在 Go 中,switch 语句允许我们在多个选择中执行一个代码块。
语法
switch expression {
case 1:
// code block 1
case 2:
// code block 2
case 3:
// code block 3
...
...
default:
// default code block
}switch 关键字后面的表达式被求值。如果 expression 的结果等于
case 1- 执行 代码块 1case 2- 执行 代码块 2case 3- 执行 代码块 3
如果没有匹配项,则执行 默认代码块。
注意:我们也可以使用 if...else 语句来代替 switch。但是,switch 的语法更简洁,编写起来也更容易。
Switch 语句流程图
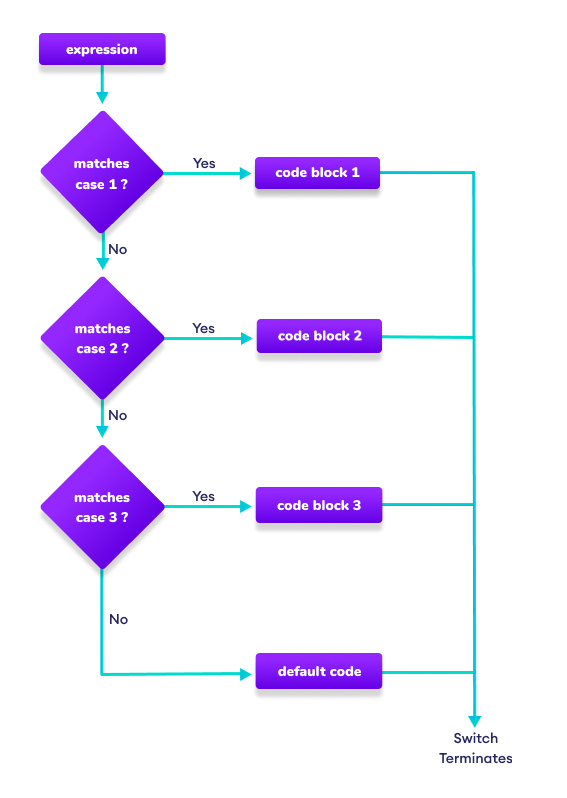
示例:Golang 中的 switch case
// Program to print the day of the week using switch case
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
dayOfWeek := 3
switch dayOfWeek {
case 1:
fmt.Println("Sunday")
case 2:
fmt.Println("Monday")
case 3:
fmt.Println("Tuesday")
case 4:
fmt.Println("Wednesday")
case 5:
fmt.Println("Thursday")
case 6:
fmt.Println("Friday")
case 7:
fmt.Println("Saturday")
default:
fmt.Println("Invalid day")
}
}输出
Tuesday
在上面的示例中,我们将 3 赋给了 dayOfWeek 变量。现在,该变量会与每个 case 语句的值进行比较。
由于该值与 case 3 匹配,因此会执行 case 中的语句 fmt.Println("Tuesday")。
注意:与其他编程语言(如 C 和 Java)不同,我们不需要在每个 case 后使用 break。这是因为在 Go 中,switch 语句在第一个匹配的 case 后终止。
Go switch case with fallthrough
如果我们需要在匹配的 case 之后执行其他 case,可以在 case 语句中使用 fallthrough。例如:
// Program to print the day of the week using fallthrough in switch
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
dayOfWeek := 3
switch dayOfWeek {
case 1:
fmt.Println("Sunday")
case 2:
fmt.Println("Monday")
case 3:
fmt.Println("Tuesday")
fallthrough
case 4:
fmt.Println("Wednesday")
case 5:
fmt.Println("Thursday")
case 6:
fmt.Println("Friday")
case 7:
fmt.Println("Saturday")
default:
fmt.Println("Invalid day")
}
}输出
Tuesday Wednesday
在上面的示例中,switch 中的表达式匹配 case 3,因此打印 Tuesday。但是,即使 case 不匹配,也打印了 Wednesday。
这是因为我们在 case 3 中使用了 fallthrough。
Go switch with multiple cases
我们也可以在一个 case 块中使用多个值。在这种情况下,如果表达式与 case 值之一匹配,则执行该 case 块。
让我们看一个例子,
// Program to check if the day is a weekend or a weekday
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
dayOfWeek := "Sunday"
switch dayOfWeek {
case "Saturday", "Sunday":
fmt.Println("Weekend")
case "Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday":
fmt.Println("Weekday")
default:
fmt.Println("Invalid day")
}
}输出
Weekend
在上面的示例中,我们为每个 case 使用了多个值
- case "Saturday", "Sunday" - 如果 dayOfWeek 是 Saturday 或 Sunday,则执行
- case "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday" - 如果 dayOfWeek 是其中一个值,则执行
Golang switch without expression
在 Go 中,switch 中的表达式是可选的。如果我们不使用表达式,switch 语句默认计算为 true。例如:
// Program to check if it's February or not using switch without expression
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
numberOfDays := 28
// switch without any expression
switch {
case 28 == numberOfDays:
fmt.Println("It's February")
default:
fmt.Println("Not February")
}
}输出
It's February
在上面的示例中,switch 没有表达式。因此,该语句默认为 true。
Go switch optional statement
在 Golang 中,我们也可以在表达式中使用可选语句。语句和表达式由分号分隔。例如:
// Program to check the day of a week using optional statement
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// switch with statement
switch day := 4; day {
case 1:
fmt.Println("Sunday")
case 2:
fmt.Println("Monday")
case 3:
fmt.Println("Tuesday")
case 4:
fmt.Println("Wednesday")
case 5:
fmt.Println("Thursday")
case 6:
fmt.Println("Friday")
case 7:
fmt.Println("Saturday")
default:
fmt.Println("Invalid Day!")
}
}输出
Wednesday
在上面的示例中,我们使用了可选语句 day := 4 和表达式 day。它匹配 case 4,因此打印 Wednesday。