从 JavaScript ES6 开始,我们可以为函数参数提供默认值。
当调用函数时未传递相应的参数时,将使用这些默认值。
以下是 JavaScript 默认参数的快速示例。有关更多详细信息,您可以阅读本教程的其余部分。
示例
function greet(name = "Guest") {
console.log(`Hello, ${name}!`);
}
greet();
// Output: Hello, Guest!在此示例中,greet() 函数有一个默认参数 name,其字符串值为 Guest。由于我们未向函数传递任何参数,因此它将使用默认值。
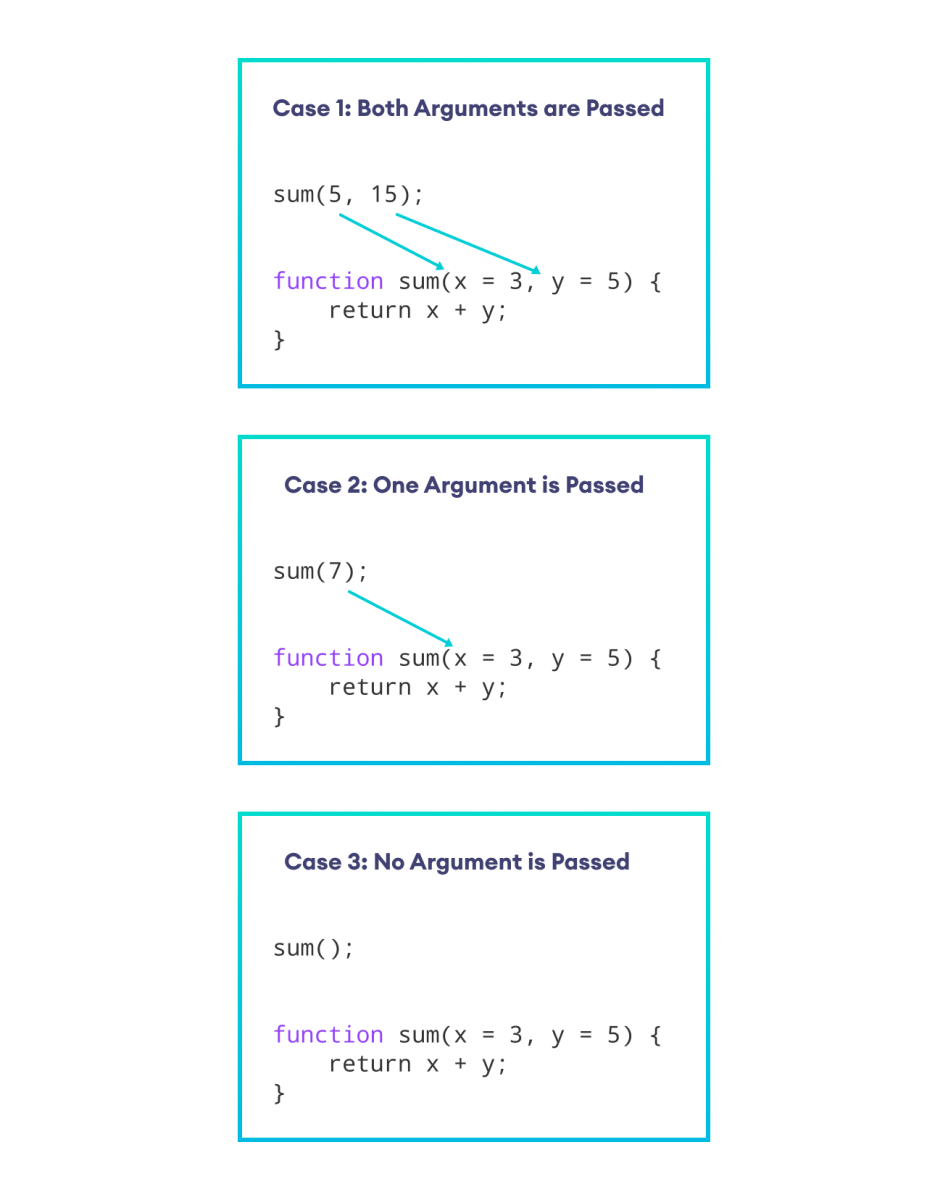
示例:JavaScript 默认参数
function sum(x = 3, y = 5) {
// return sum
return x + y;
}
// pass arguments to x and y
var result = sum(5, 15);
console.log(`Sum of 5 and 15: ${result}`);
// pass argument to x but not to y
result = sum(7);
console.log(`Sum of 7 and default value (5): ${result}`);
// pass no arguments
// use default values for x and y
result = sum();
console.log(`Sum of default values (3 and 5): ${result}`);输出
Sum of 5 and 15: 20 Sum of 7 and default value (5): 12 Sum of default values (3 and 5): 8
在上面的示例中,x 的默认值为 3,y 的默认值为 5。
sum(5, 15)- 当两个参数都传递时,x 为 5,y 为 15。sum(7)- 当传递 7 时,x 为 7,y 取默认值 5。sum()- 当未传递参数时,x 和 y 分别取默认值 3 和 5。
更多关于默认参数
将一个参数作为另一个参数的默认值
在 JavaScript 中,您可以将一个参数作为另一个参数的默认值。例如,
function sum(x = 1, y = x, z = x + y) {
console.log( x + y + z );
}
sum();
// Output: 4在上面的例子中:
- x 的默认值为 1。
- y 的默认值设置为 x 参数。
- z 的默认值是 x 和 y 的总和。
因此,当 sum() 在没有任何参数的情况下调用时,它将使用这些默认值,从而导致计算 1 + 1 + 2 = 4。因此,输出为 4。
将函数值作为默认值
我们也可以在 JavaScript 中将函数作为默认值传递。例如,
// use a function in default value expression
const sum = () => 15;
const calculate = function( x, y = x * sum() ) {
return x + y;
}
const result = calculate(10);
console.log(result);
// Output: 160这里,
- 将 10 传递给
calculate()函数。 - x 变为 10,y 变为 150(
sum()函数返回 15)。 - 结果将是 160。
传递 undefined 值
在 JavaScript 中,当您向默认参数函数传递 undefined 时,该函数将采用默认值。例如,
function test(x = 1) {
console.log(x);
}
// pass undefined
// takes default value 1
test(undefined);
// Output: 1另请阅读