,请访问 Java Set(官方Java文档)。
集合运算
Java Set 接口允许我们执行基本的数学集合操作,如并集、交集和子集。
- 并集 - 要获取两个集合 x 和 y 的并集,我们可以使用
x.addAll(y) - 交集 - 要获取两个集合 x 和 y 的交集,我们可以使用
x.retainAll(y) - 子集 - 要检查 x 是否是 y 的子集,我们可以使用
y.containsAll(x)
Set 接口的实现
1. 实现 HashSet 类
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.HashSet;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a set using the HashSet class
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<>();
// Add elements to the set1
set1.add(2);
set1.add(3);
System.out.println("Set1: " + set1);
// Creating another set using the HashSet class
Set<Integer> set2 = new HashSet<>();
// Add elements
set2.add(1);
set2.add(2);
System.out.println("Set2: " + set2);
// Union of two sets
set2.addAll(set1);
System.out.println("Union is: " + set2);
}
}输出
Set1: [2, 3] Set2: [1, 2] Union is: [1, 2, 3]
2. 实现 TreeSet 类
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a set using the TreeSet class
Set<Integer> numbers = new TreeSet<>();
// Add elements to the set
numbers.add(2);
numbers.add(3);
numbers.add(1);
System.out.println("Set using TreeSet: " + numbers);
// Access Elements using iterator()
System.out.print("Accessing elements using iterator(): ");
Iterator<Integer> iterate = numbers.iterator();
while(iterate.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterate.next());
System.out.print(", ");
}
}
}输出
Set using TreeSet: [1, 2, 3] Accessing elements using iterator(): 1, 2, 3,
现在我们知道了 Set 是什么,我们将在接下来的教程中介绍它在 EnumSet、HashSet、LinkedHashSet 和 TreeSet 等类中的实现。