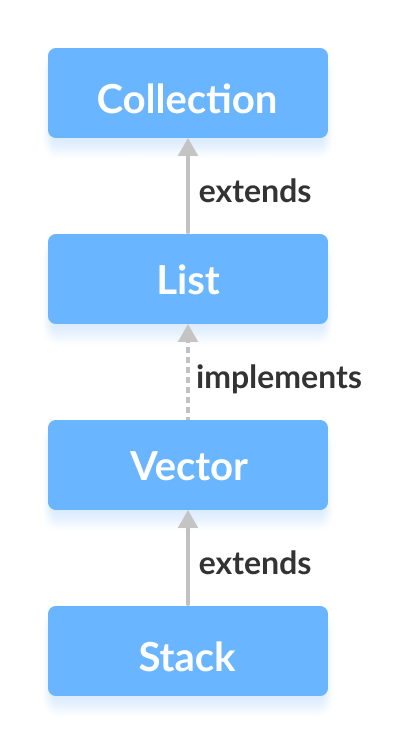
Java 的Java 集合框架中有一个名为 Stack 的类,它提供了栈数据结构的功能。
Stack 类扩展了 Vector 类。
Stack 实现
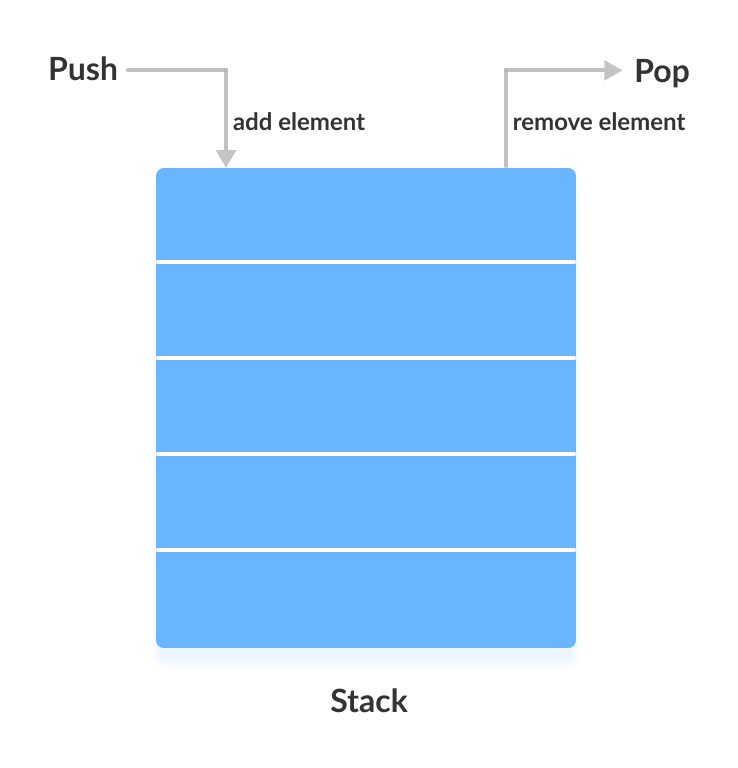
在栈中,元素以后进先出的方式存储和访问。也就是说,元素被添加到栈顶,并从栈顶移除。
创建 Stack
要创建栈,我们必须首先导入 java.util.Stack 包。导入包后,我们可以在 Java 中这样创建栈。
Stack<Type> stacks = new Stack<>();这里,Type 表示栈的类型。例如,
// Create Integer type stack
Stack<Integer> stacks = new Stack<>();
// Create String type stack
Stack<String> stacks = new Stack<>();Stack 方法
由于 Stack 扩展了 Vector 类,它继承了 Vector 的所有方法。要了解不同的 Vector 方法,请访问Java Vector 类。
除了这些方法之外,Stack 类还包含 5 个额外的方法,这些方法使其与 Vector 区别开来。
push() 方法
要向栈顶添加元素,我们使用 push() 方法。例如,
import java.util.Stack;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Stack: " + animals);
}
}输出
Stack: [Dog, Horse, Cat]
pop() 方法
要从栈顶移除元素,我们使用 pop() 方法。例如,
import java.util.Stack;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Initial Stack: " + animals);
// Remove element stacks
String element = animals.pop();
System.out.println("Removed Element: " + element);
}
}输出
Initial Stack: [Dog, Horse, Cat] Removed Element: Cat
peek() 方法
peek() 方法返回栈顶的对象。例如,
import java.util.Stack;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Stack: " + animals);
// Access element from the top
String element = animals.peek();
System.out.println("Element at top: " + element);
}
}输出
Stack: [Dog, Horse, Cat] Element at top: Cat
search() 方法
要搜索栈中的元素,我们使用 search() 方法。它返回元素从栈顶开始的位置。例如,
import java.util.Stack;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Stack: " + animals);
// Search an element
int position = animals.search("Horse");
System.out.println("Position of Horse: " + position);
}
}输出
Stack: [Dog, Horse, Cat] Position of Horse: 2
empty() 方法
要检查栈是否为空,我们使用 empty() 方法。例如,
import java.util.Stack;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> animals= new Stack<>();
// Add elements to Stack
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Horse");
animals.push("Cat");
System.out.println("Stack: " + animals);
// Check if stack is empty
boolean result = animals.empty();
System.out.println("Is the stack empty? " + result);
}
}输出
Stack: [Dog, Horse, Cat] Is the stack empty? false
使用 ArrayDeque 替代 Stack
Stack 类提供了栈数据结构的直接实现。但是,不建议使用它。而是使用 ArrayDeque 类(实现 Deque 接口)在 Java 中实现栈数据结构。
另请阅读