JavaScript 的 if...else 语句用于根据条件执行/跳过一段代码。
以下是 if...else 语句的简要示例。如果您想更详细地了解 if...else,可以阅读本教程的其余部分。
示例
let score = 45;
// check if score is fifty or greater
if (score >= 50) {
console.log("You passed the examination.");
}
else {
console.log("You failed the examination.");
}
// Output: You failed the examination.在上面的示例中,如果 score 变量等于 50,程序将显示 You passed the examination.。否则,它将显示 You failed the examination.。
JavaScript if...else 语句
在计算机编程中,if...else 语句是一种条件语句,它仅在满足特定条件时执行一段代码。例如,
假设我们需要根据学生的成绩分配不同的等级。
- 如果学生成绩高于 90,则分配等级 A。
- 如果学生成绩高于 75,则分配等级 B。
- 如果学生成绩高于 65,则分配等级 C。
这些条件任务可以使用 if...else 语句来实现。
JavaScript if 语句
我们使用 if 关键字根据某些特定条件执行代码。
if 语句的语法是
if (condition) {
// block of code
}if 关键字会检查括号 () 中的条件。
- 如果条件求值为
true,则执行{ }中的代码。 - 如果条件求值为
false,则跳过{ }中的代码。
注意: { } 中的代码也称为 if 语句的主体。
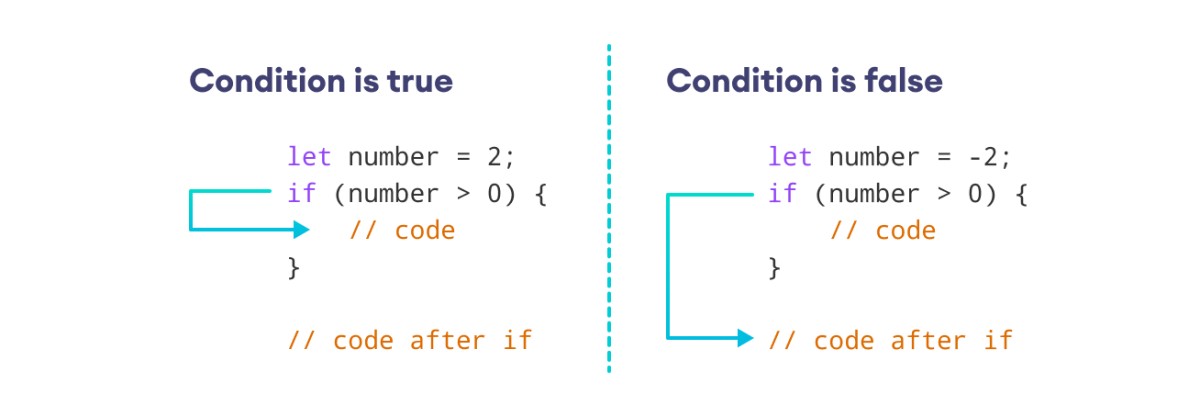
示例 1:JavaScript if 语句
// Program to check if the number is positive
const number = prompt("Enter a number: ");
// check if number is greater than 0
if (number > 0) {
// the body of the if statement
console.log("positive number");
}
console.log("nice number");示例输出 1
Enter a number: 5 positive number nice number
在上面的程序中,当我们输入 5 时,条件 number > 0 求值为 true。因此,执行了 if 语句的主体。
示例输出 2
Enter a number: -1 nice number
同样,当我们输入 -1 时,条件 number > 0 求值为 false。因此,跳过了 if 语句的主体。
由于 console.log("nice number"); 位于 if 语句主体之外,因此它始终被执行。
注意:我们在 if 条件中使用比较运算符和逻辑运算符。要了解更多信息,您可以访问 JavaScript 比较和逻辑运算符。
JavaScript else 语句
当我们希望在前一个 if 语句中指定的条件求值为 false 时执行代码,则使用 else 关键字。
else 语句的语法是
if (condition) {
// block of code
// execute this if condition is true
}
else {
// block of code
// execute this if condition is false
}if...else 语句通过两种方式检查 condition 并执行代码:
- 如果
condition为 true,则执行if中的代码。同时,跳过else中的代码。 - 如果
condition为 false,则跳过if中的代码。而是执行else中的代码。
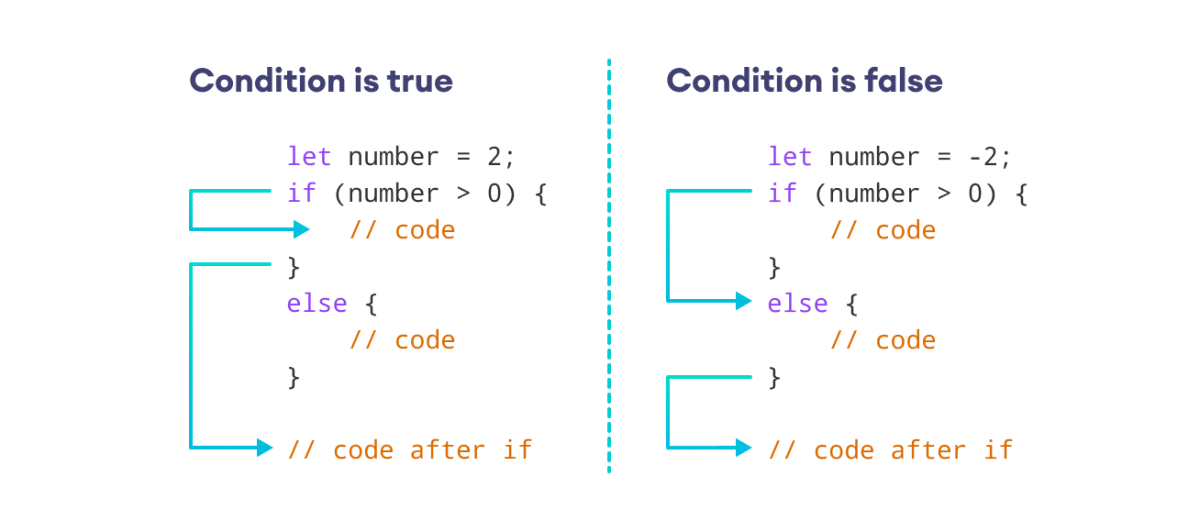
示例 2:JavaScript if…else 语句
let age = 17;
// if age is 18 or above, you are an adult
// otherwise, you are a minor
if (age >= 18) {
console.log("You are an adult");
}
else {
console.log("You are a minor");
}
// Output: You are a minor在上面的示例中,if 语句检查条件 age >= 18。
由于我们将 age 的值设置为 17,因此条件求值为 false。
因此,跳过了 if 中的代码。并执行了 else 中的代码。
当只有一行代码需要执行时,我们可以省略 if…else 语句中的 { }。例如,
let num = 4;
// if condition
if (num % 2 == 0)
console.log("even number");
else
console.log("odd number");
// Output: even numberJavaScript else if 语句
我们可以使用 else if 关键字来检查多个条件。
else if 语句的语法是
// check for first condition
if (condition1) {
// if body
}
// check for second condition
else if (condition2){
// else if body
}
// if no condition matches
else {
// else body
}这里,
- 首先,检查
if语句中的条件。如果条件计算为true,则执行if的主体,并跳过其余部分。 - 否则,将检查
else if语句中的条件。如果为true,则执行其主体,并跳过其余部分。 - 最后,如果没有条件匹配,则执行
else中的代码块。
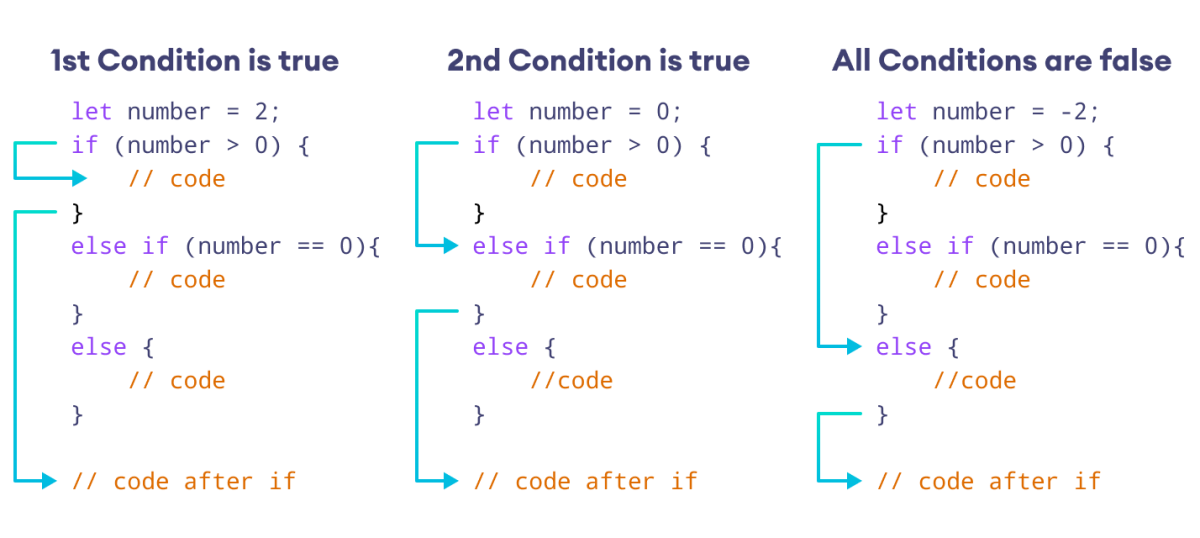
示例 3:JavaScript if...else if 语句
let rating = 4;
// rating of 2 or below is bad
// rating of 4 or above is good
// else, the rating is average
if (rating <= 2) {
console.log("Bad rating");
}
else if (rating >= 4) {
console.log("Good rating!");
}
else {
console.log("Average rating");
}
// Output: Good rating!在上面的示例中,我们使用 if 语句检查条件 rating <= 2。
同样,我们使用 else if 语句检查另一个条件 rating >= 4。
由于满足了 else if 条件,因此执行了其中的代码。
我们可以根据需要多次使用 else if 关键字。例如,
let alphabet = "c";
if (alphabet == "a") {
console.log("a for apple");
}
// first else if statement
else if (alphabet == "b") {
console.log("b for banana");
}
// second else if statement
else if (alphabet == "c") {
console.log("c for cat");
}
// use more else if statements if needed
// otherwise, use an else statement
else {
console.log("unknown alphabet");
}
// Output: c for cat在上面的示例中,我们使用了两个 else if 语句。
执行了第二个 else if 语句,因为它满足了条件。
嵌套 if...else 语句
当我们使用嵌套在另一个 if...else 语句中的 if...else 语句时,我们就创建了一个嵌套 if...else 语句。例如,
let marks = 60;
// outer if...else statement
// student passed if marks 40 or above
// otherwise, student failed
if (marks >= 40) {
// inner if...else statement
// Distinction if marks is 80 or above
if (marks >= 80) {
console.log("Distinction");
}
else {
console.log("Passed");
}
}
else {
console.log("Failed");
}
// Output: Passed外部 if...else
在上面的示例中,外部 if 条件使用 marks >= 40 来检查学生是否及格。如果它求值为 false,则外部 else 语句将打印 Failed。
另一方面,如果 marks >= 40 求值为 true,程序将进入内部 if...else 语句。
内部 if...else 语句
内部 if 条件使用 marks >= 80 来检查学生是否以优异成绩及格。
如果 marks >= 80 求值为 true,则内部 if 语句将打印 Distinction。
否则,内部 else 语句将打印 Passed。
注意:为保持代码可读性并简化调试,请避免嵌套多个 if…else 语句。
更多关于 JavaScript if...else 语句
如果我们要执行的操作非常简单,我们可以使用 三元运算符 ?: 来代替 if...else 语句。例如,
let grade = 40;
let result;
if (grade >= 50)
result = 'pass'
else
result = 'fail'
console.log(result)可以写成
let grade = 40;
let result = (grade >= 50) ? 'pass' : 'fail';
console.log(result)当我们需要处理大量条件时,我们可以用 switch 语句 替换 if…else 语句。
例如,
let grade = "C";
// using if else for many conditions
// first condition
if (grade === "A") {
console.log("Excellent!");
}
// second condition
else if (grade === "B") {
console.log("Good!");
}
// third condition
else if (grade === "C") {
console.log("Average");
}
// fourth condition
else if (grade === "D") {
console.log("Bad");
}
// otherwise, execute else block
else {
console.log("Fail");
}
// Output: Average在上面的示例中,我们使用 if…else 来评估五个条件,包括 else 块。
现在,让我们使用 switch 语句来实现相同的功能。
let grade = "C";
// using switch...case
switch (grade) {
// first condition
case "A":
console.log("Excellent!");
break;
// second condition
case "B":
console.log("Good!");
break;
// third condition
case "C":
console.log("Average");
break;
// fourth condition
case "D":
console.log("Bad");
break;
default:
console.log("Fail");
}
// Output: Average如您所见,switch 语句使我们的代码更具可读性和可维护性。
此外,switch 比长串的 if…else 语句运行更快。
我们可以在 if 语句中使用逻辑运算符,如 && 和 || 来添加多个条件。例如,
let age = 35;
let salary = 6000;
// combine two conditions
// using the "and" operator &&
if (age >= 30 && salary >= 5000) {
console.log("Eligible for premium membership.");
}
else {
console.log("Not eligible for premium membership.");
}
// Output: Eligible for premium membership.在这里,我们使用了逻辑运算符 && 在 if 语句中添加了两个条件。
另请阅读